Testing Types

Functional Vs Non-Functional


Use this slide if there is no Heading
Note - Create Content inside Red Layout
[Delete Red Outline After creating slide]

Learning Outcome
4
Differentiate between Functional and Non-Functional testing
3
Identify scenarios for each type
2
Understand what is Non-Functional Testing
1
Understand what is Functional Testing

Testing Techniques
What is software testing

Why Do We Need Functional and Non-Functional Testing?
A software can work correctly but still be slow or unstable
Both correctness and quality are important for users
A software can be fast but may not work correctly
To release good software, we must check both what the system does and how it behaves




Login Functionality
Feature Working
User enters valid username and password
User is able to log in
You are checking whether the feature works as expected
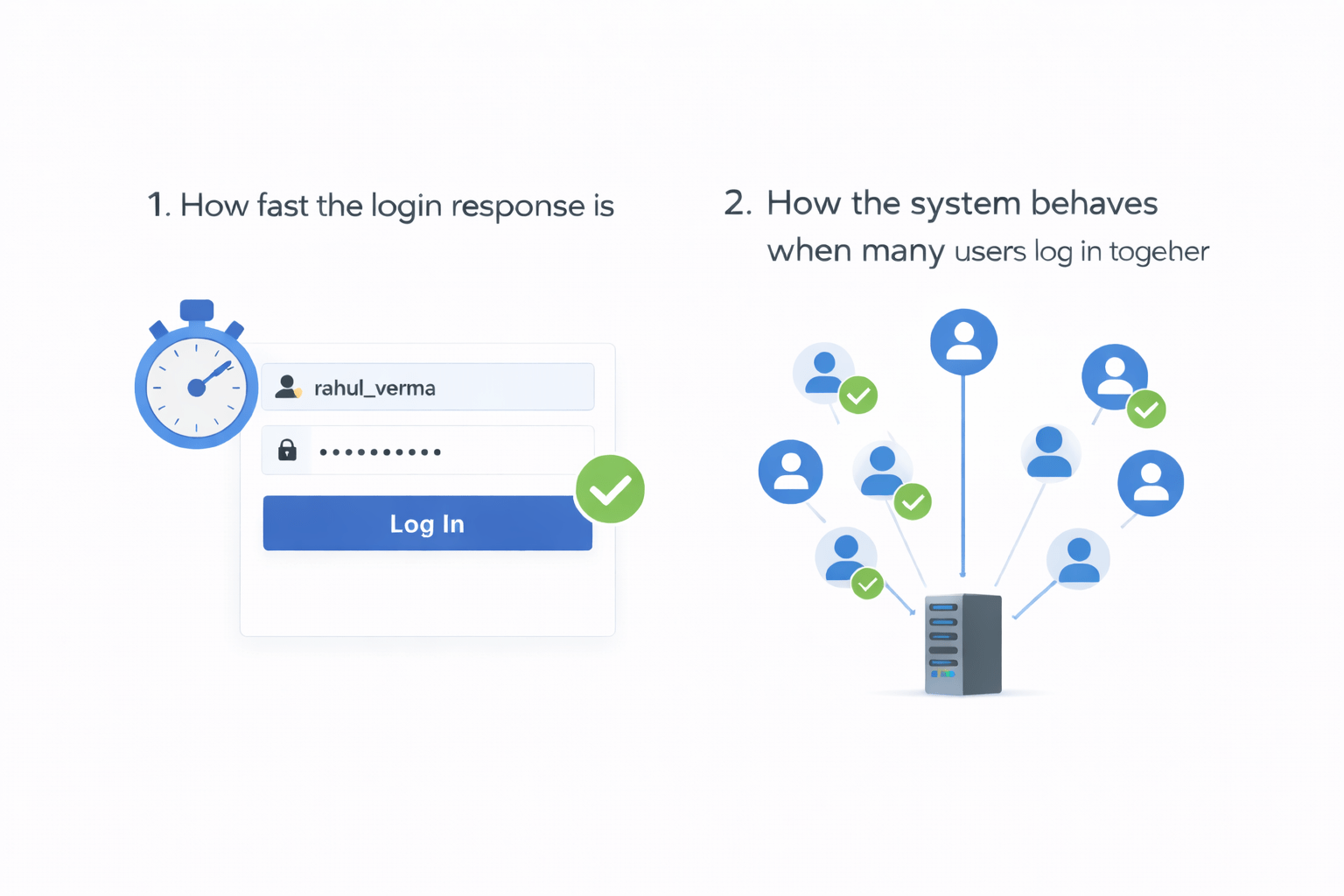

