AWS X-Ray
Hands-On
Demo
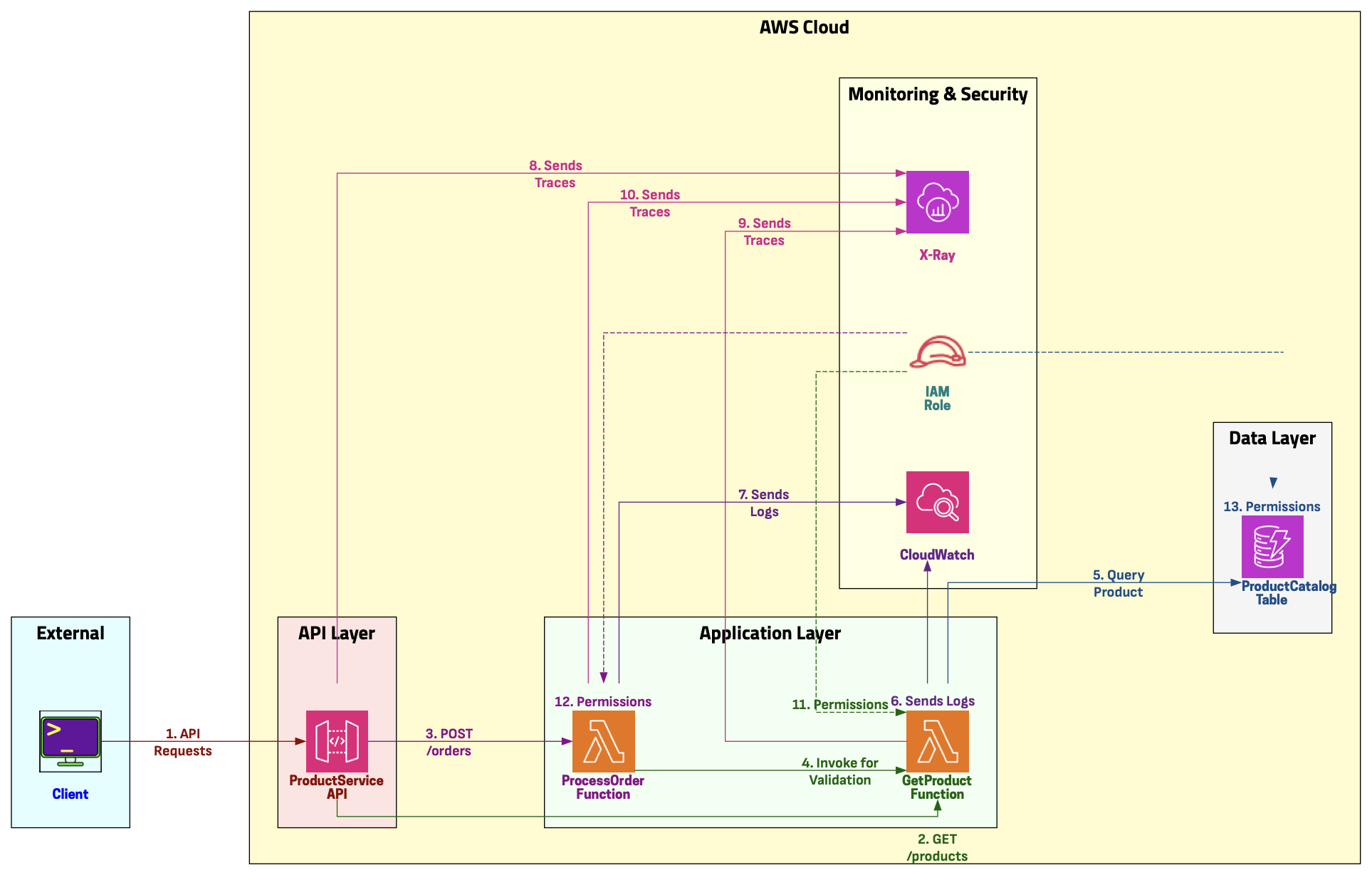
In this demo, we will:
- Set up IAM roles for X-Ray integration
- Create Lambda functions with X-Ray tracing
- Configure API Gateway with X-Ray tracing
- Deploy a DynamoDB table and enable tracing
- Create a multi-tier application workflow
- Generate traffic and analyze traces
- Use X-Ray Service Map to visualize architecture
- Clean up resources
Agenda
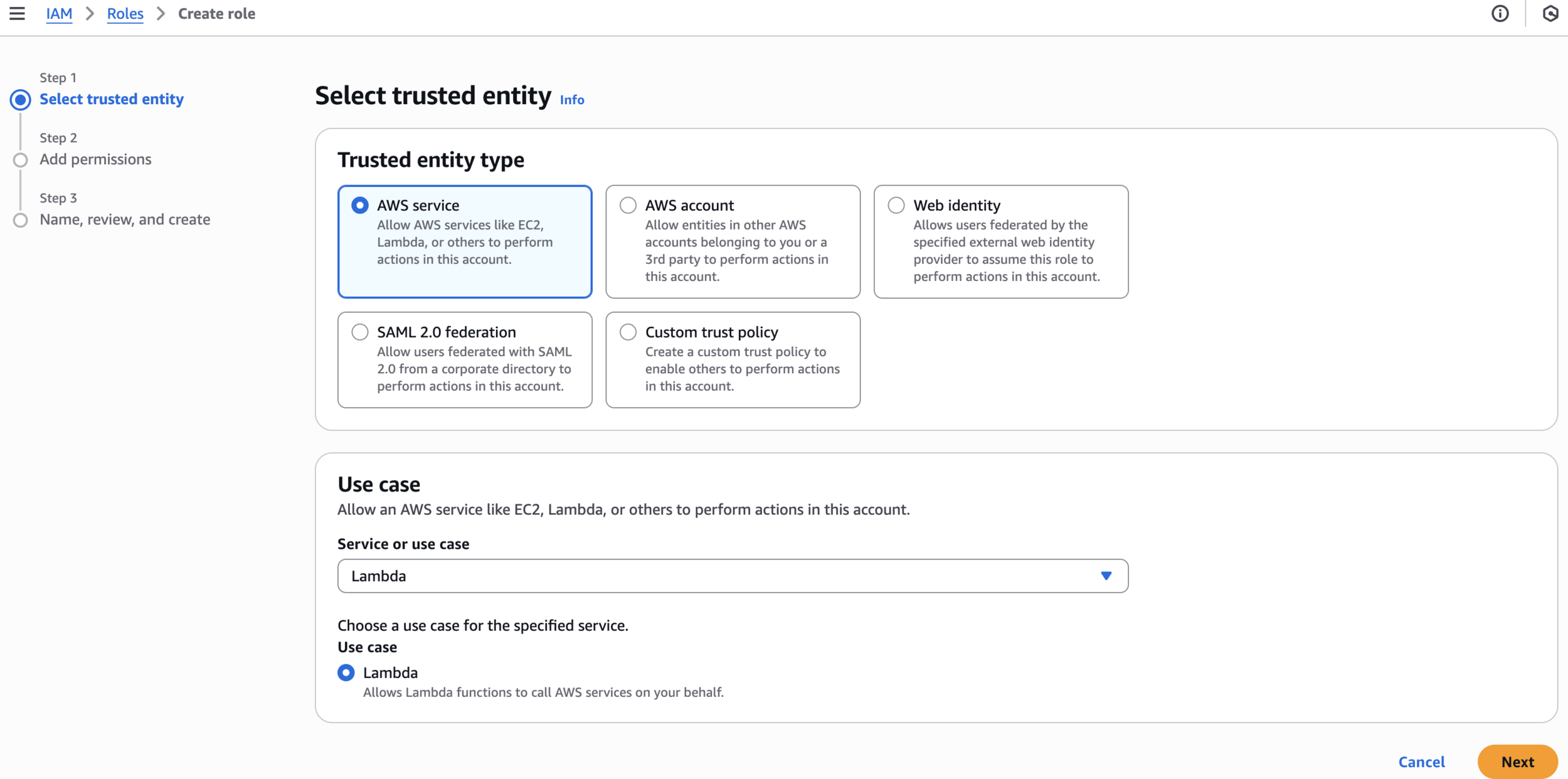
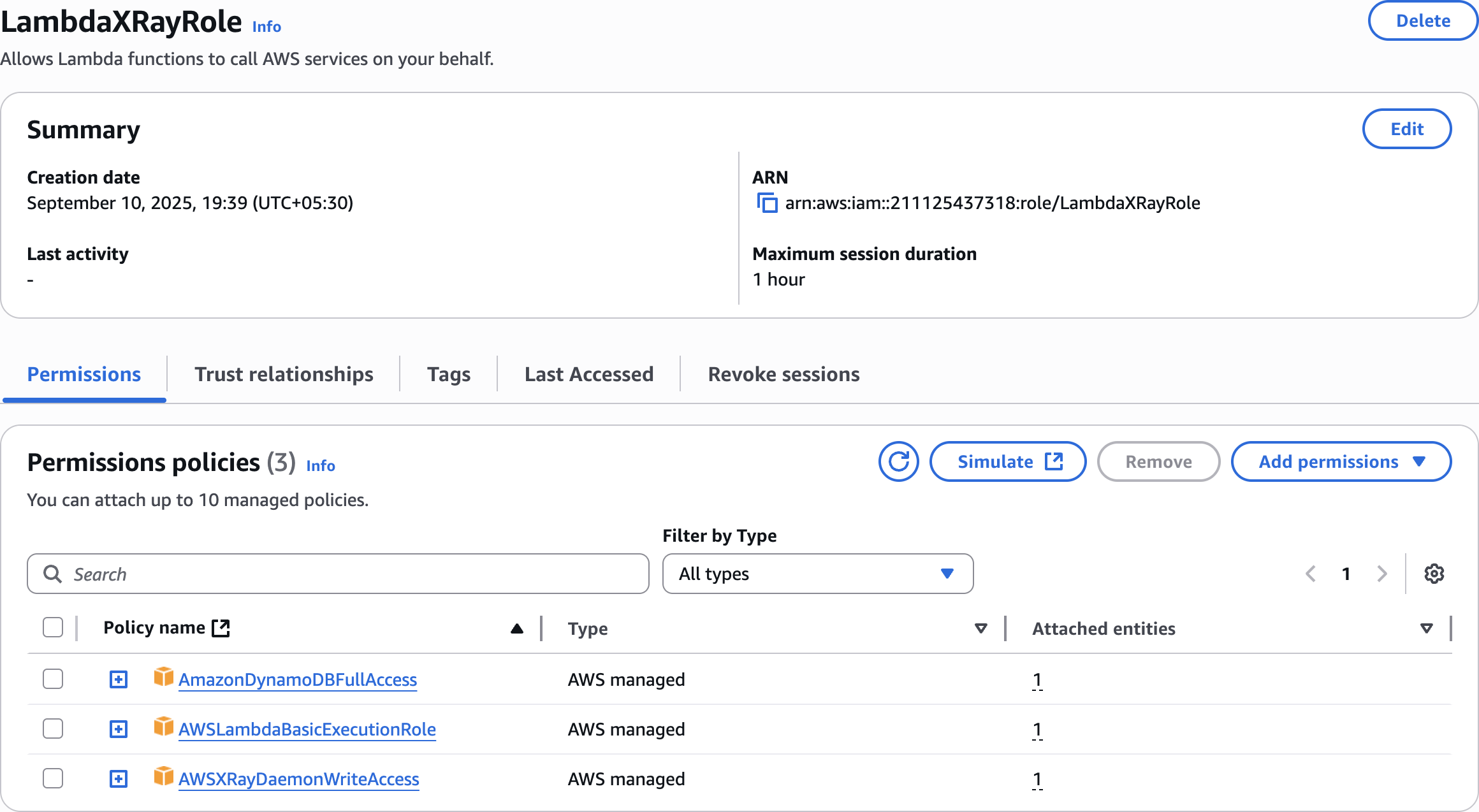
Step 1: Set up IAM Roles for X-Ray Integration
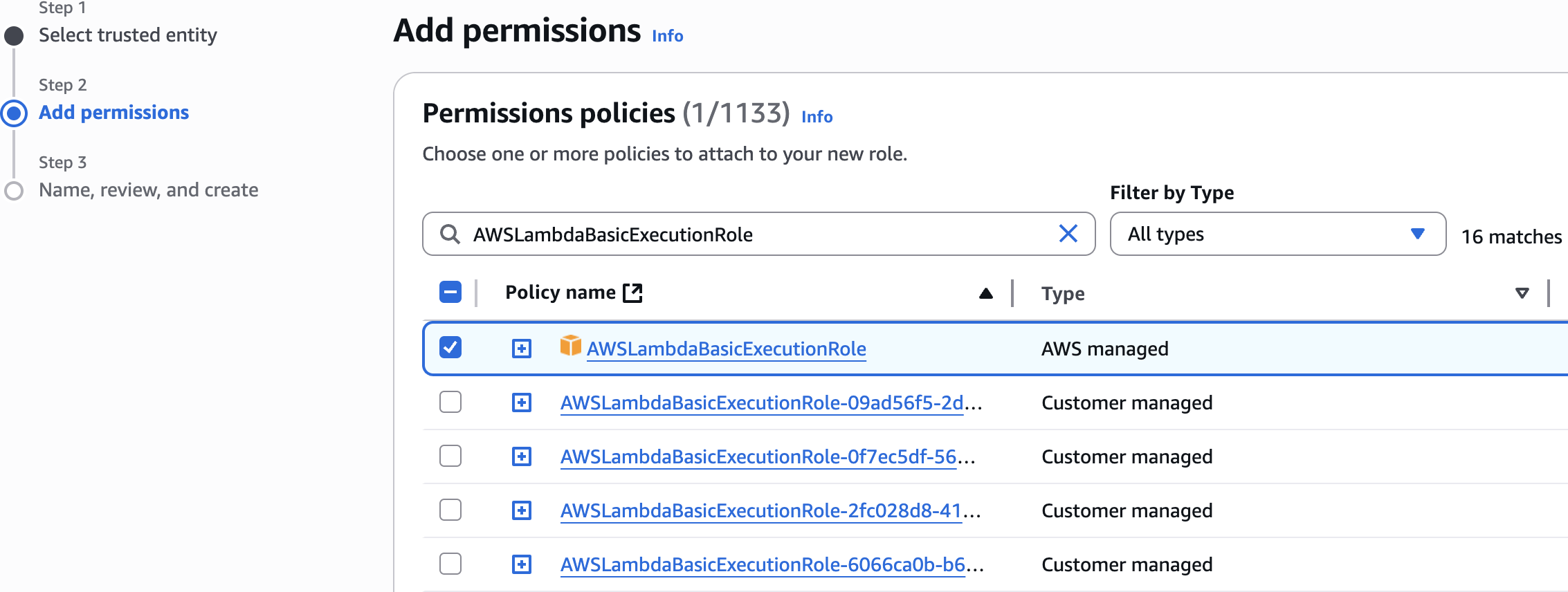
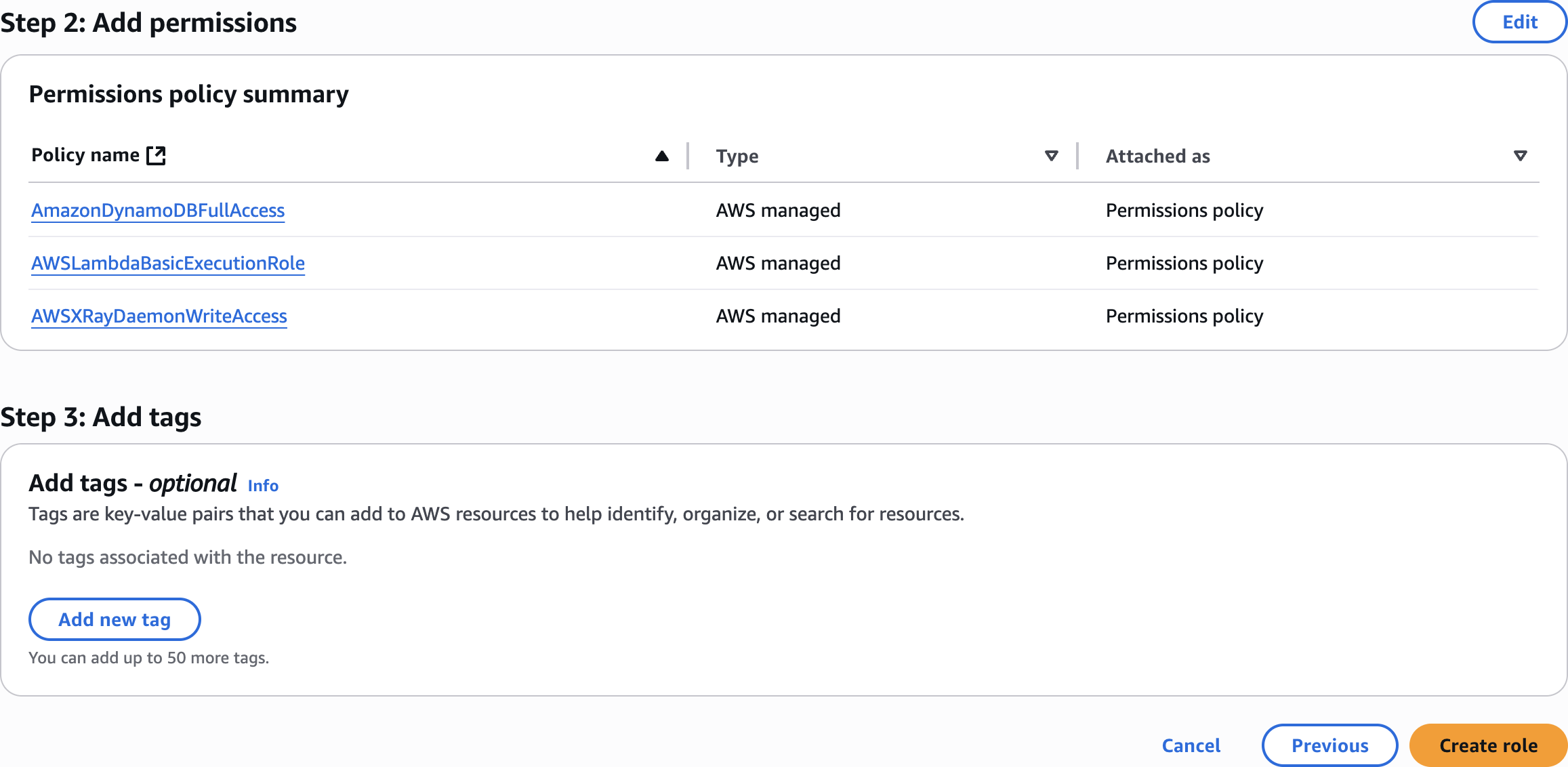
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole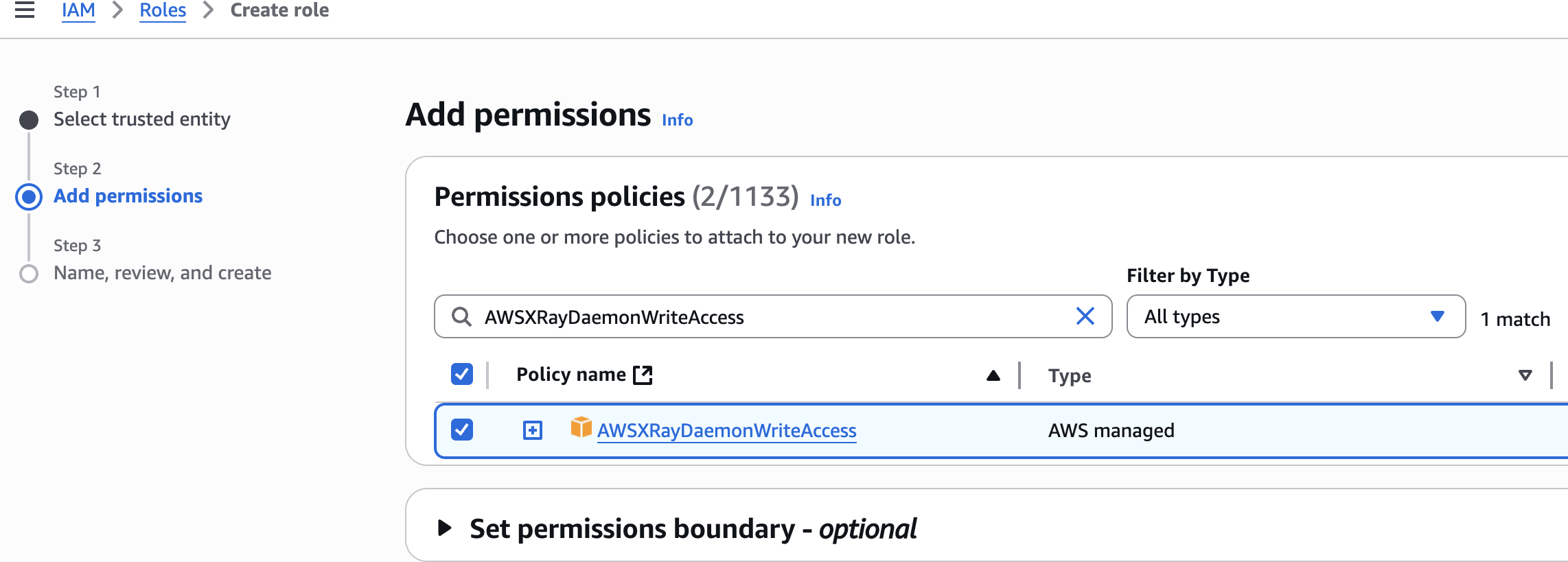
AWSXRayDaemonWriteAccess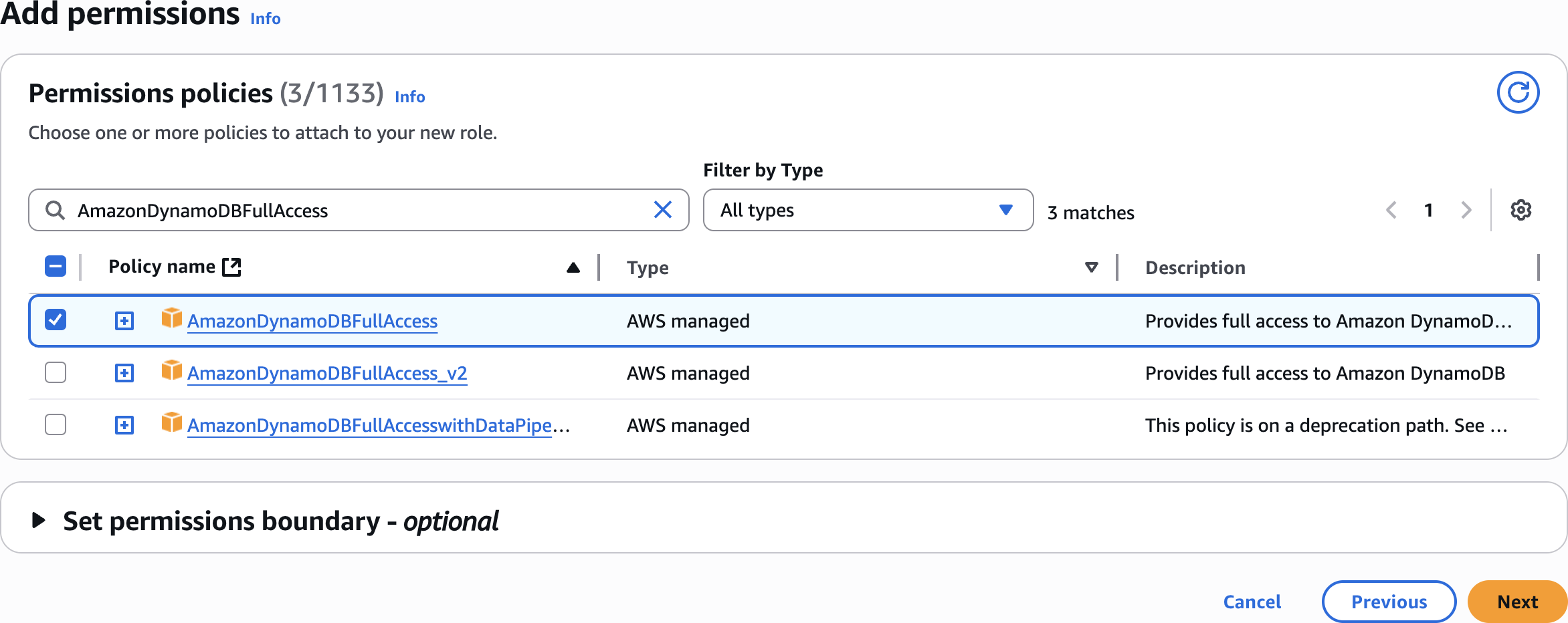
AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess
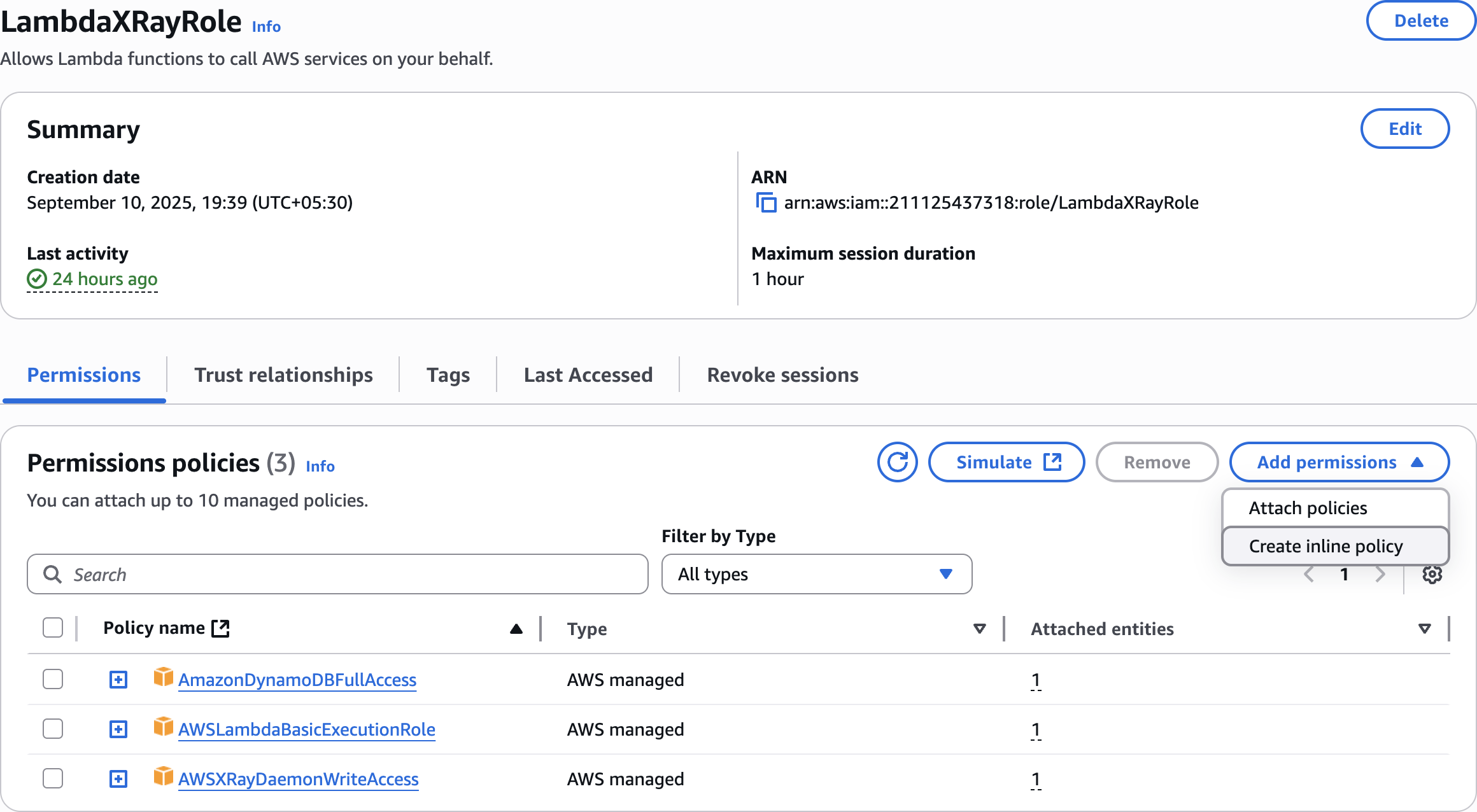
LambdaXRayRole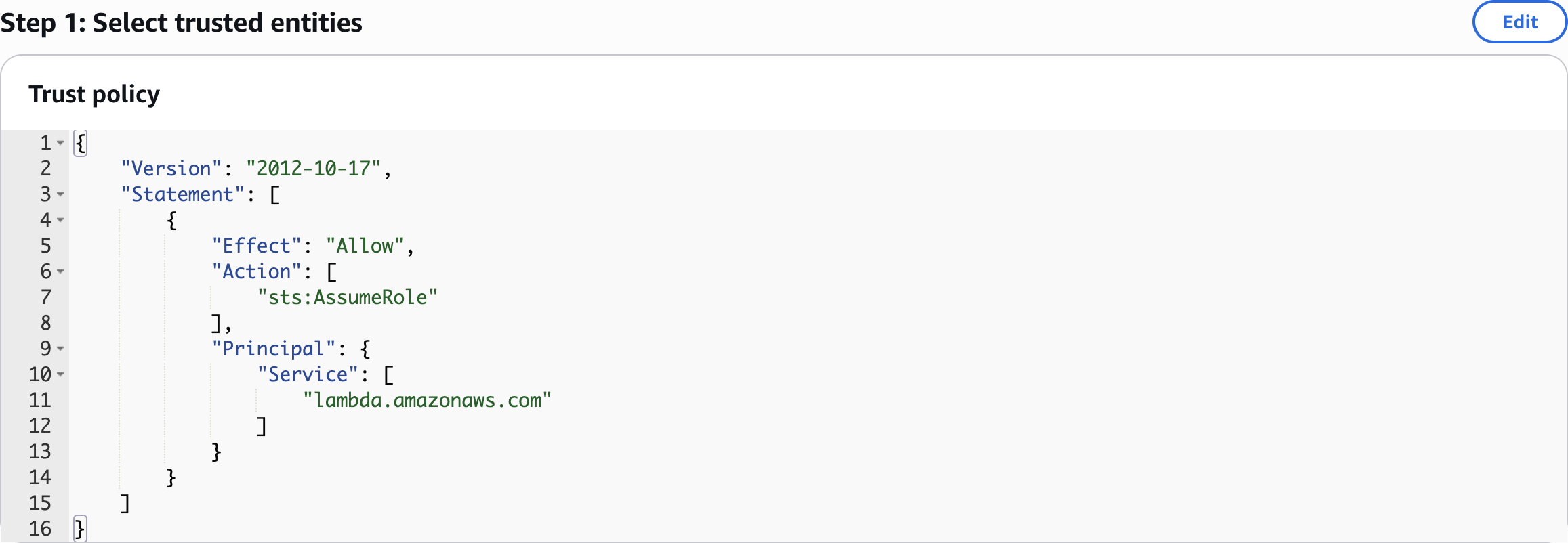
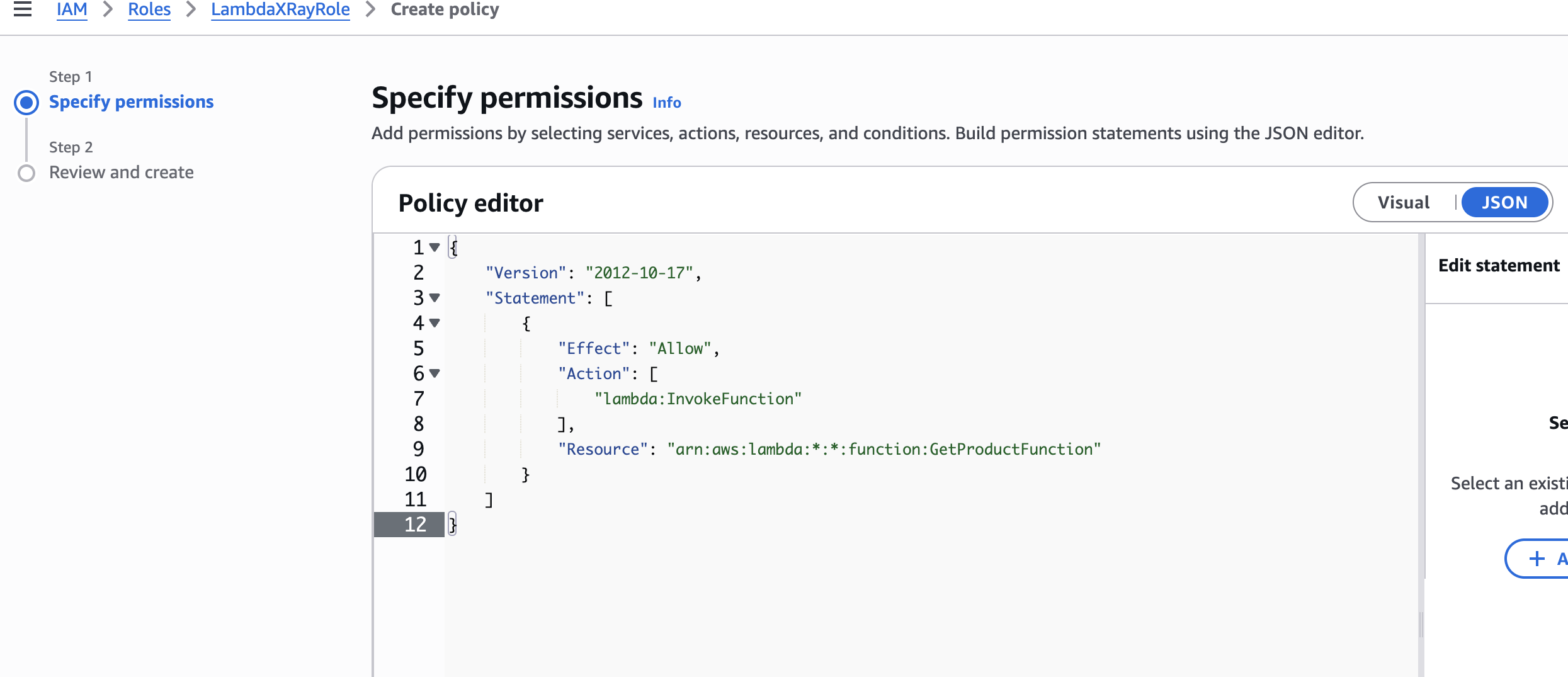
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:InvokeFunction"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:*:*:function:GetProductFunction"
}
]
}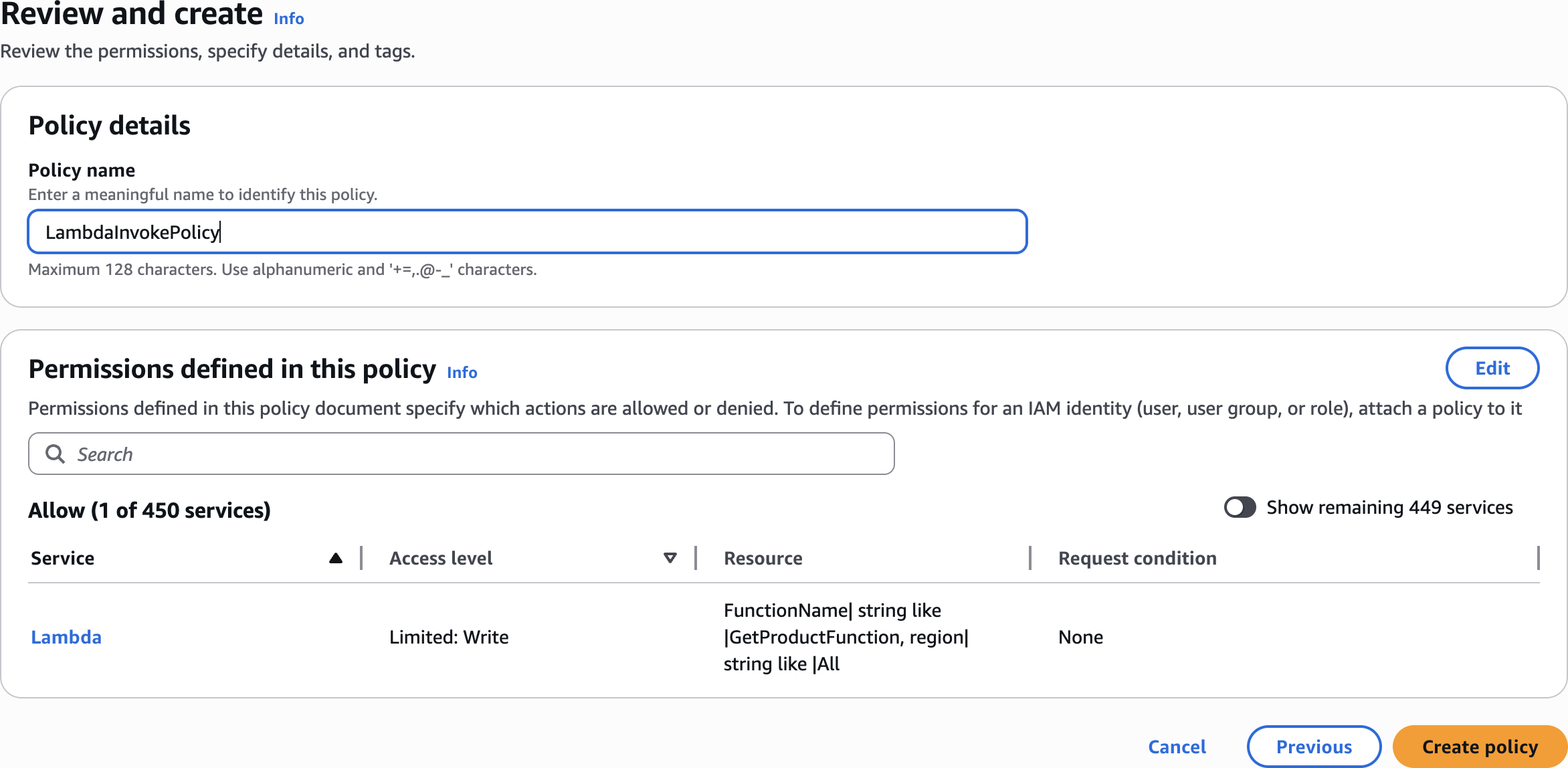
