Framework Fusion


Mastering Java


Learning Outcome
3
Identify the limitations of arrays and how collections solve them.
2
Explain the purpose and structure of the Java Collection Framework
1
Understand the concept of a framework

Basic Java concepts: OOPs (class, object, inheritance, polymorphism)
Generics (e.g., List<String>)
Wrapper classes & Autoboxing
Equals() and hashCode() methods
Iteration concepts (for-each loop, Iterator)

Before Starting ,Lets Recall





What is a Framework in Java?
Standard Interface
A framework is a predefined structure or set of reusable classes and interfaces that helps developers build applications efficiently. It acts as a skeleton or scaffolding for software development.
Offers pre-built standard functionalities so developers don't have to write common code from scratch.
Provides essential tools, comprehensive libraries, and API sets needed for development.
Key Features:

Standard Interface
What is the Collection Framework?
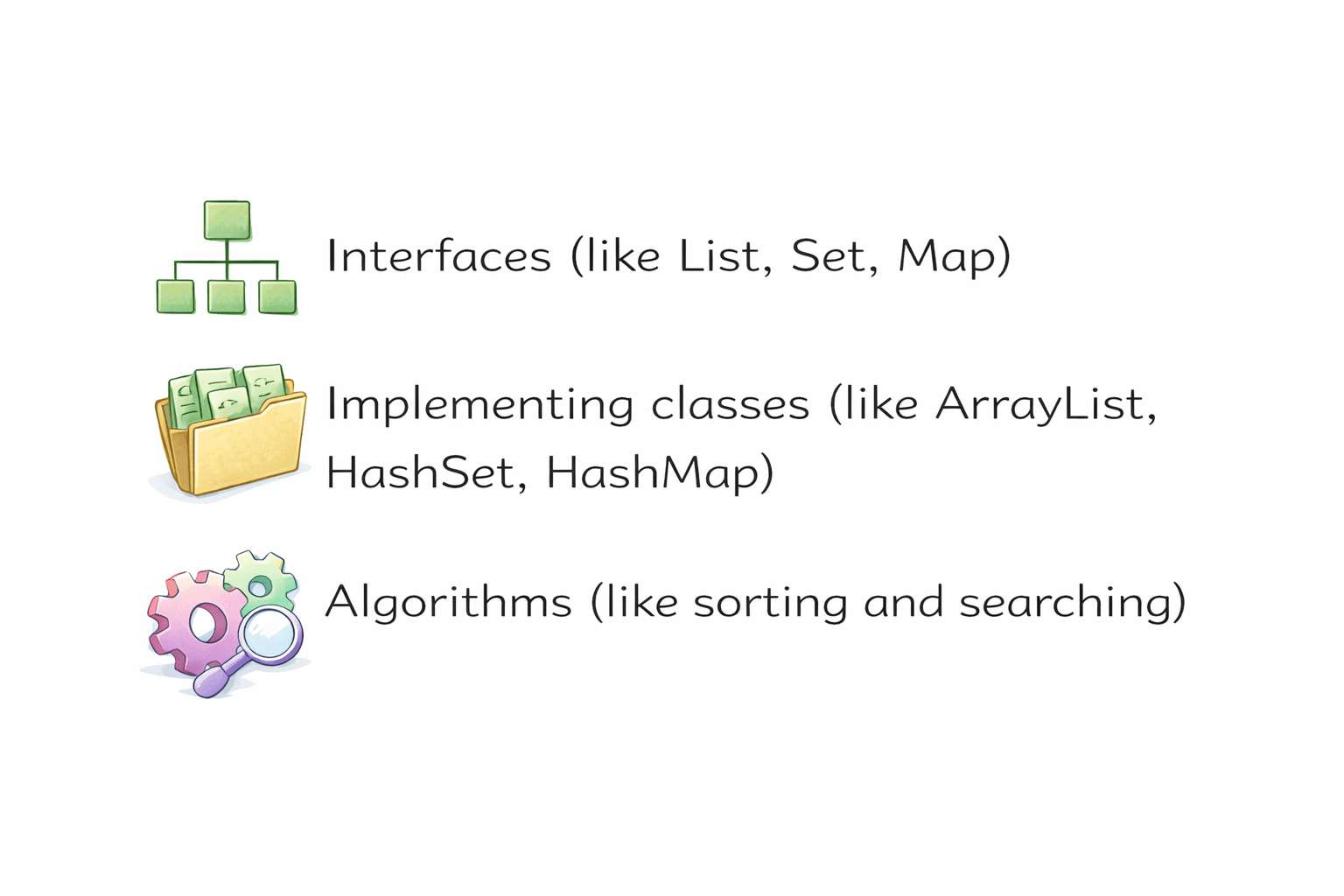
The Java Collection Framework (JCF) is a unified architecture for storing, retrieving, and manipulating groups of objects.
It includes:

Standard Interface
- Fixed size
- No built-in methods for sorting, searching, etc.
- Poor performance for dynamic data management
Before collections, Java used arrays, which had several limitations:
- Dynamic memory management
- Ready-made data structures (List, Set, Map)
- Efficient algorithms for sorting, searching, shuffling
- Interoperability between different collection types
Advantages of Collection Framework

Why Needed?