How the system behaves when many users log in together
How fast the login response is
Quality
You are checking now performance and Behaviour of the System

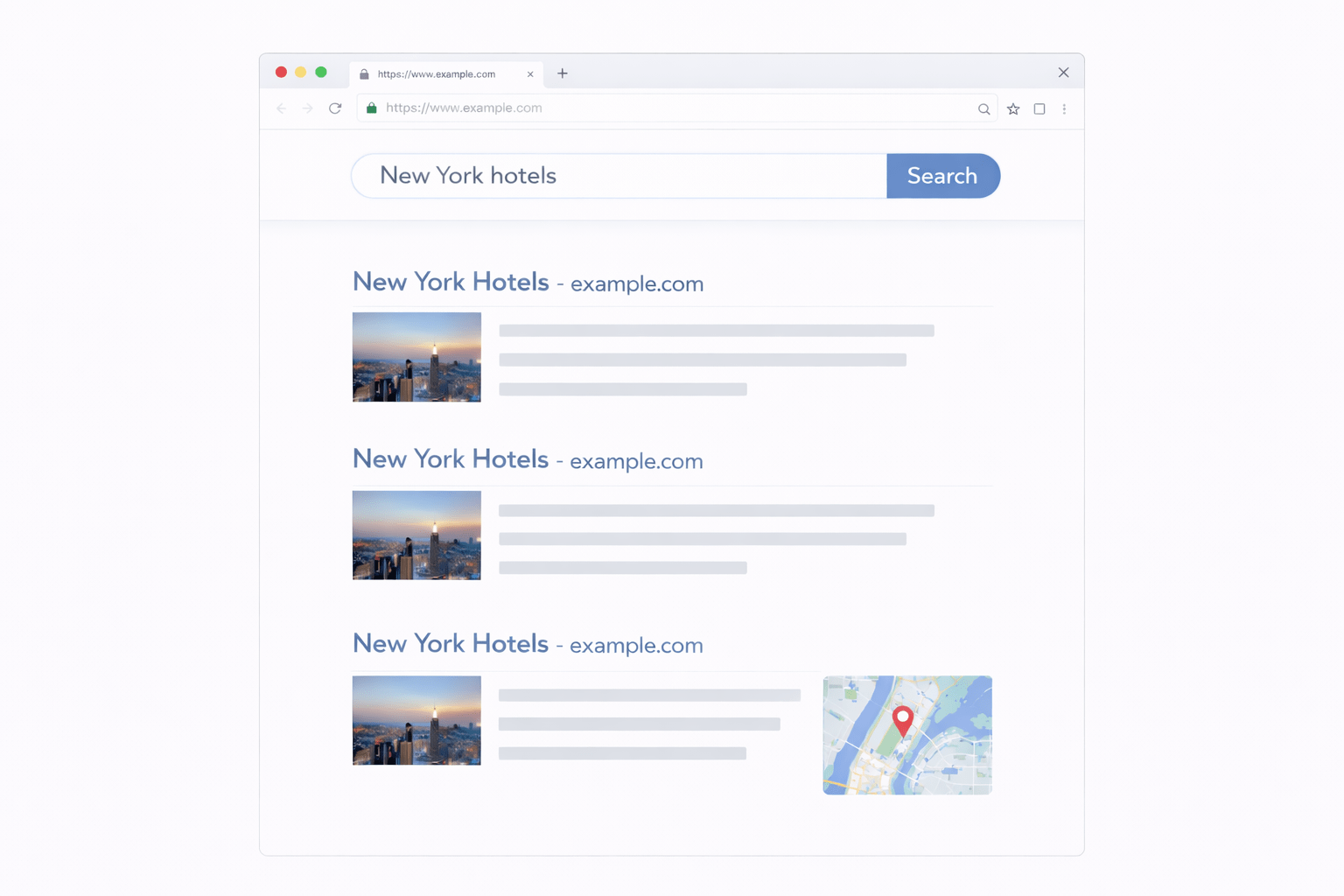