LambdaInvokePolicyStep 2: Create DynamoDB Table for Application Data
DynamoDB
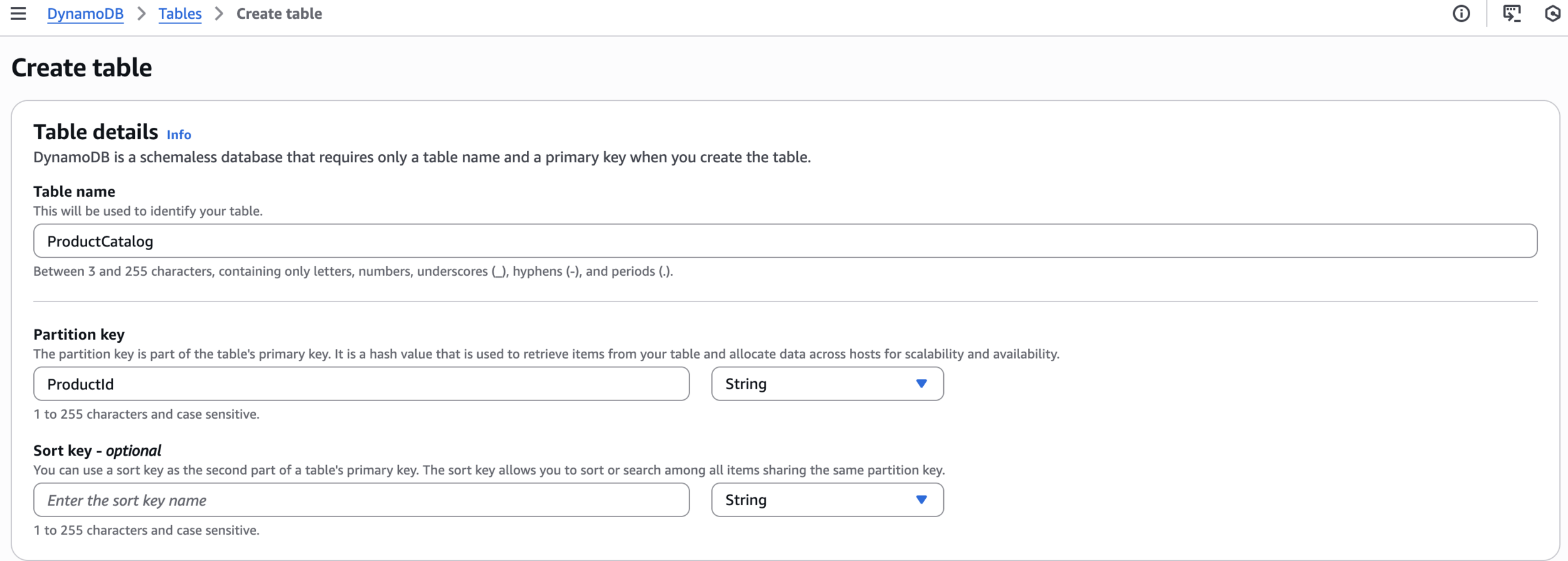
ProductCatalogProductIdCreate table
Table settings

Capacity calculator
Read/write capacity settings

Warm throughput
Secondary indexes
Encryption at rest
Deletion protection
Tags
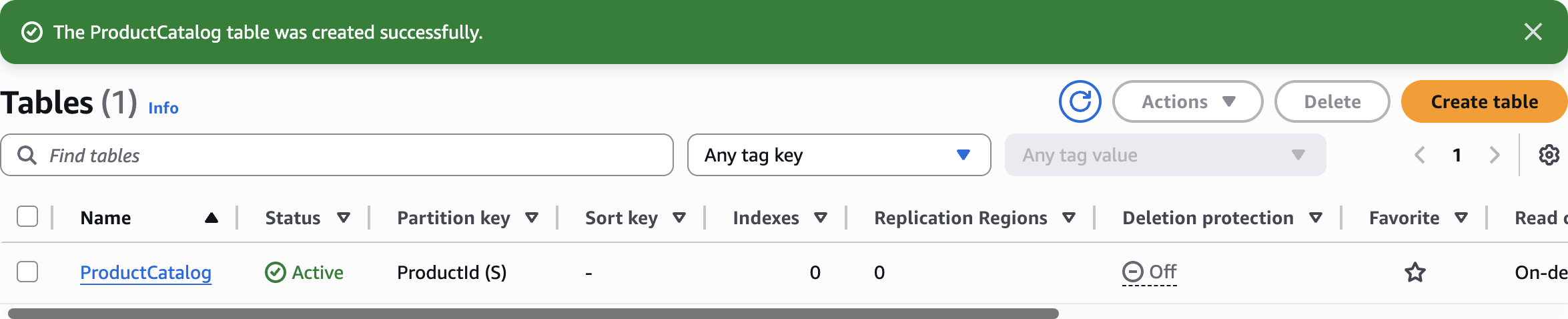
The ProductCatalog table was created successfully
Explore table items
Create item
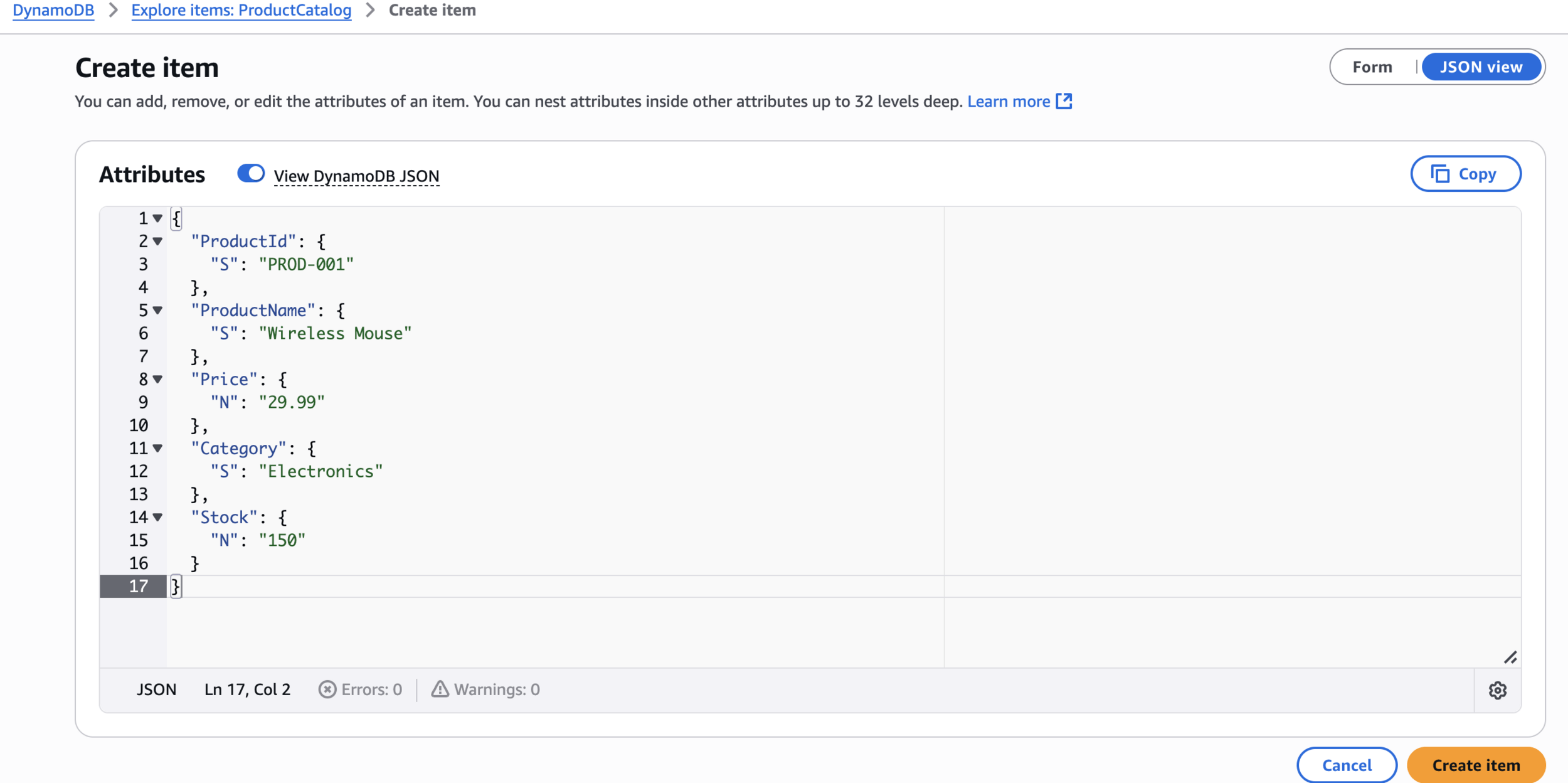
{
"ProductId": {
"S": "PROD-001"
},
"ProductName": {
"S": "Wireless Mouse"
},
"Price": {
"N": "29.99"
},
"Category": {
"S": "Electronics"
},
"Stock": {
"N": "150"
}
}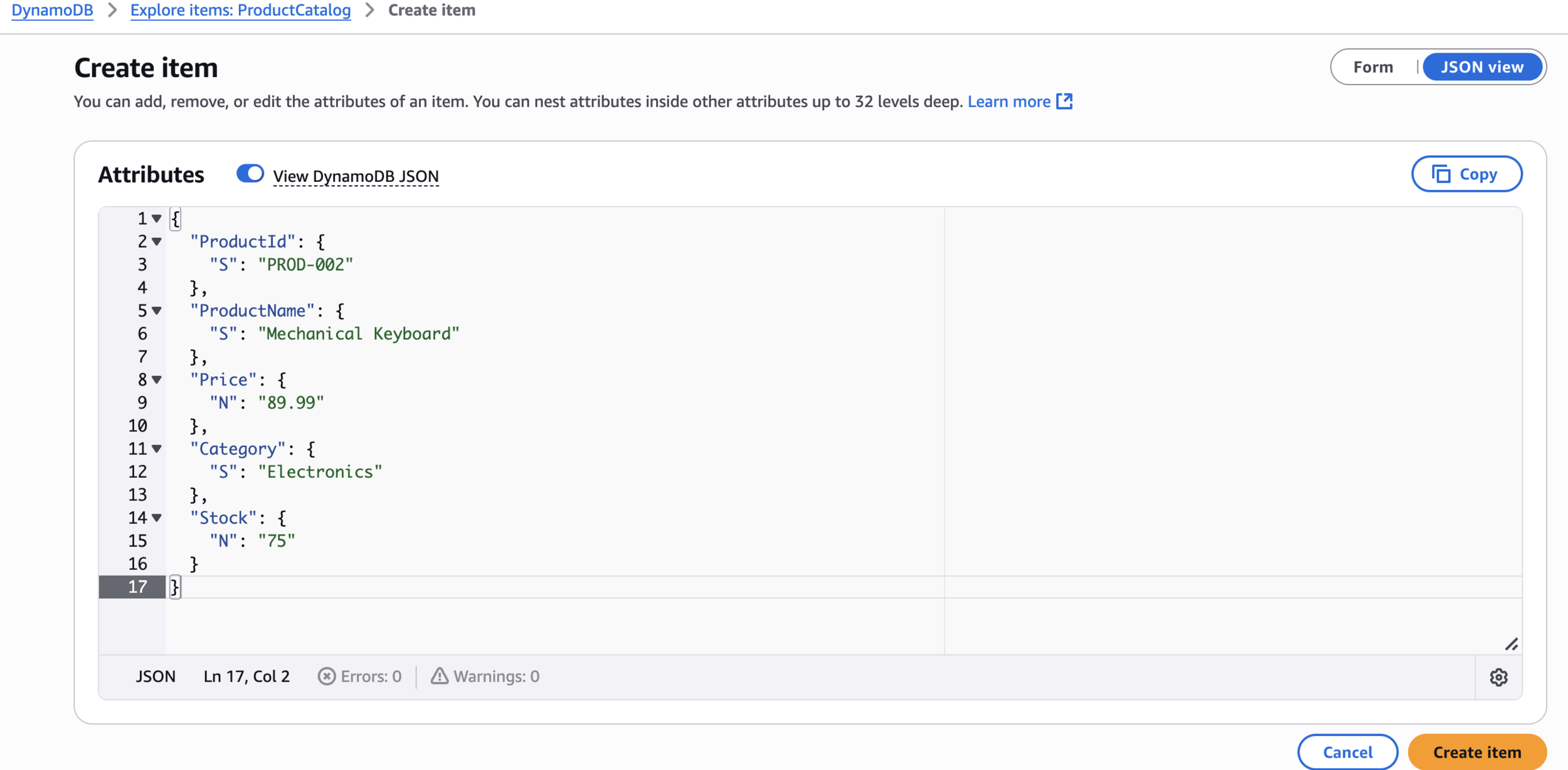
{
"ProductId": {
"S": "PROD-002"
},
"ProductName": {
"S": "Mechanical Keyboard"
},
"Price": {
"N": "89.99"
},
"Category": {
"S": "Electronics"
},
"Stock": {
"N": "75"
}
}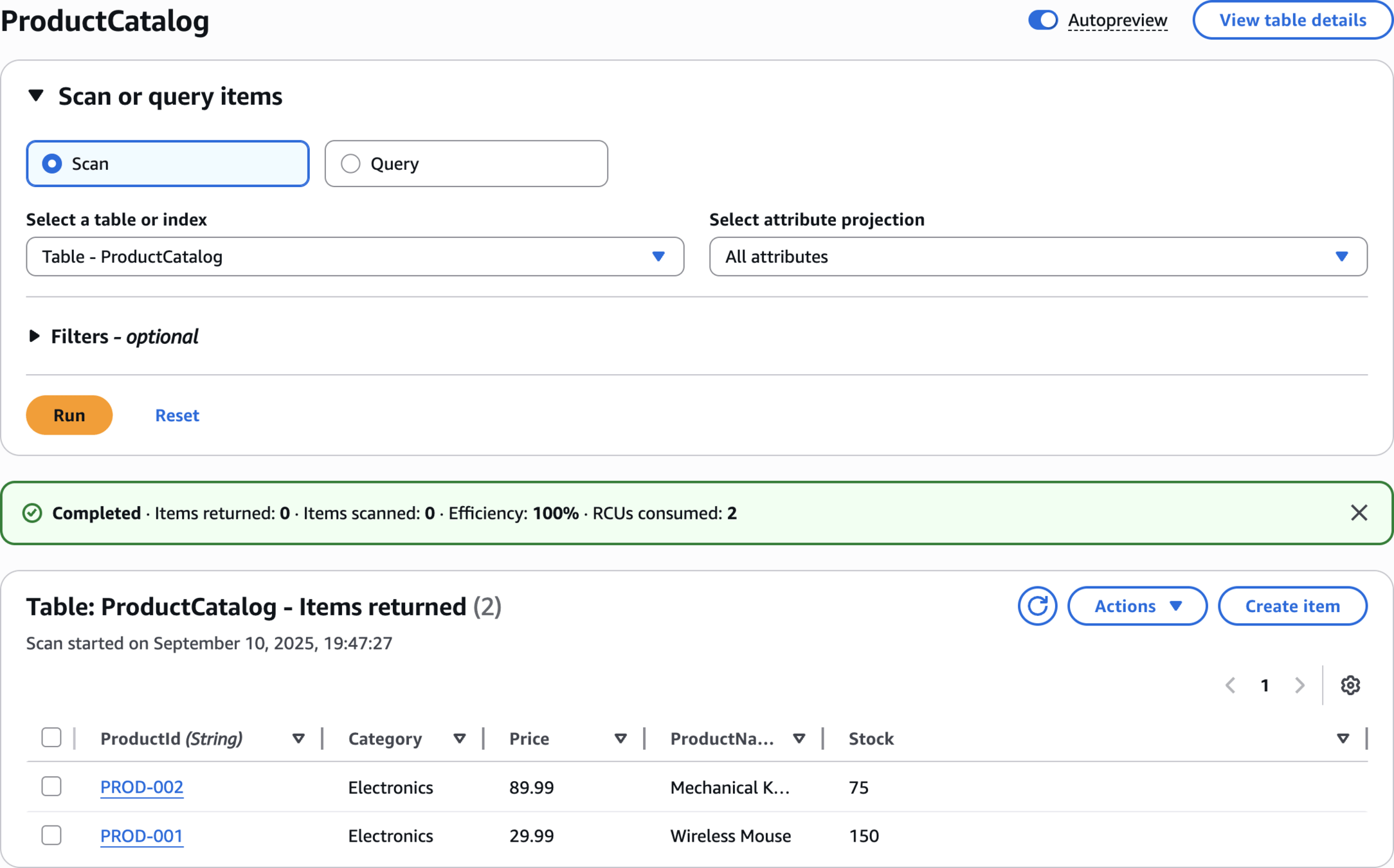
ProductCatalog
Step 3: Create Lambda Functions with X-Ray Tracing
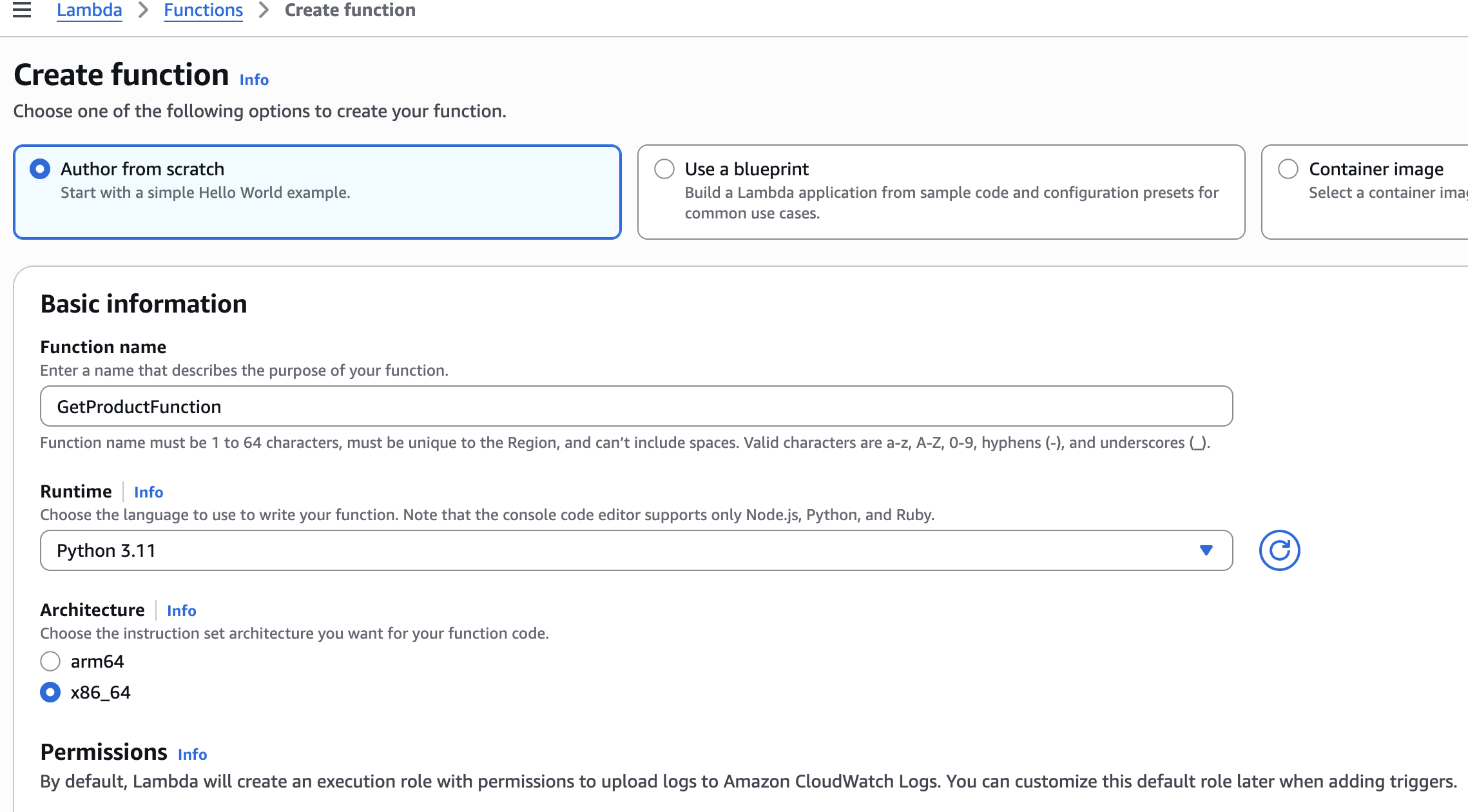
GetProductFunction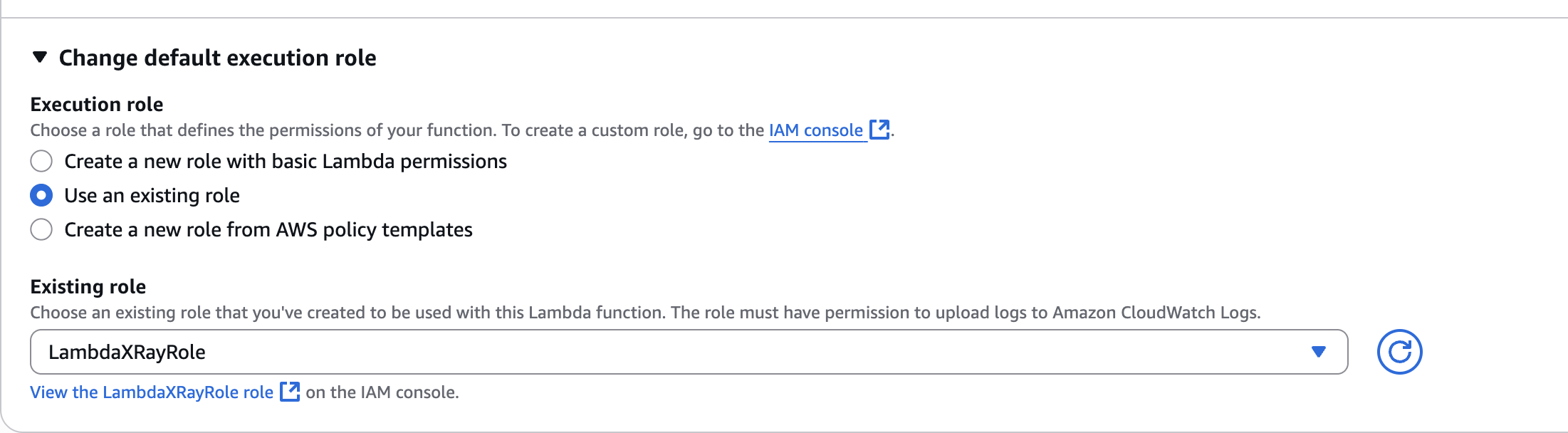
Change default execution role
Additional configurations
Logging configuration
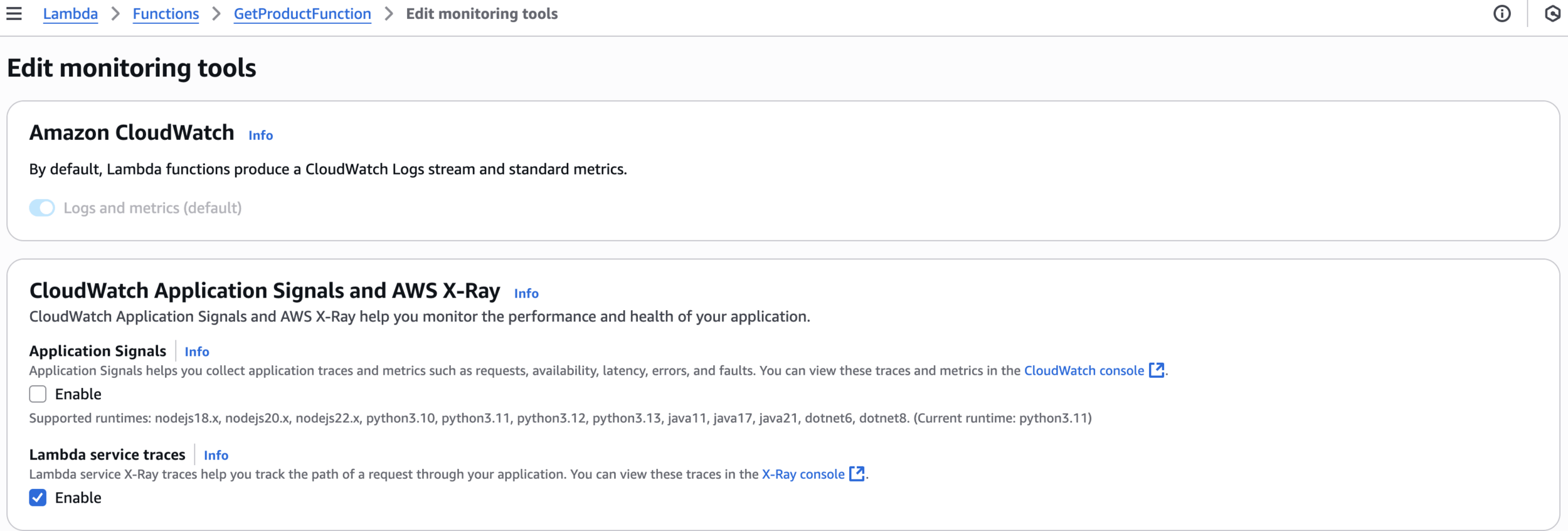
Lambda service traces
Save
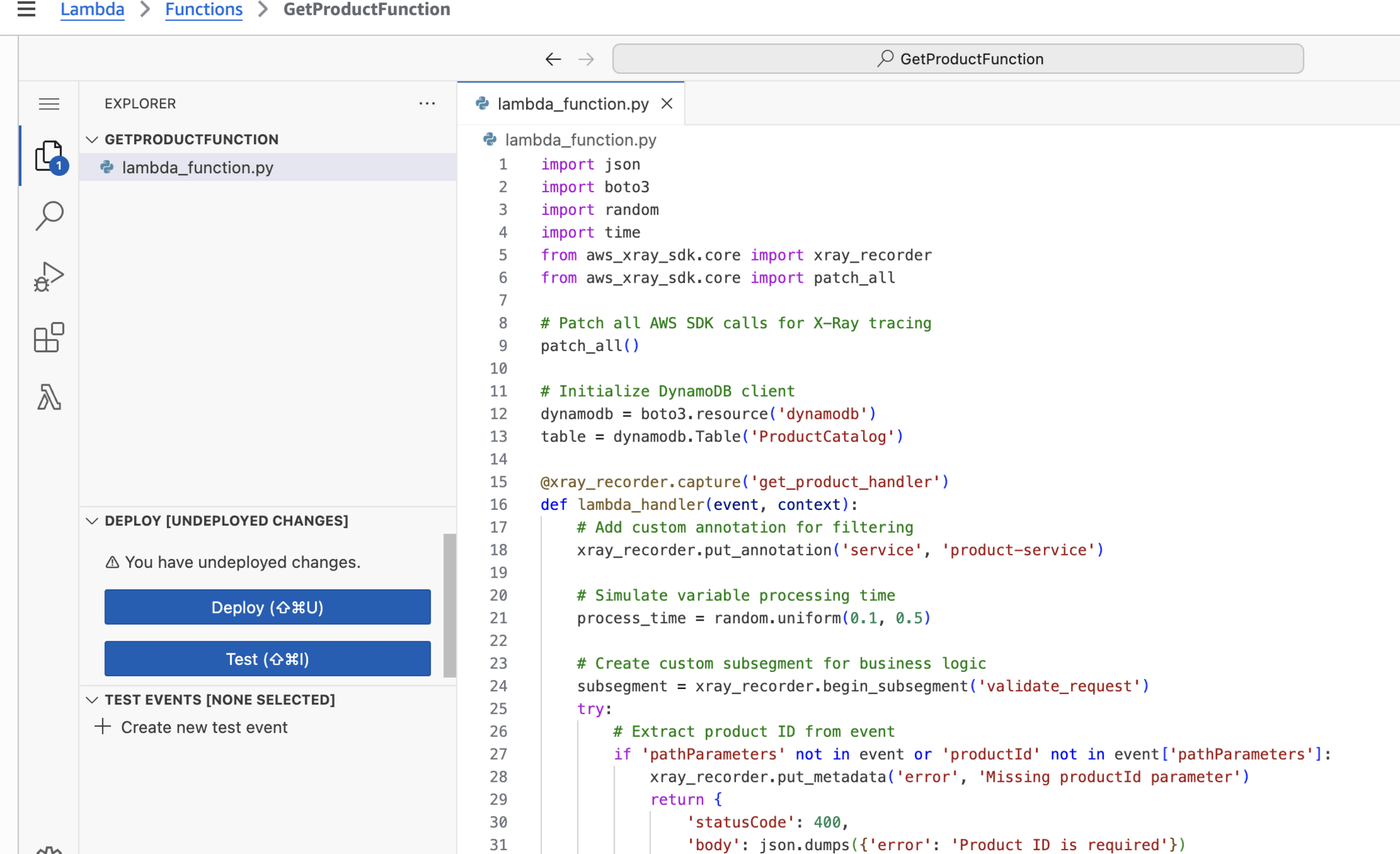