Java Collections Framework Hierarchy
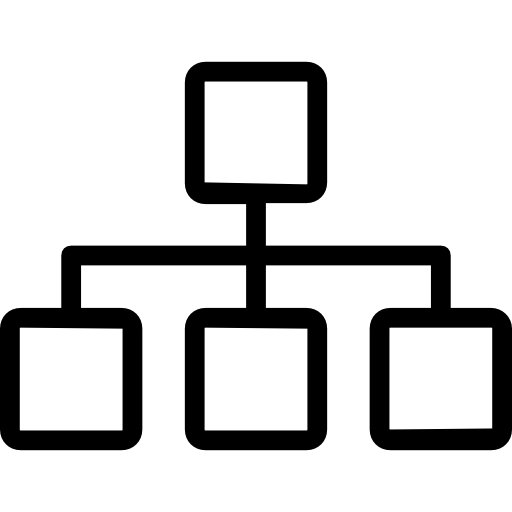
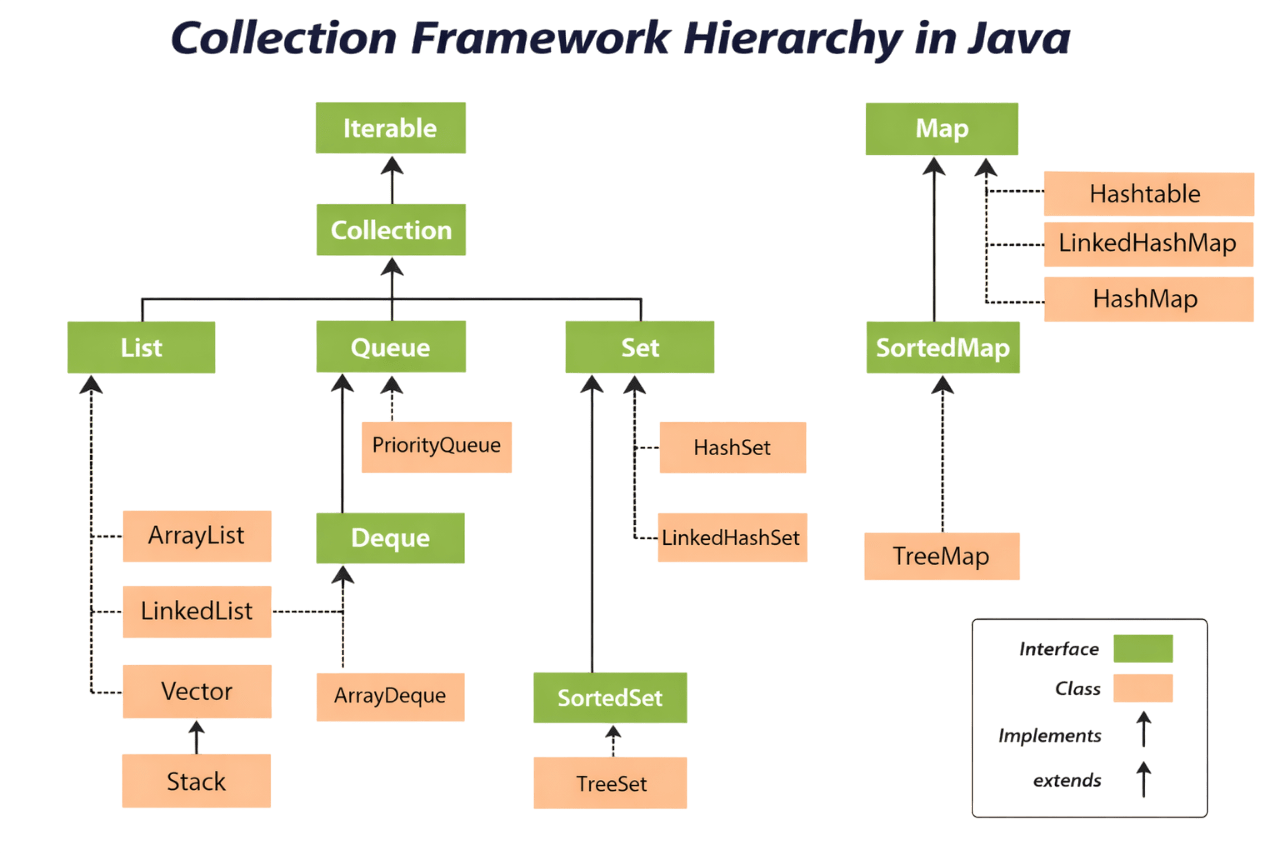

Core Interfaces and Purpose
Interface
Purpose
List
Set
Queue
Deque
Map
|
Ordered collection, allows duplicates |
No duplicate elements
|
Processes elements in FIFO order |
|
Allows insertion/removal from both ends |
|
Stores key–value pairs (unique keys) |






Summary
4
Advantages: ready-made data structures and efficient algorithms.
3
Solves array limitations
2
JCF manages groups of objects with List, Set, Queue, Map.
1
Framework are reusable classes and interfaces for efficient coding.

Quiz
Which interface in the Collection Framework is the root of all collection types?
A. List
B. Map
C. Collection
D. Queue


Which interface in the Collection Framework is the root of all collection types?
A. List
B. Map
C. Collection
D. Queue
Quiz-Answer