Search Feature
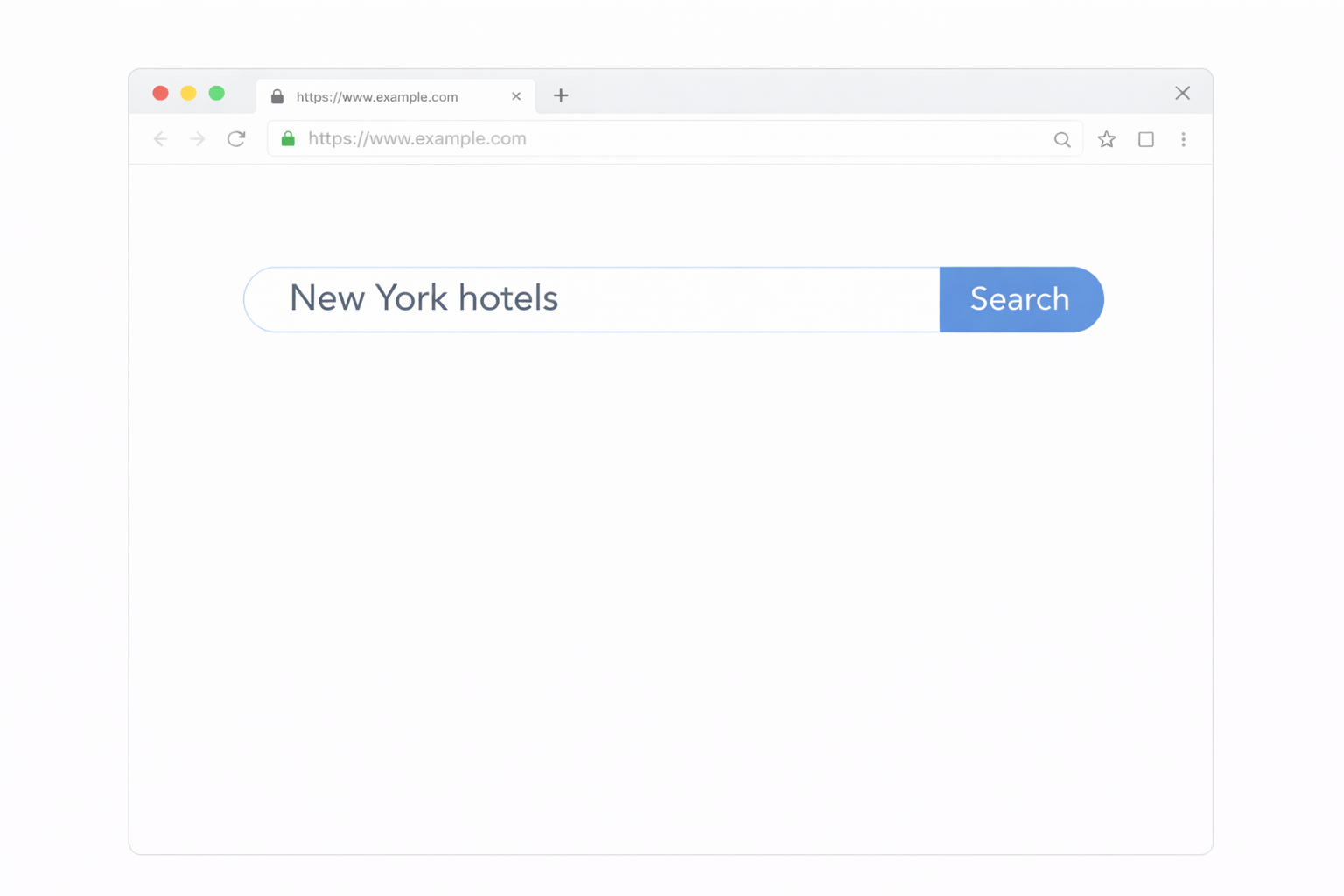
User searches for a product
Feature working
Correct results are displayed
You are checking whether the Feature works as expected