import json
import boto3
import random
import time
# Initialize DynamoDB client
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table('ProductCatalog')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Simulate variable processing time
process_time = random.uniform(0.1, 0.5)
try:
# Extract product ID from event
if 'pathParameters' not in event or 'productId' not in event['pathParameters']:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Product ID is required'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
product_id = event['pathParameters']['productId']
print(f"Fetching product: {product_id}")
# Simulate validation processing
time.sleep(process_time)
# Query DynamoDB
response = table.get_item(Key={'ProductId': product_id})
if 'Item' not in response:
print(f"Product not found: {product_id}")
return {
'statusCode': 404,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Product not found'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
print(f"Product found: {product_id}")
# Simulate post-processing
time.sleep(0.1)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps(response['Item'], default=str),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
return {
'statusCode': 500,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Internal server error', 'details': str(e)}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
ProcessOrderFunctionCreate 2nd function
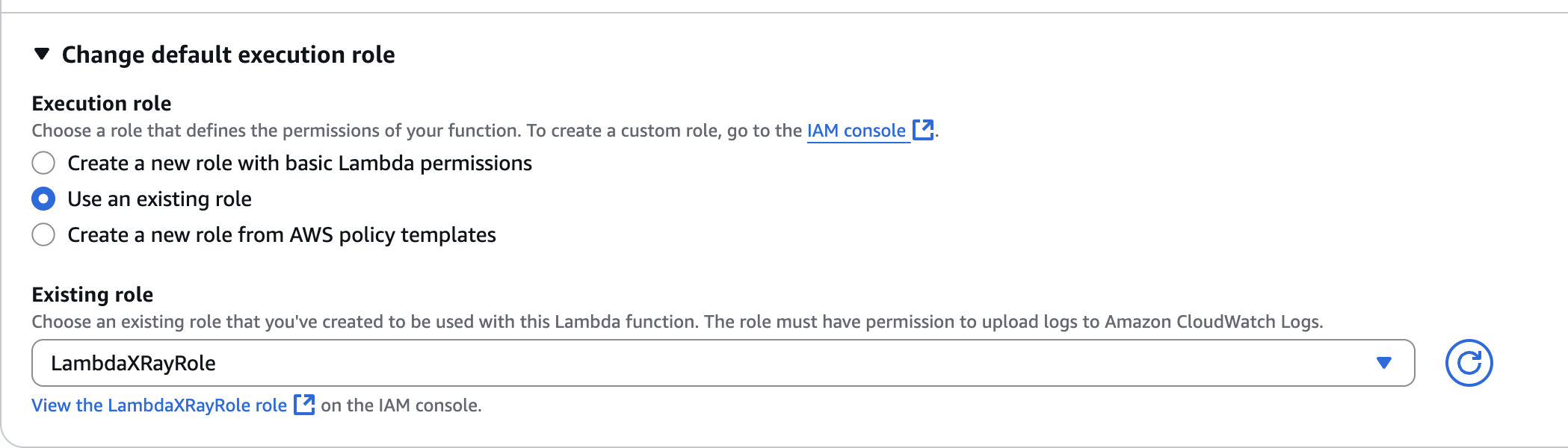
Change default execution role
Additional configurations
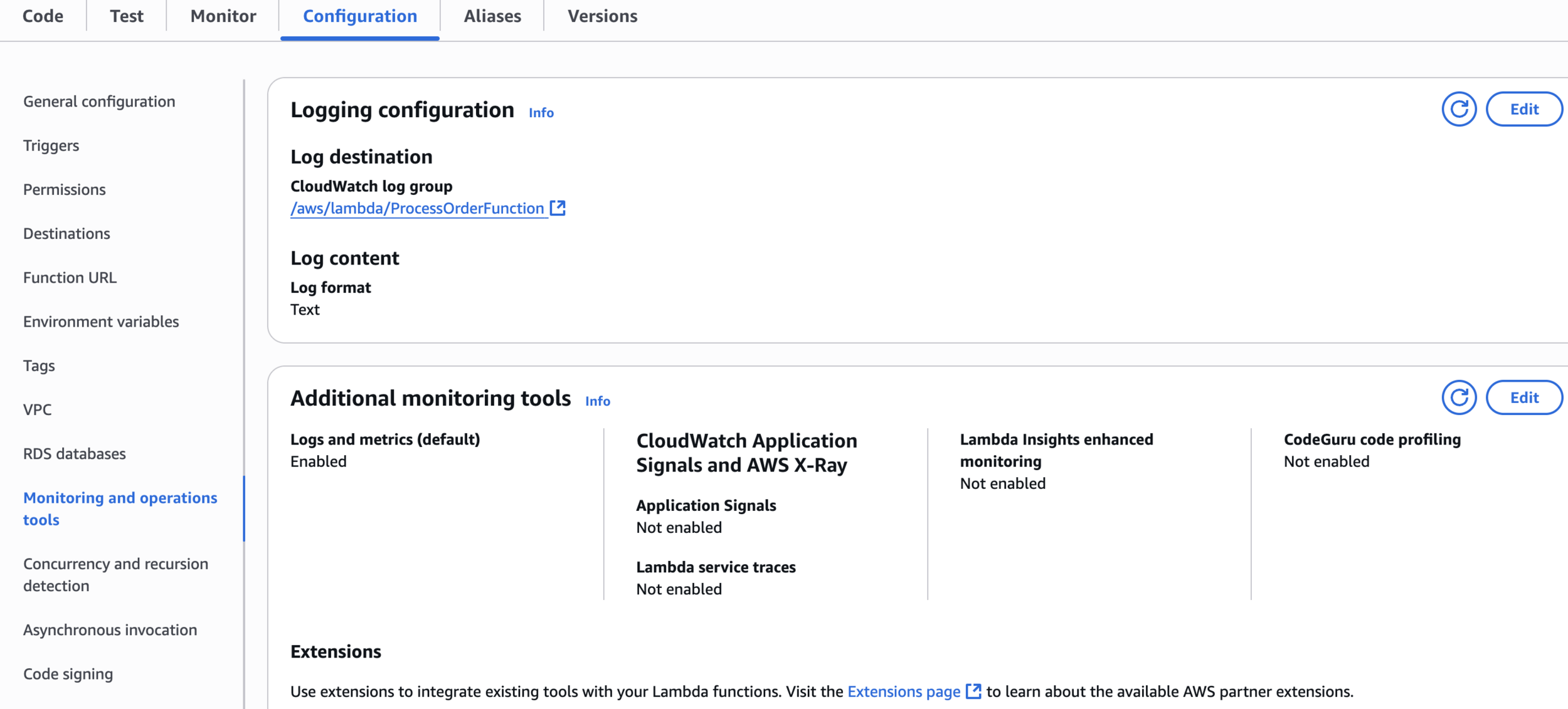
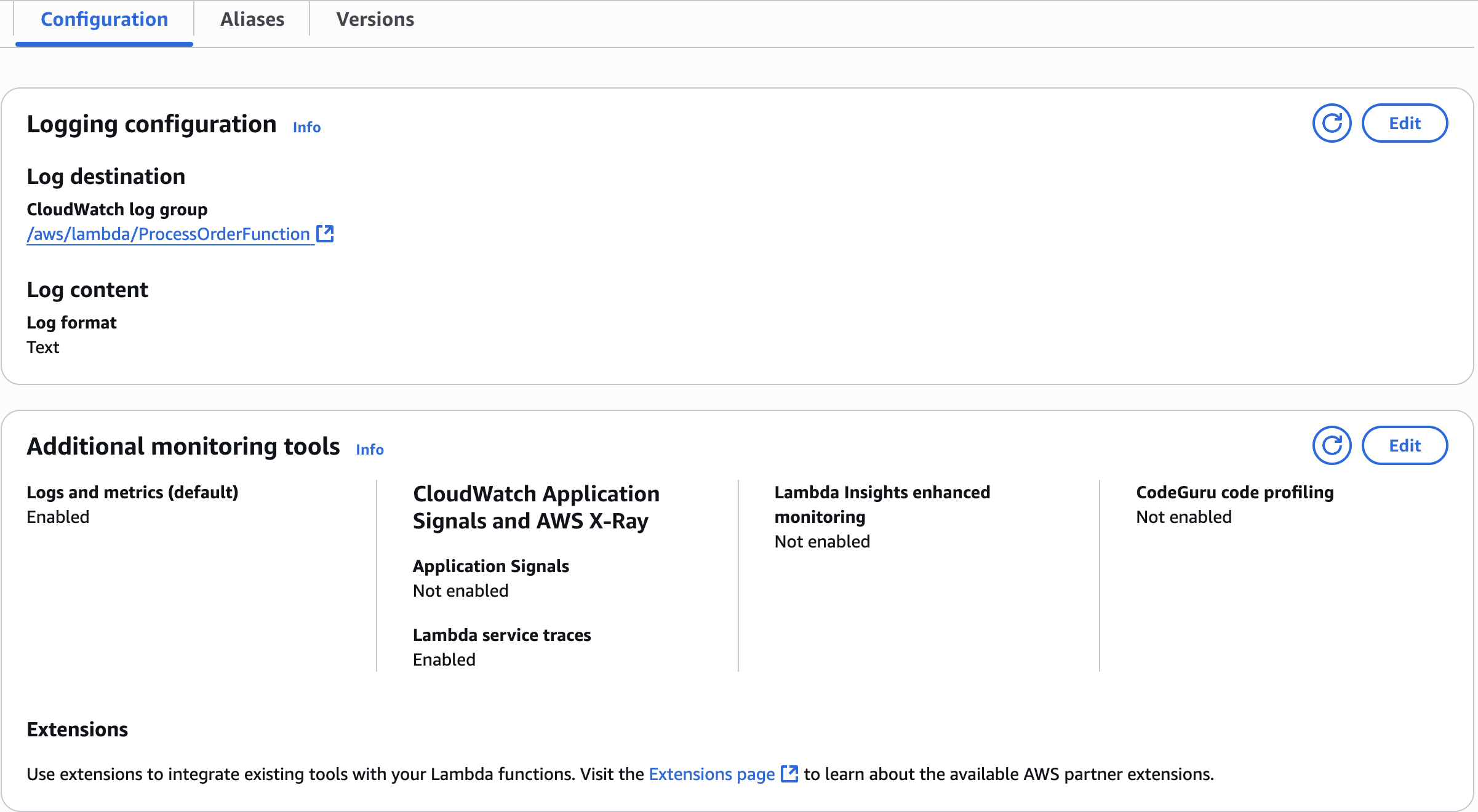
Logging configuration
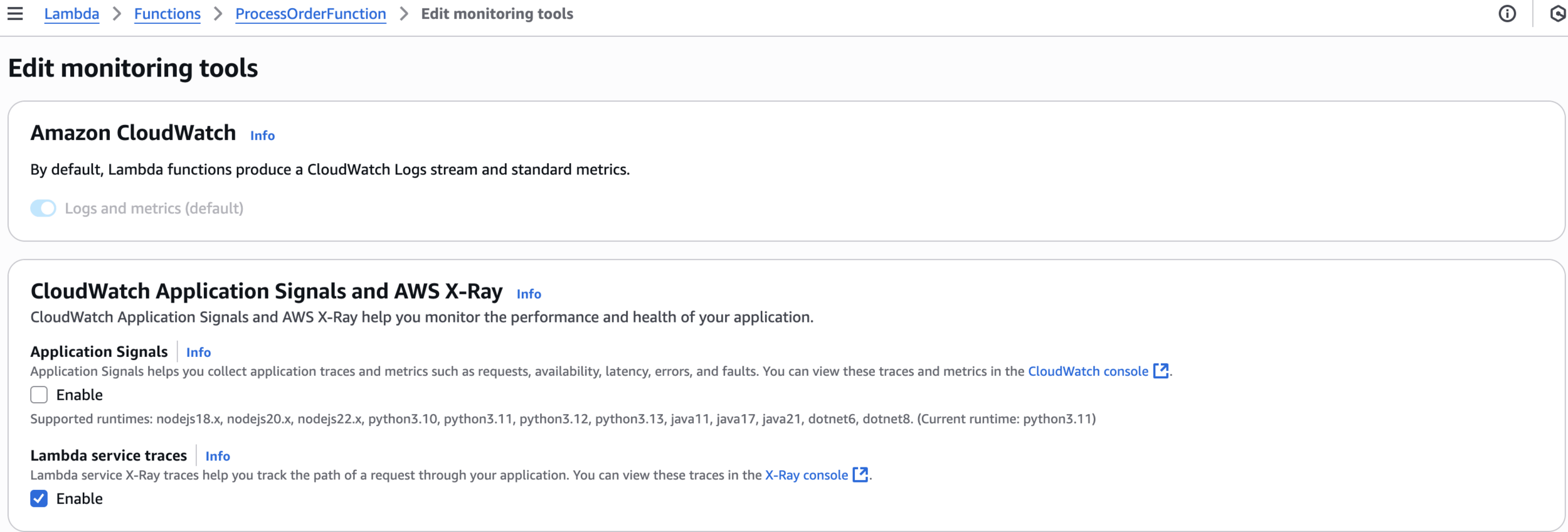
Lambda service traces
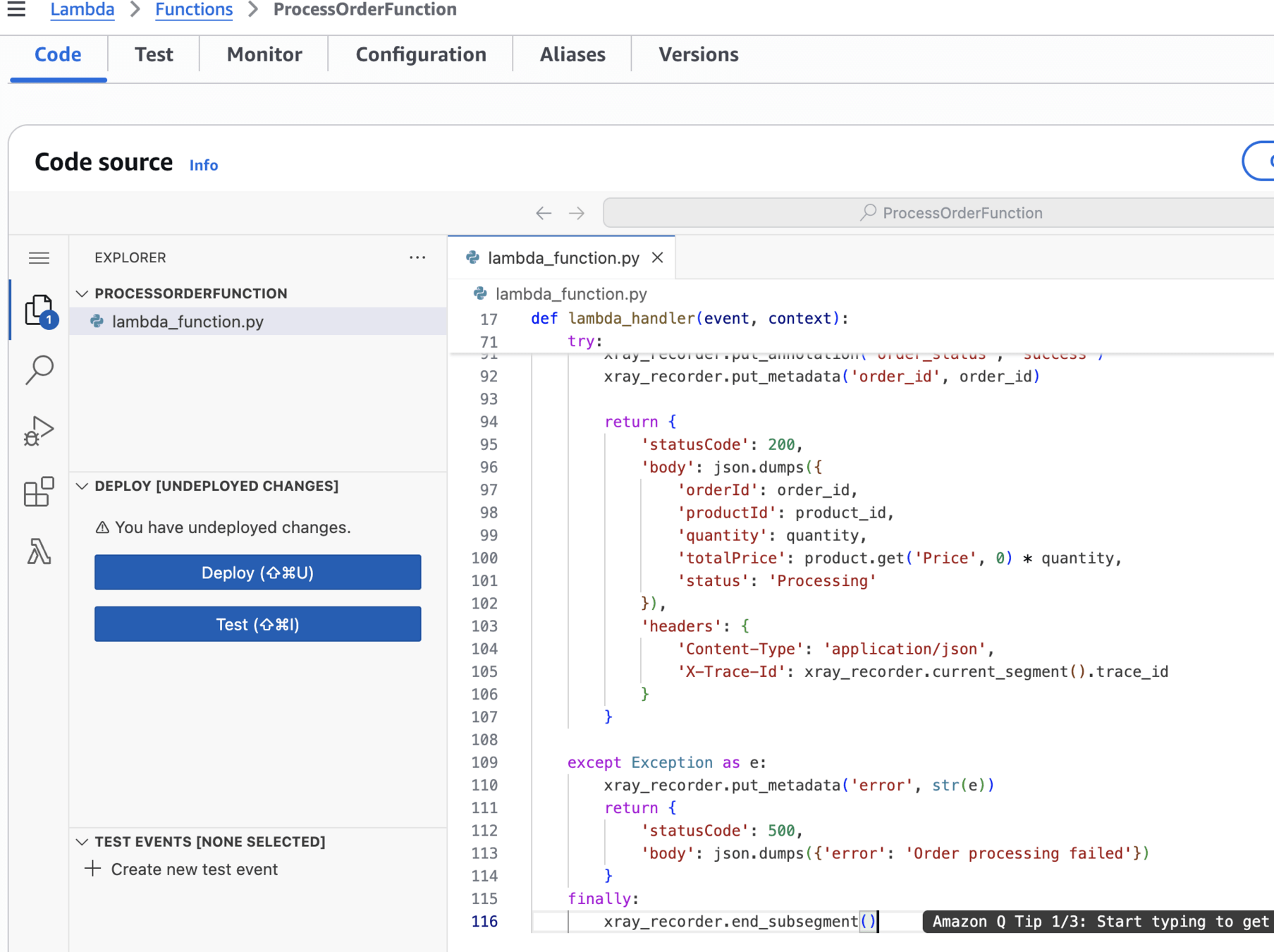
import json
import boto3
import random
import time
from datetime import datetime
# Initialize clients
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
table = dynamodb.Table('ProductCatalog')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Parse request body
try:
if 'body' in event:
body = json.loads(event['body'])
else:
body = event
product_id = body.get('productId')
quantity = body.get('quantity', 1)
print(f"Processing order - Product: {product_id}, Quantity: {quantity}")
except Exception as e:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Invalid request body'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
try:
# Call GetProductFunction to validate product exists
invoke_response = lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName='GetProductFunction',
InvocationType='RequestResponse',
Payload=json.dumps({
'pathParameters': {'productId': product_id}
})
)
response_payload = json.loads(invoke_response['Payload'].read())
if response_payload['statusCode'] != 200:
return {
'statusCode': 404,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Product not found'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
product = json.loads(response_payload['body'])
# Simulate inventory check with random delay
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.2, 0.6))
stock = float(product.get('Stock', 0)) # Convert to float for comparison
if stock < quantity:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Insufficient stock'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
# Simulate order processing
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.3, 0.7))
# Occasionally simulate a slow operation
if random.random() > 0.8:
print("Slow operation triggered")
time.sleep(2.0)
order_id = f"ORD-{int(time.time())}"
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
'orderId': order_id,
'productId': product_id,
'quantity': quantity,
'totalPrice': float(product.get('Price', 0)) * quantity,
'status': 'Processing'
}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing order: {str(e)}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
return {
'statusCode': 500,
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Order processing failed'}),
'headers': {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
}
Step 4: Configure API Gateway with X-Ray Tracing

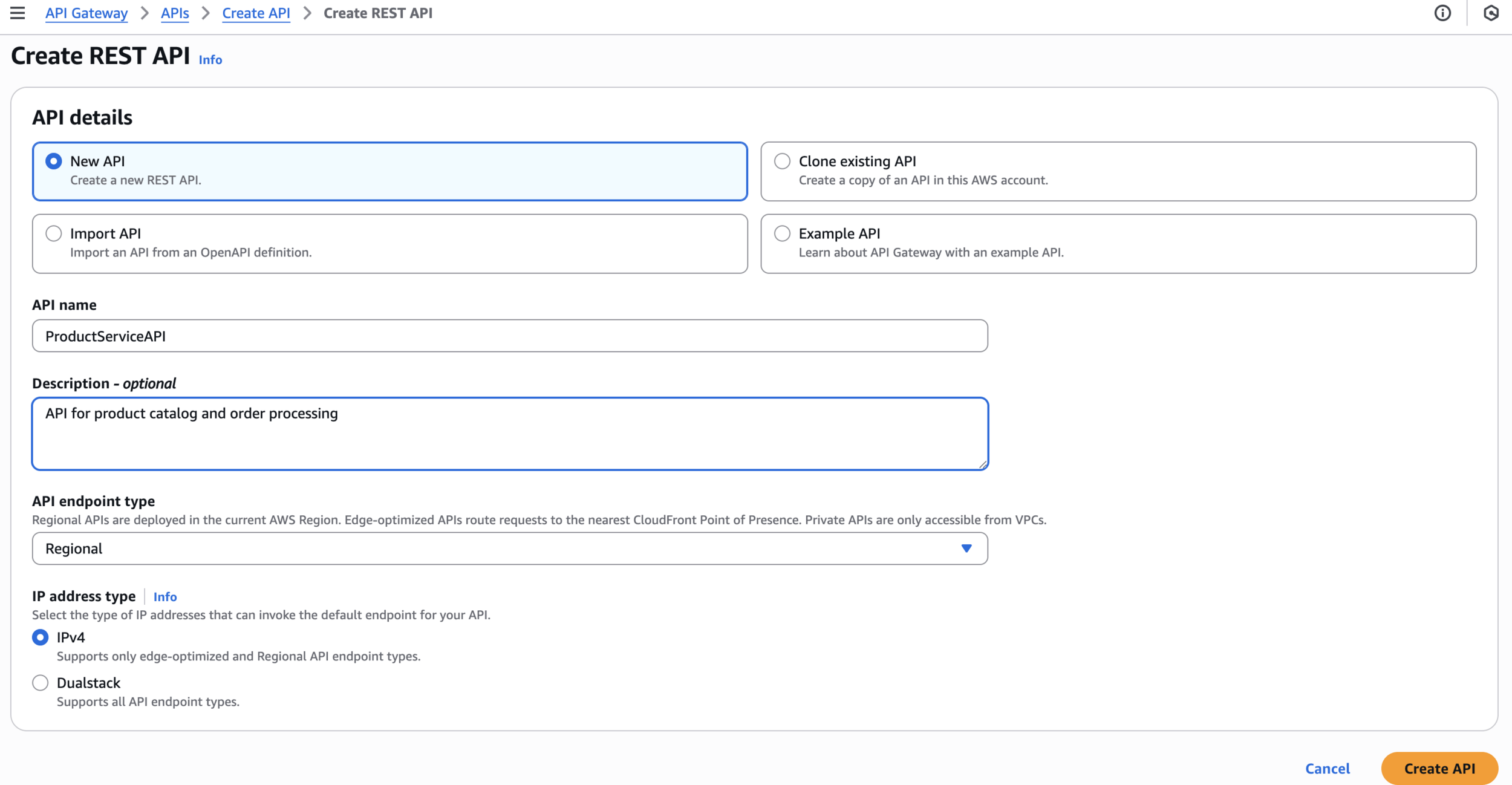
ProductServiceAPIAPI for product catalog and order processingCreate REST API
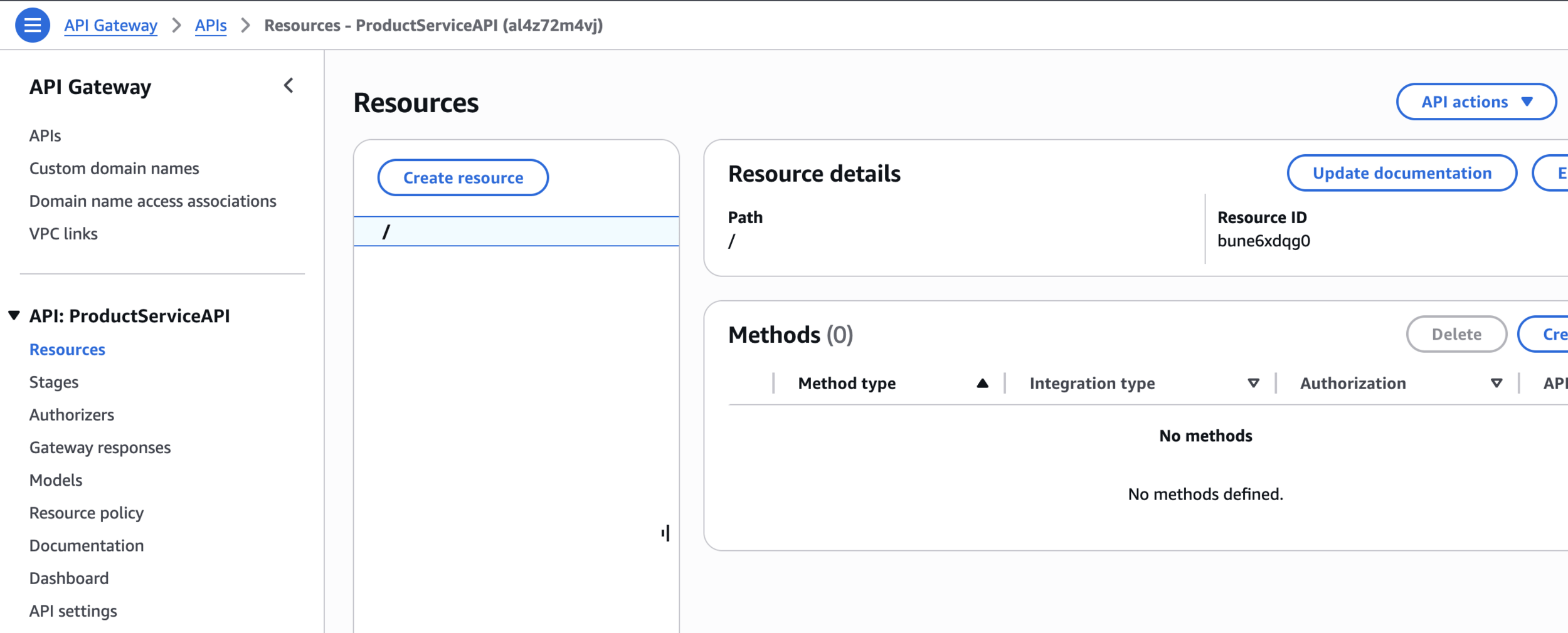
Create resource
productsCreate resource
{productId}Create resource
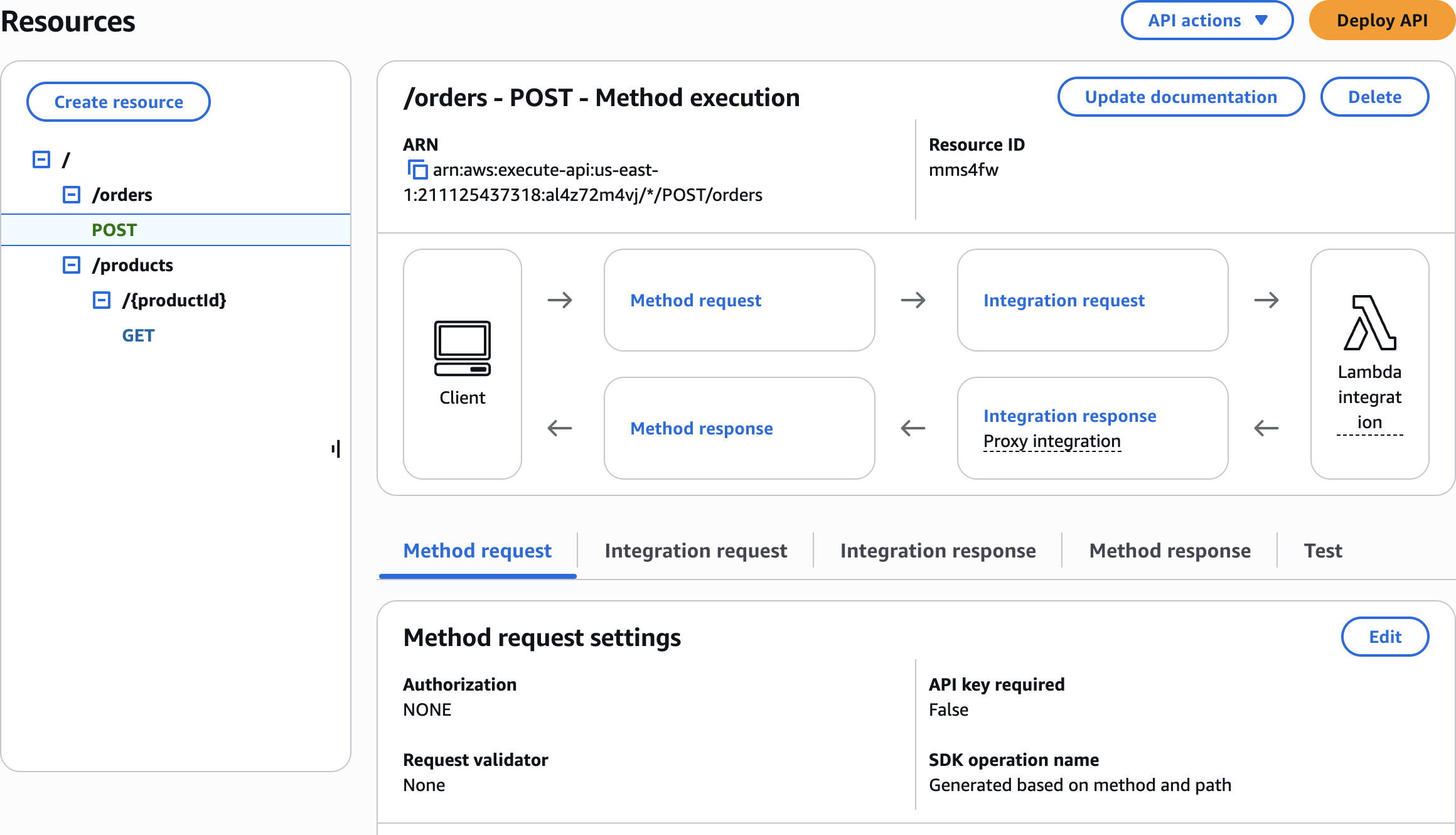
Resources
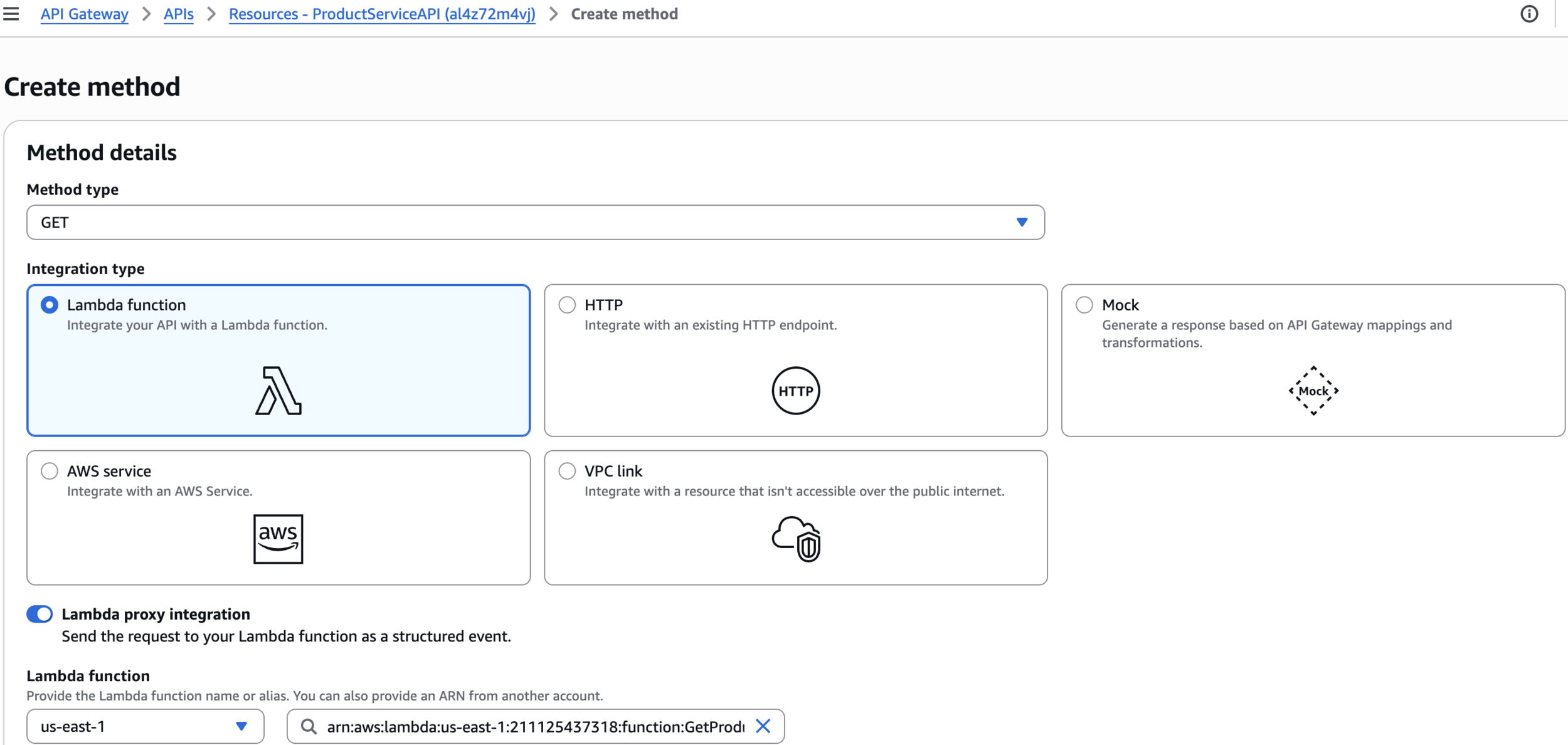
Create method
Create method
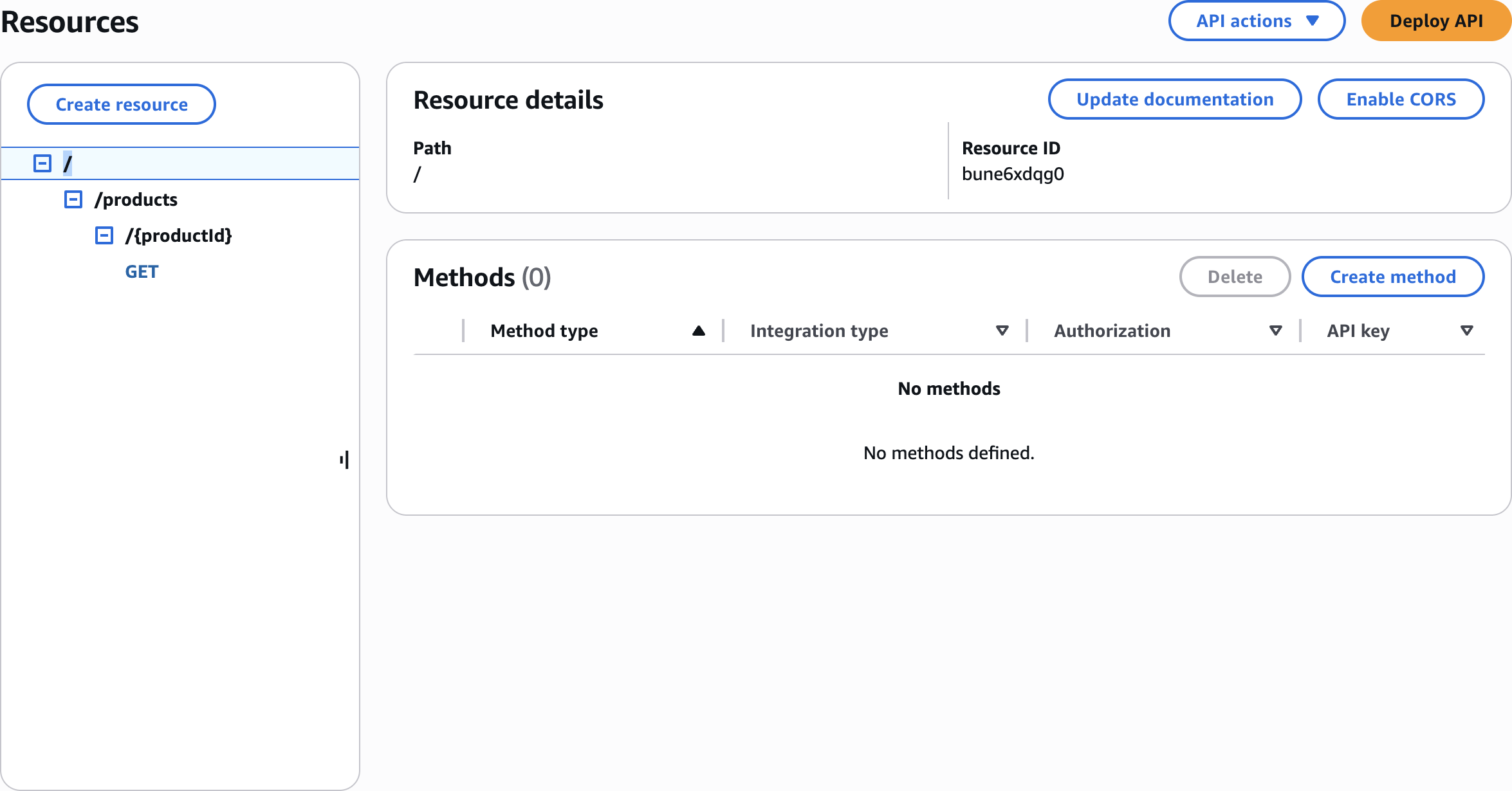
Resources
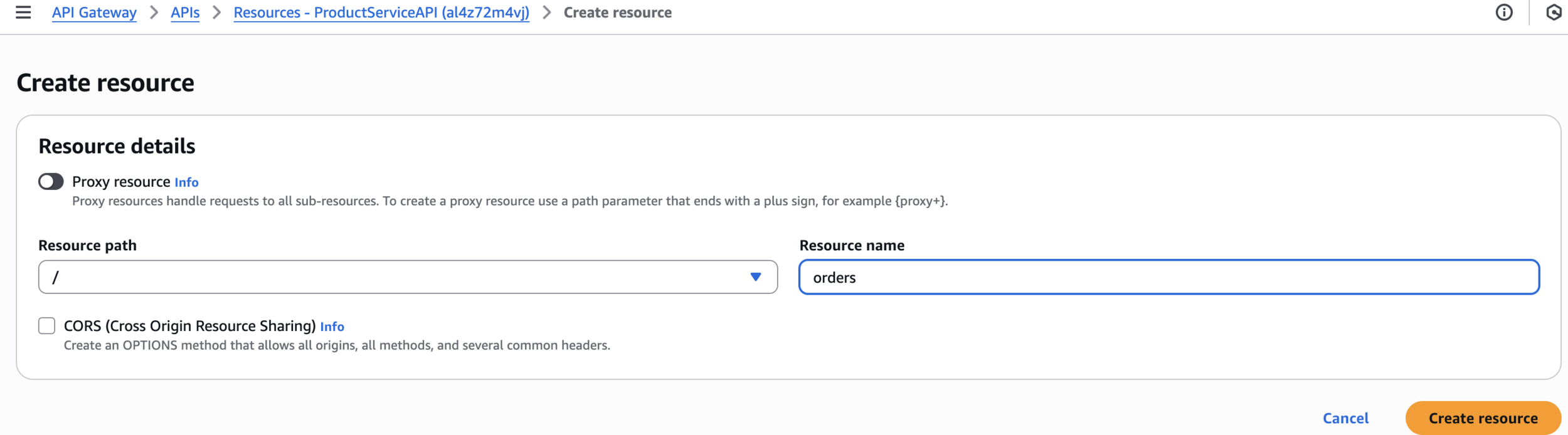
ordersCreate resource
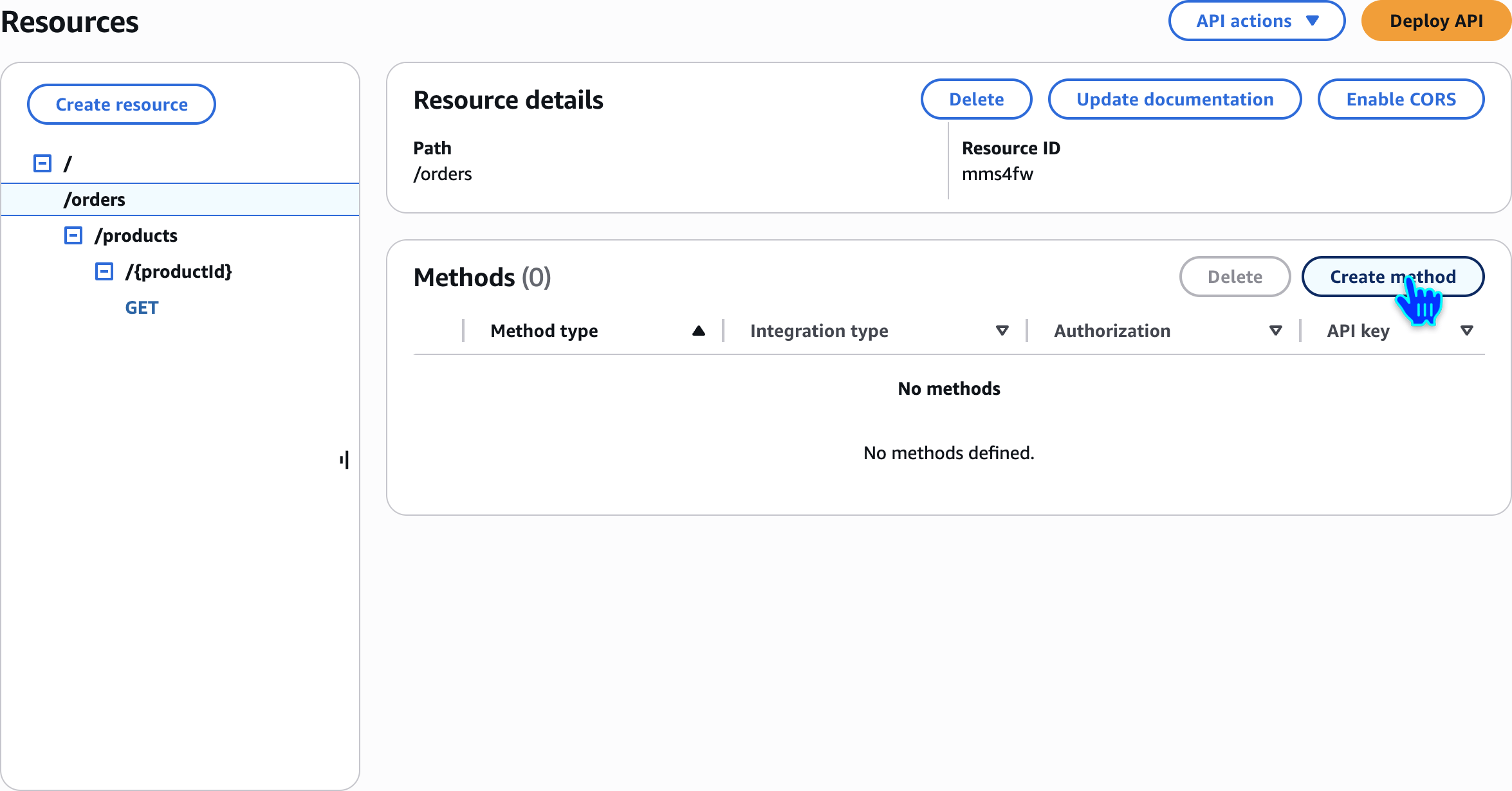
Create method
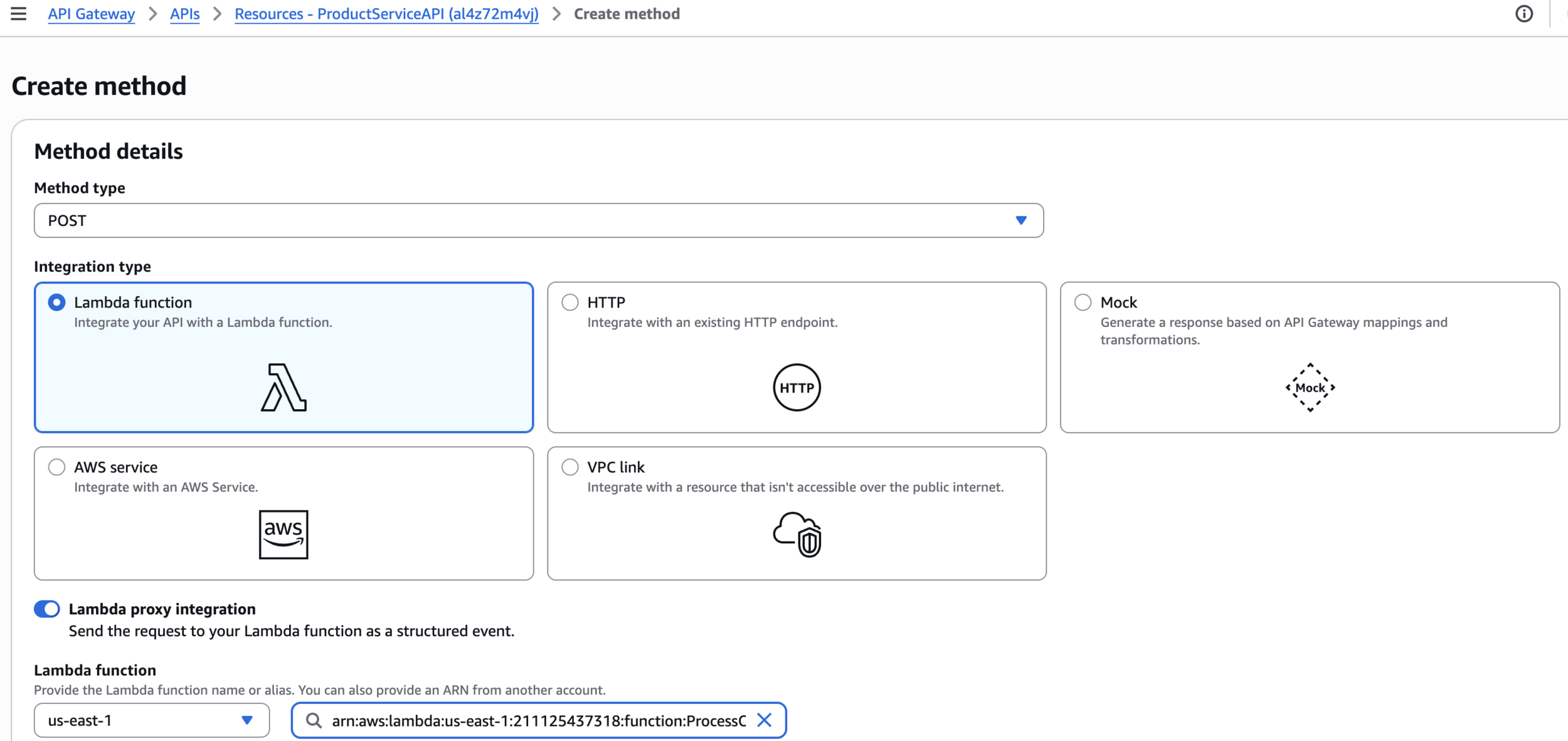
Lambda function
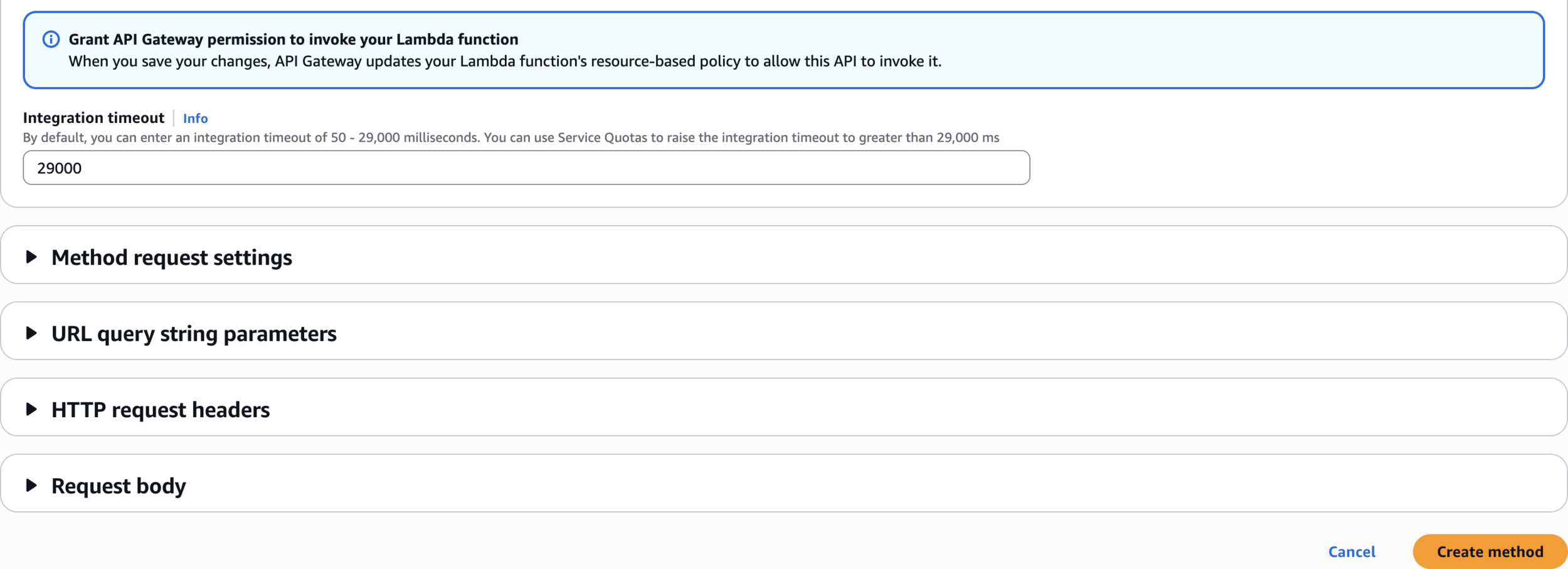
Create method
Deploy API
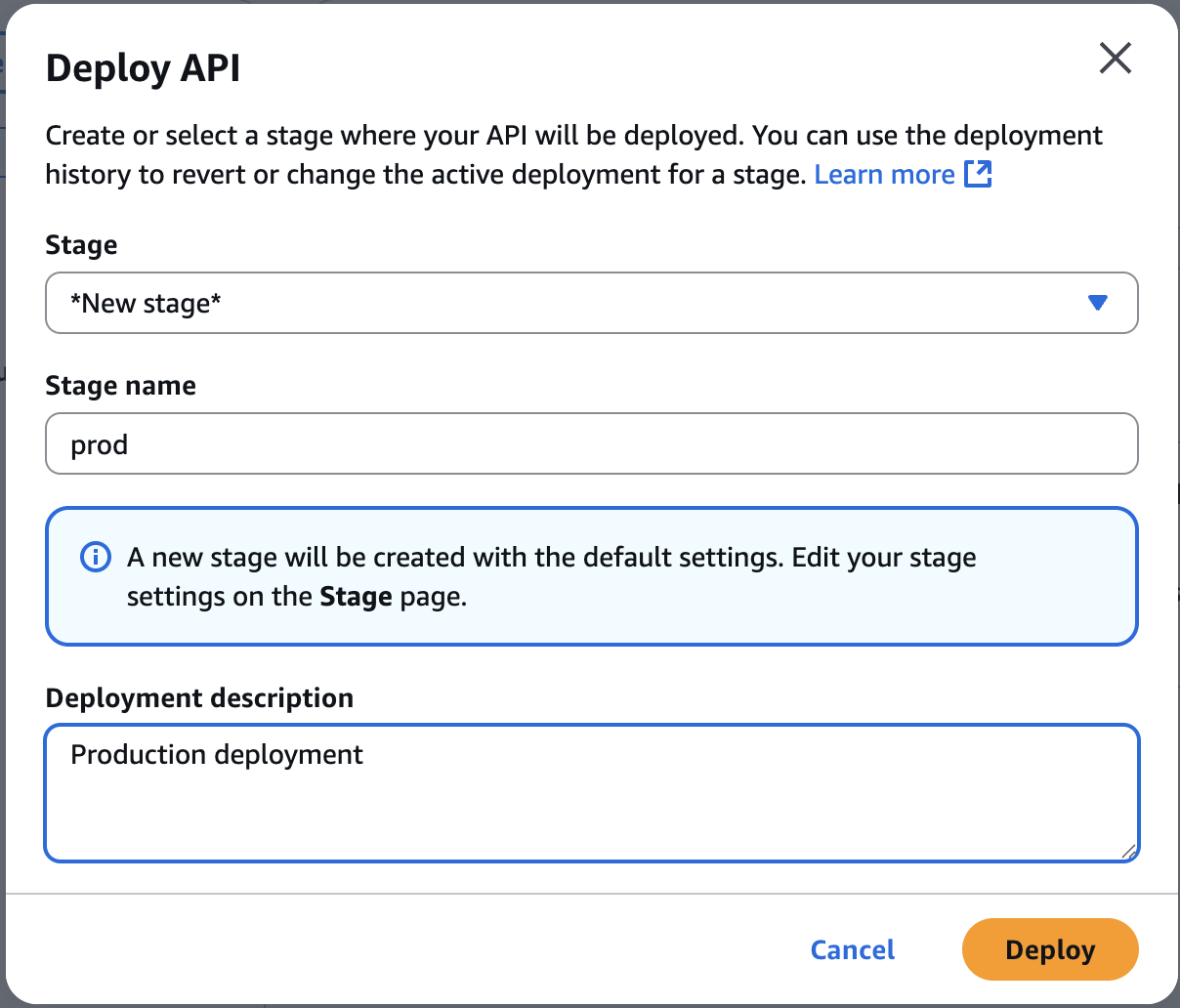
prodDeploy API
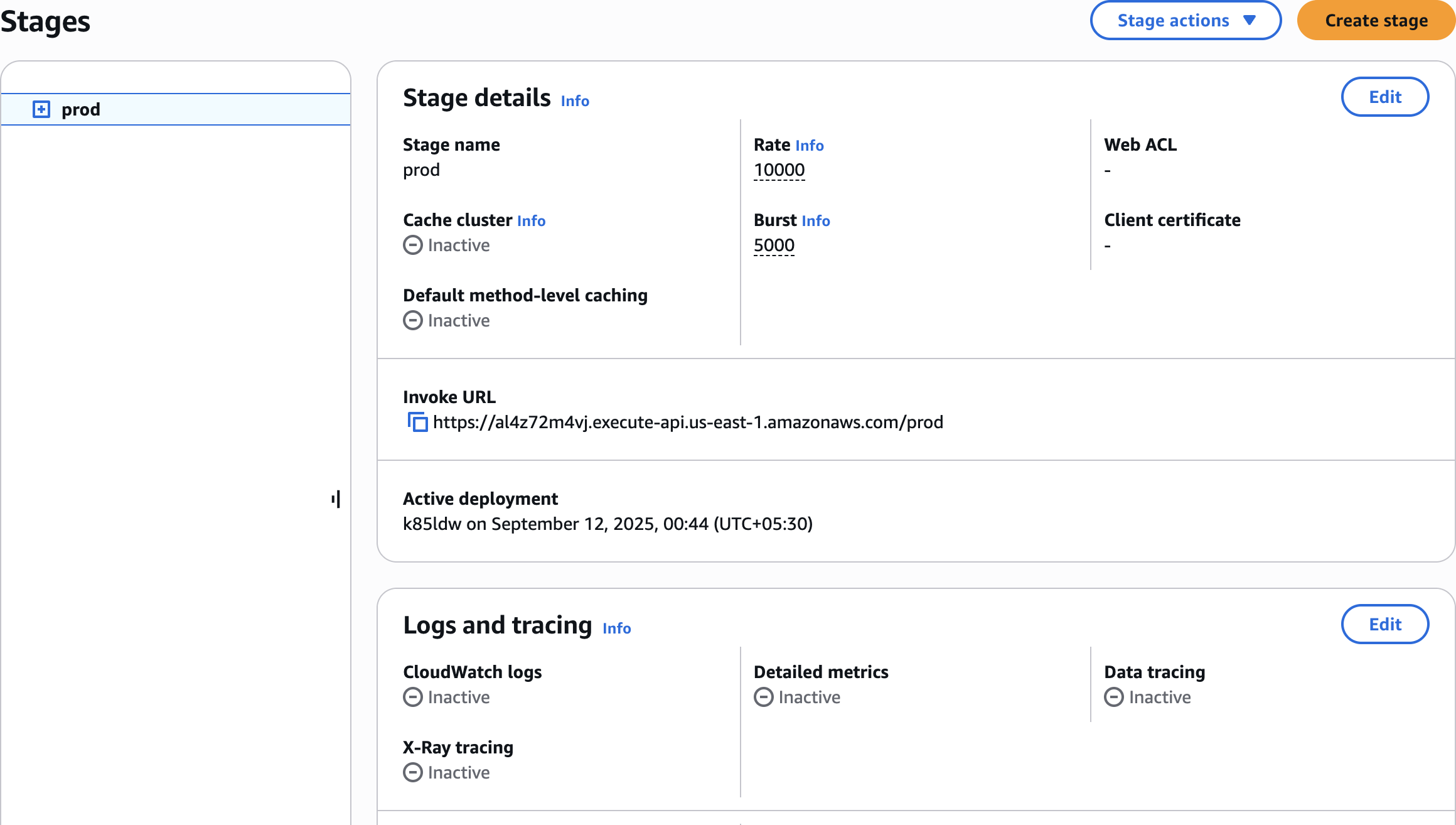
Edit Stage
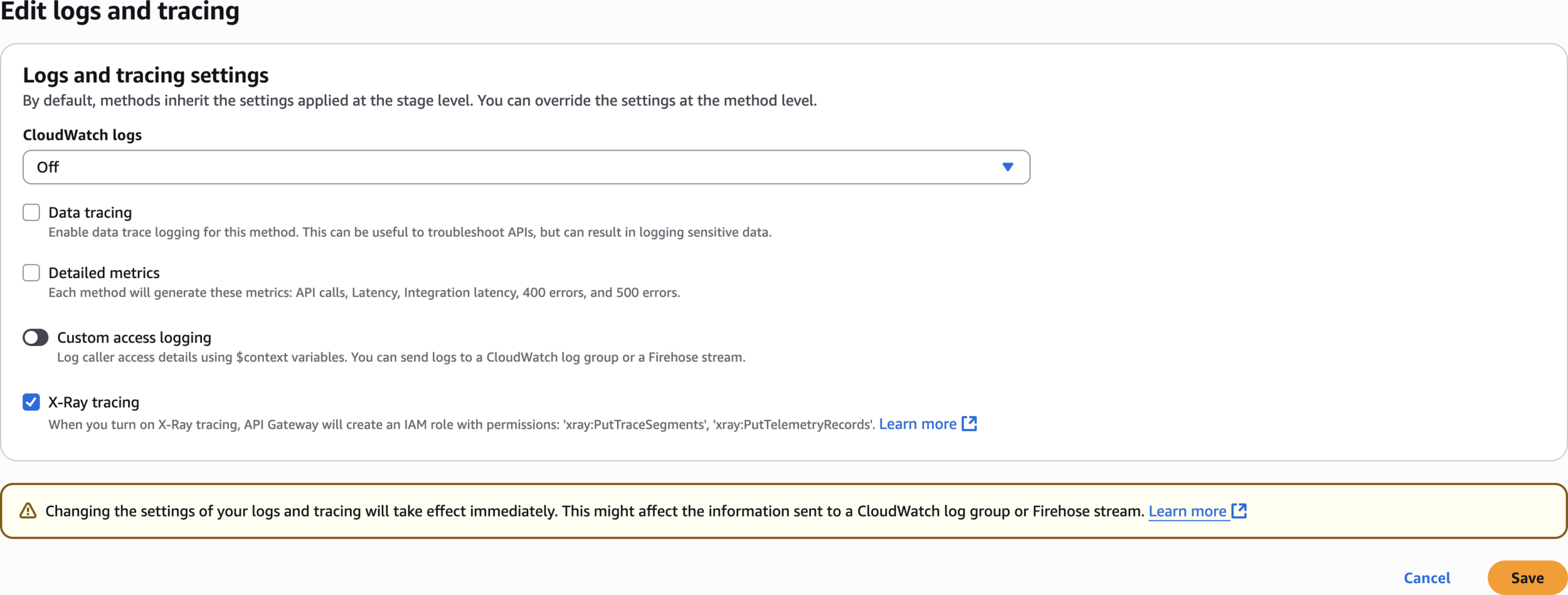