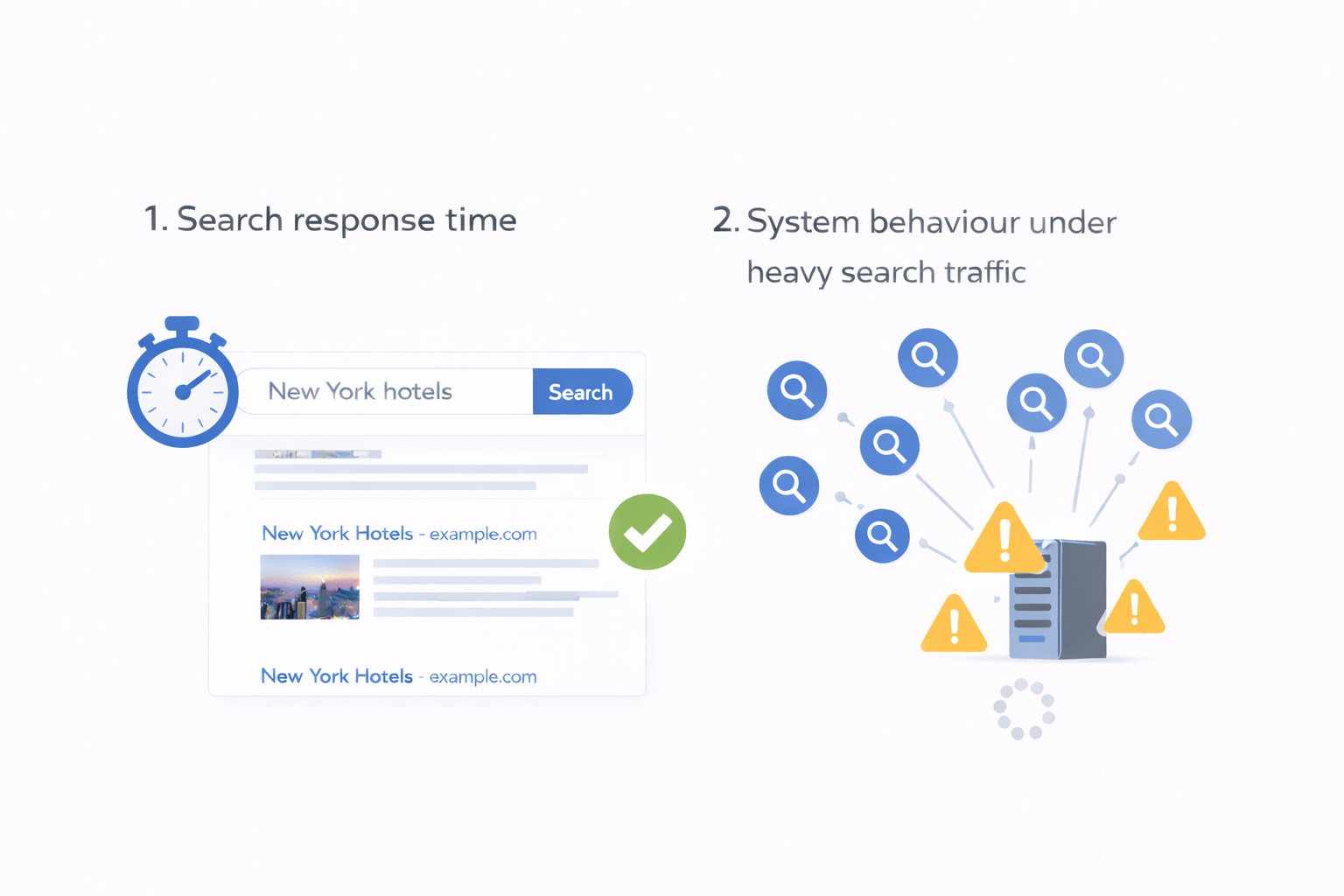
You are checking performance and behaviour of the system
Search response time
System behaviour under heavy search traffic
Feature Quality


What is Functional Testing
-
Verifies features and functions of the application
-
Based on business and functional requirements
-
Focuses on what the system does
-
Checks input and output behavior
Form validation and submission testing
Login and registration feature testing
Search functionality testing



Example

To verify that all features work as per business requirement
Key Objectives of Functional Testing
To ensure the application meets user and use-case expectations
To validate the behaviour of the system using inputs and expected output



Process of Functional Testing
1.Understand functional requirements and use cases
2. Identify test scenarios and test cases for features
4. Execute test cases and observe results
3. Report defects if expected behaviour is not met





What is Non-Functional Testing
-
Verifies quality and performance of the system
-
Focuses on how the system behaves
-
Not related to individual business features


Page load and response time
System recovery after crash
Usability of the application
Behaviour under heavy load
Example

Types of Non-Functional Testing
Performance/Load Testing
Measures response times under normal and peak loads, Identifies bottlenecks
Security Testing
Finds vulnerabilities in software defenses, Prevents unauthorized access to systems
Usability Testing
Evaluates user interface design, Ensures intuitive navigation and accessibility
Compatibility Testing
Verifies software works across different devices and environments
1
2
3
4




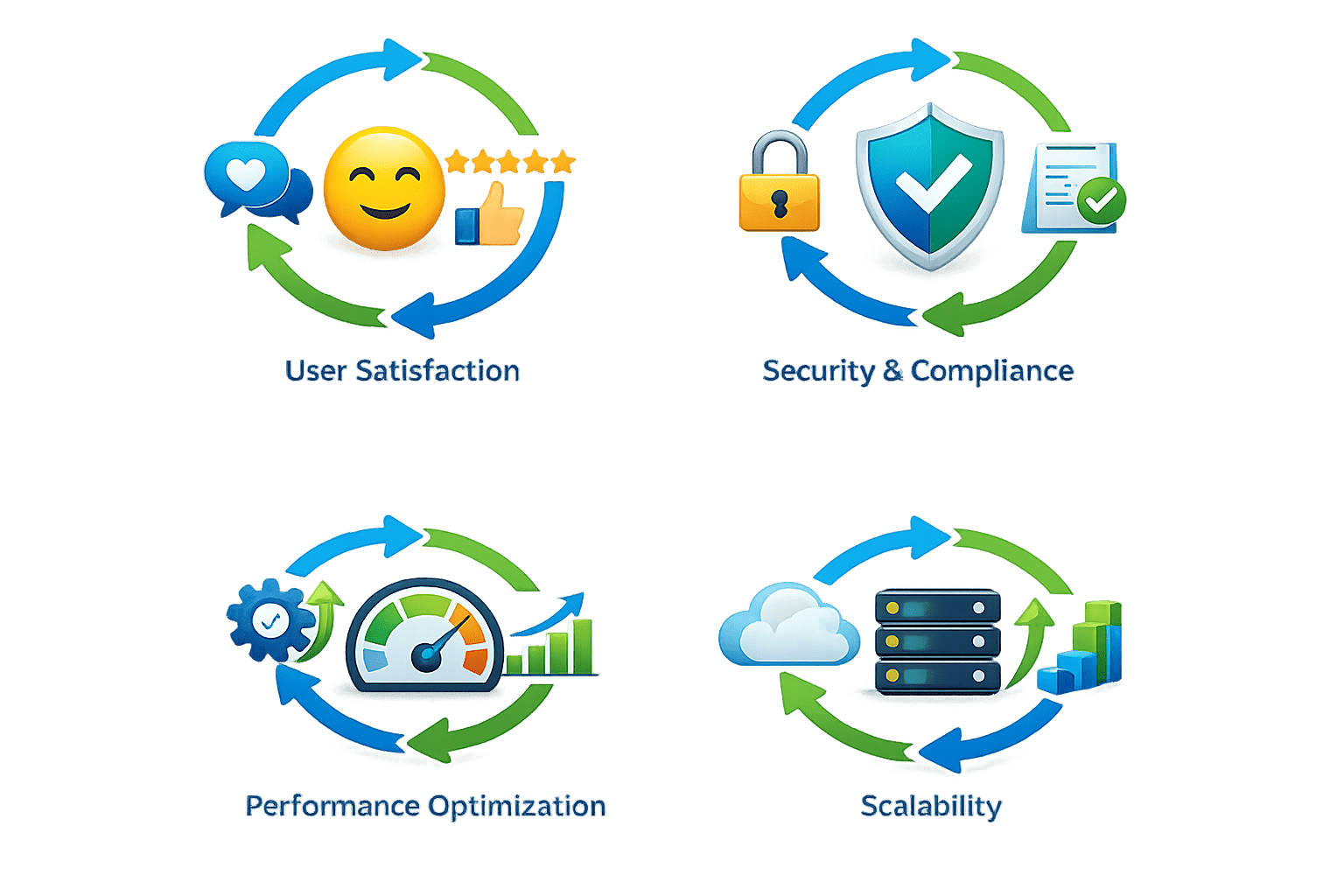
1. User Satisfaction
Create delightful user experiences
2. Security & Compliance
Meet regulatory requirements
3. Performance Optimization
Ensure speed and responsiveness
4. Scalability
Support growth and peak loads
Key Objectives of Non-Functional Testing




Functional Testing VS Non-Functional Testing
Pointer
Functional Testing
Non-Functional Testing
Focus
Purpose
Example
Based on
What the system does
(features and functions)
Business and functional requirements
To verify that required features work correctly
Can the user register successfully?
How the system behaves
(quality and performance)
Performance and quality
criteria
To verify system performance, usability, reliability and security
How fast does the page load with many users?

Summary
1
Functional testing verifies that features and functions work as per requirements
2
Non-functional testing verifies the quality and behaviour of the system
3
Both functional and non-functional testing are required for successful software release

Quiz
Which of the following is an example of Non-Functional testing?
A. Verifying that a user can reset the password
B. Checking whether the login form validates email correctly
C. Verifying that a user can register successfully
D. Measuring how fast a search page responds when many users access it


Quiz
Which of the following is an example of Non-Functional testing?
A. Verifying that a user can reset the password
B. Checking whether the login form validates email correctly
C. Verifying that a user can register successfully
D. Measuring how fast a search page responds when many users access it