Edit logs and tracing
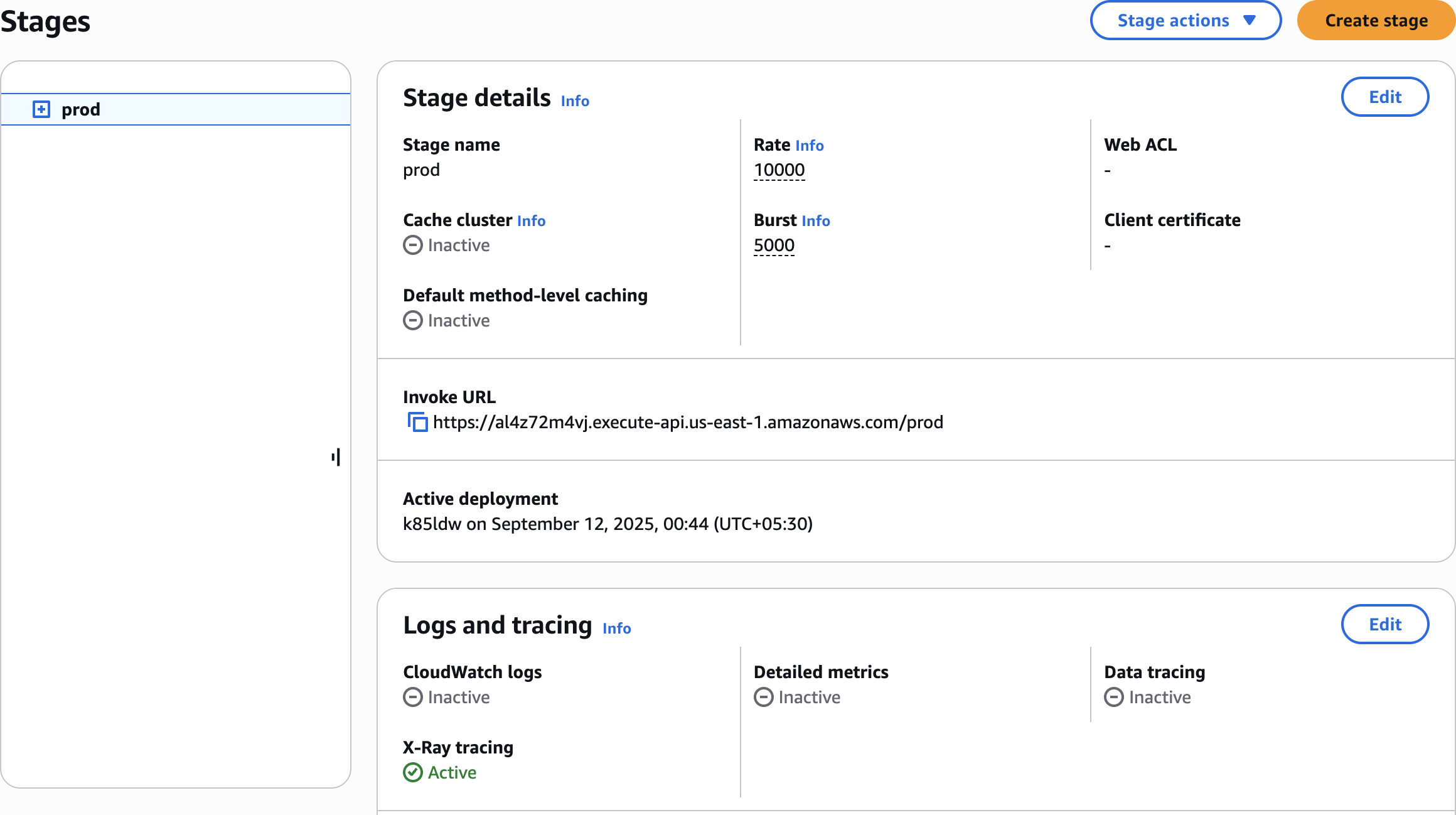
Step 5: Generate Traffic and Test the Application
# Test retrieving a product
curl -X GET "${API_ENDPOINT}/products/PROD-001"# Set your API endpoint
API_ENDPOINT=# Test non-existent product
curl -X GET "${API_ENDPOINT}/products/PROD-999"

# Process an order
curl -X POST "${API_ENDPOINT}/orders" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"productId": "PROD-001",
"quantity": 2
}'# Test with invalid product
curl -X POST "${API_ENDPOINT}/orders" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"productId": "INVALID-PRODUCT",
"quantity": 1
}'Create Bulk Traffic Script
# Generate 20 requests with varying patterns
for i in {1..20}; do
# Alternate between products
if [ $((i % 2)) -eq 0 ]; then
PRODUCT="PROD-001"
else
PRODUCT="PROD-002"
fi
# GET request
curl -s -X GET "${API_ENDPOINT}/products/${PRODUCT}" > /dev/null &
# POST request
curl -s -X POST "${API_ENDPOINT}/orders" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{\"productId\": \"${PRODUCT}\", \"quantity\": $((RANDOM % 5 + 1))}" > /dev/null &
# Small delay between requests
sleep 0.5
done
echo "Traffic generation complete. Wait for all requests to finish..."
wait
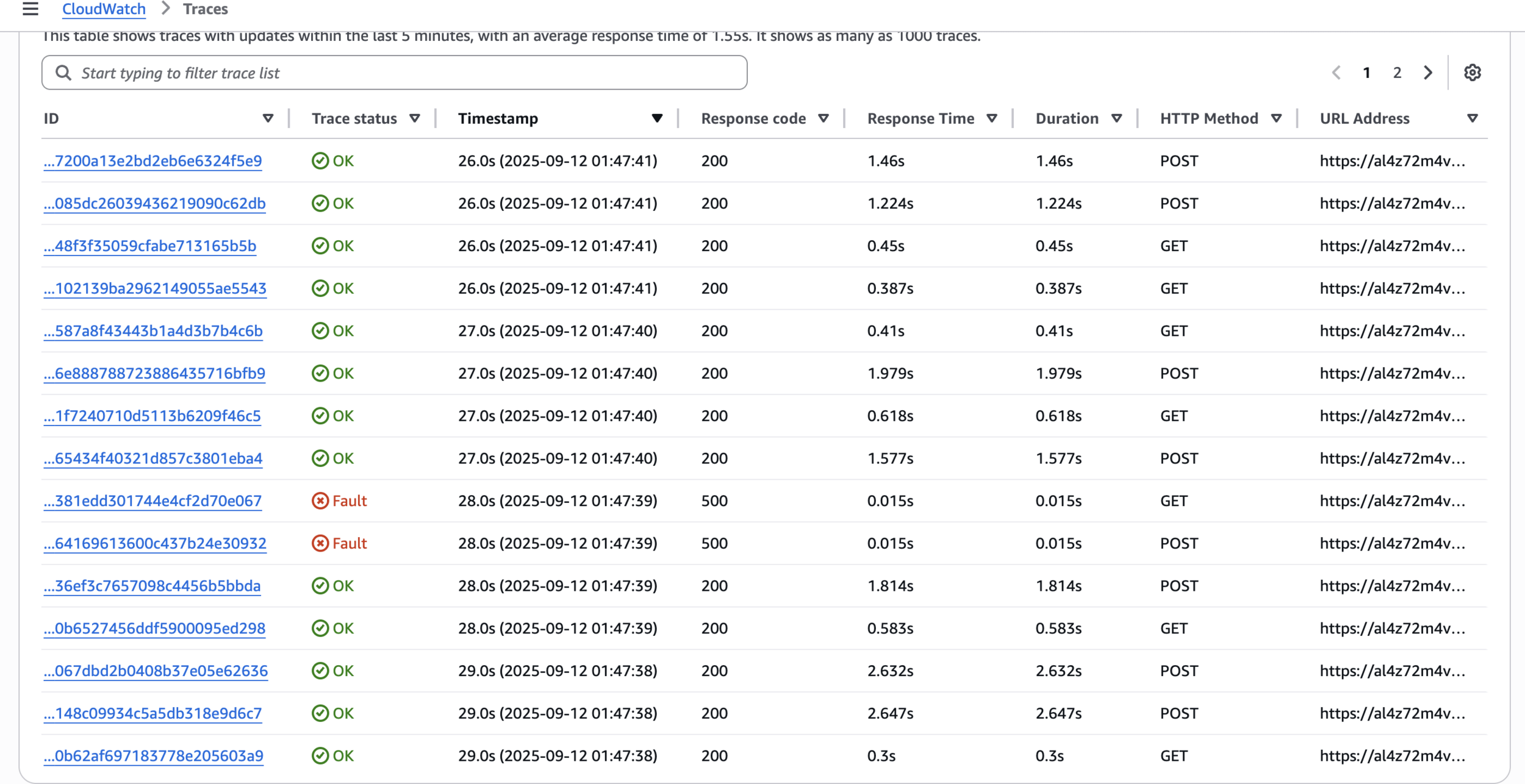
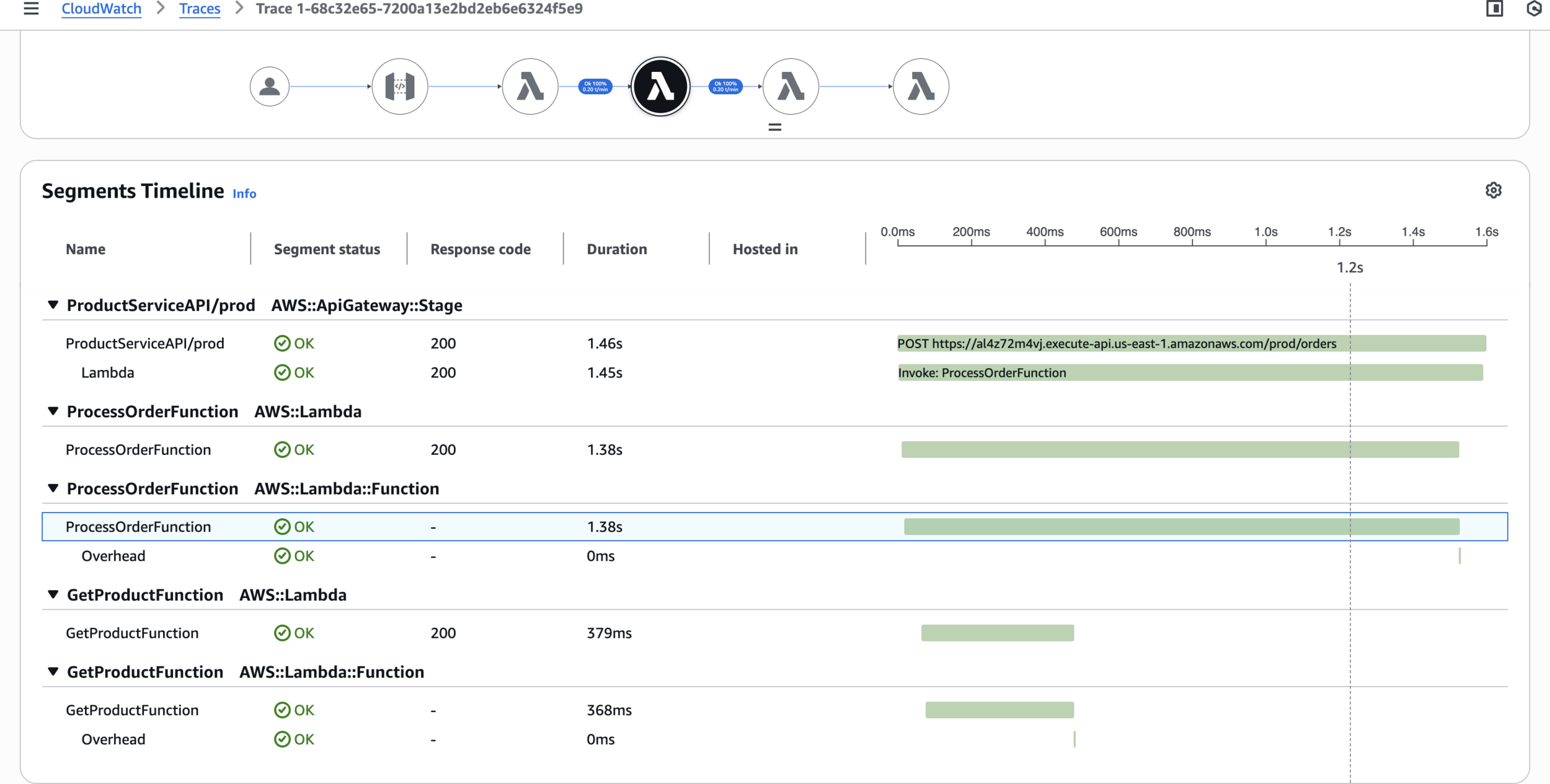
echo "All requests completed."Step 6: Analyze Traces in X-Ray Console
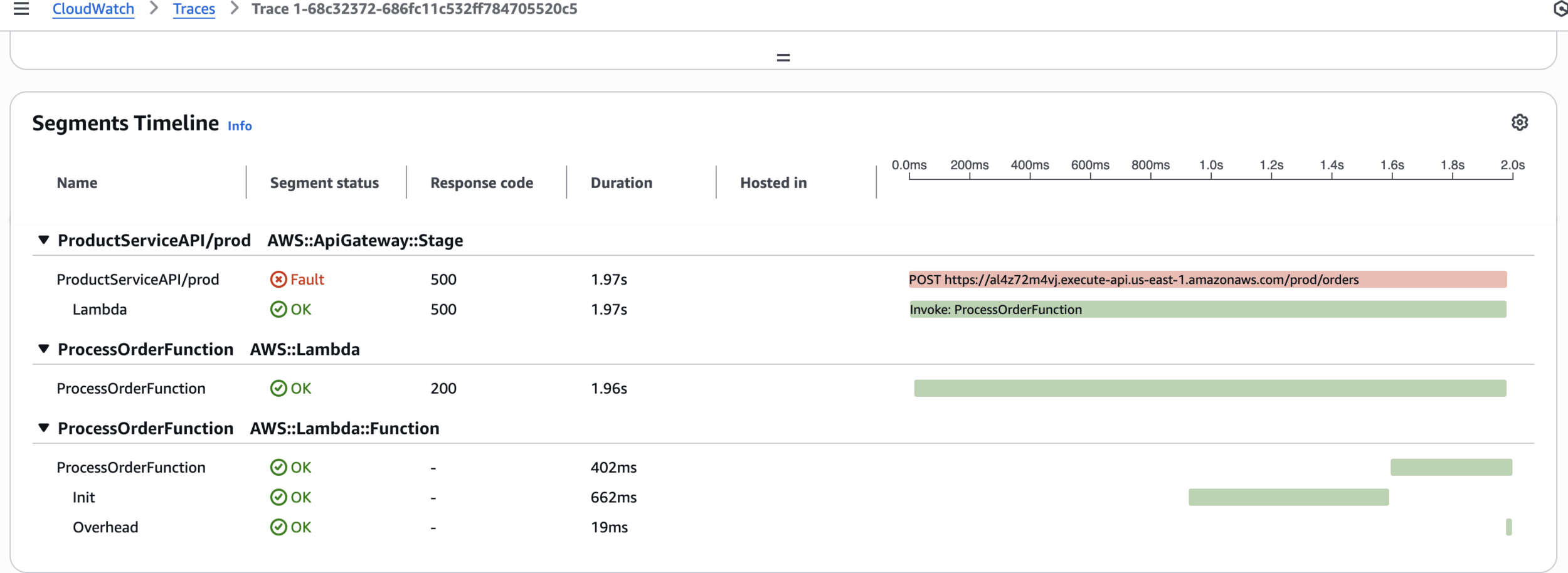
CloudWatch > Traces
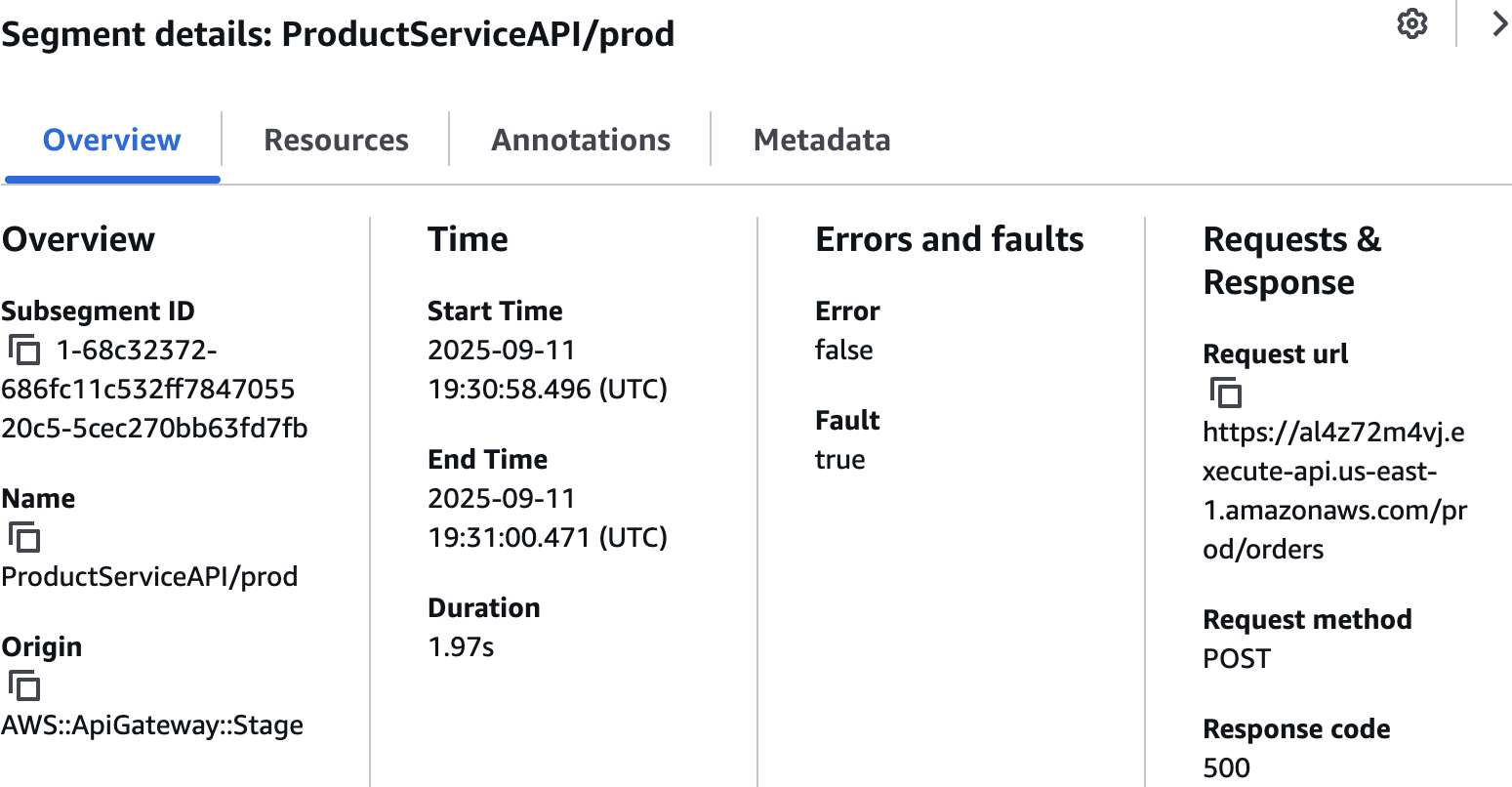
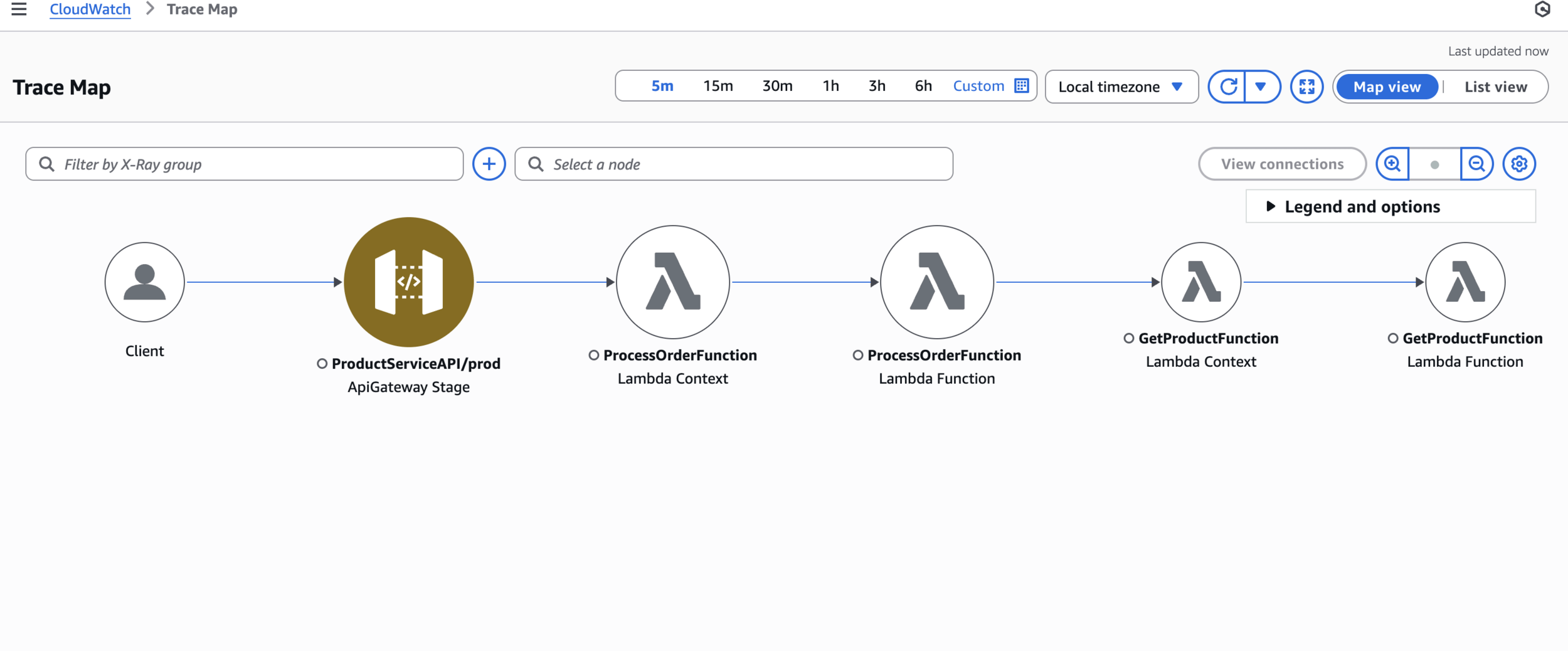
CloudWatch > Trace Map
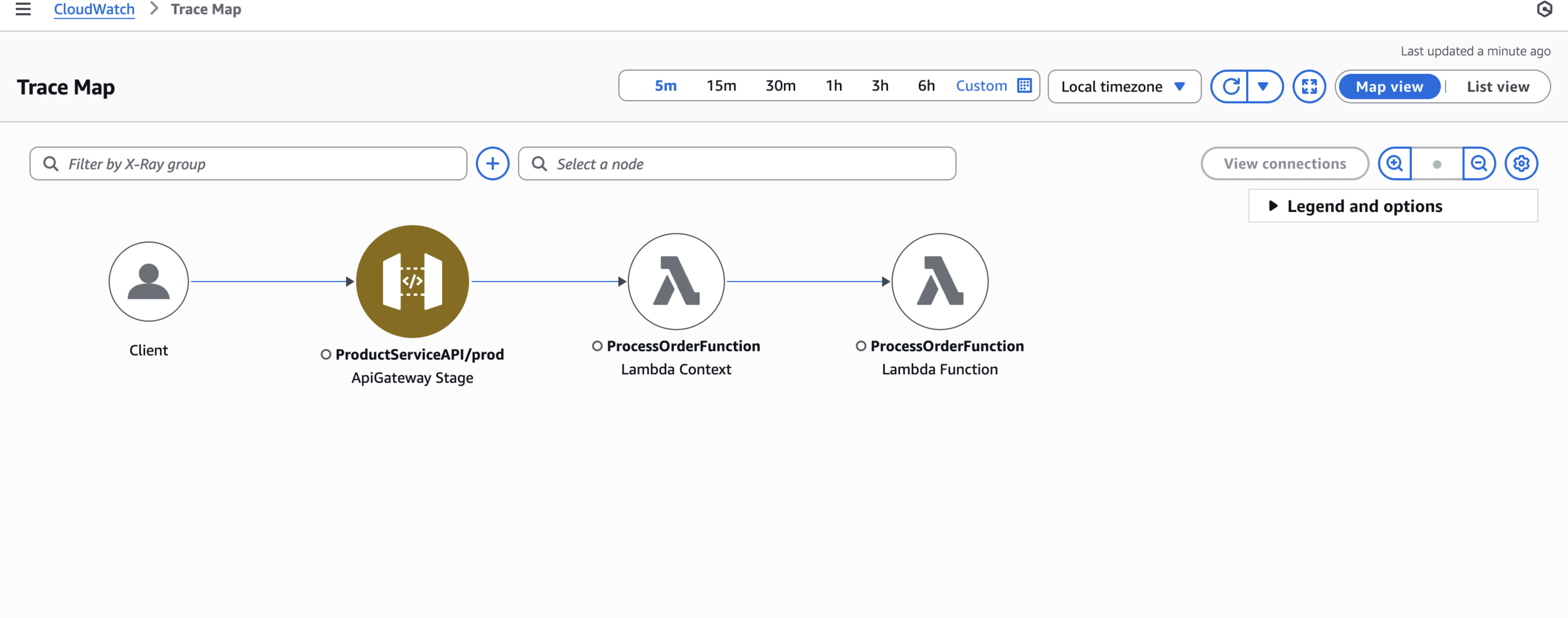
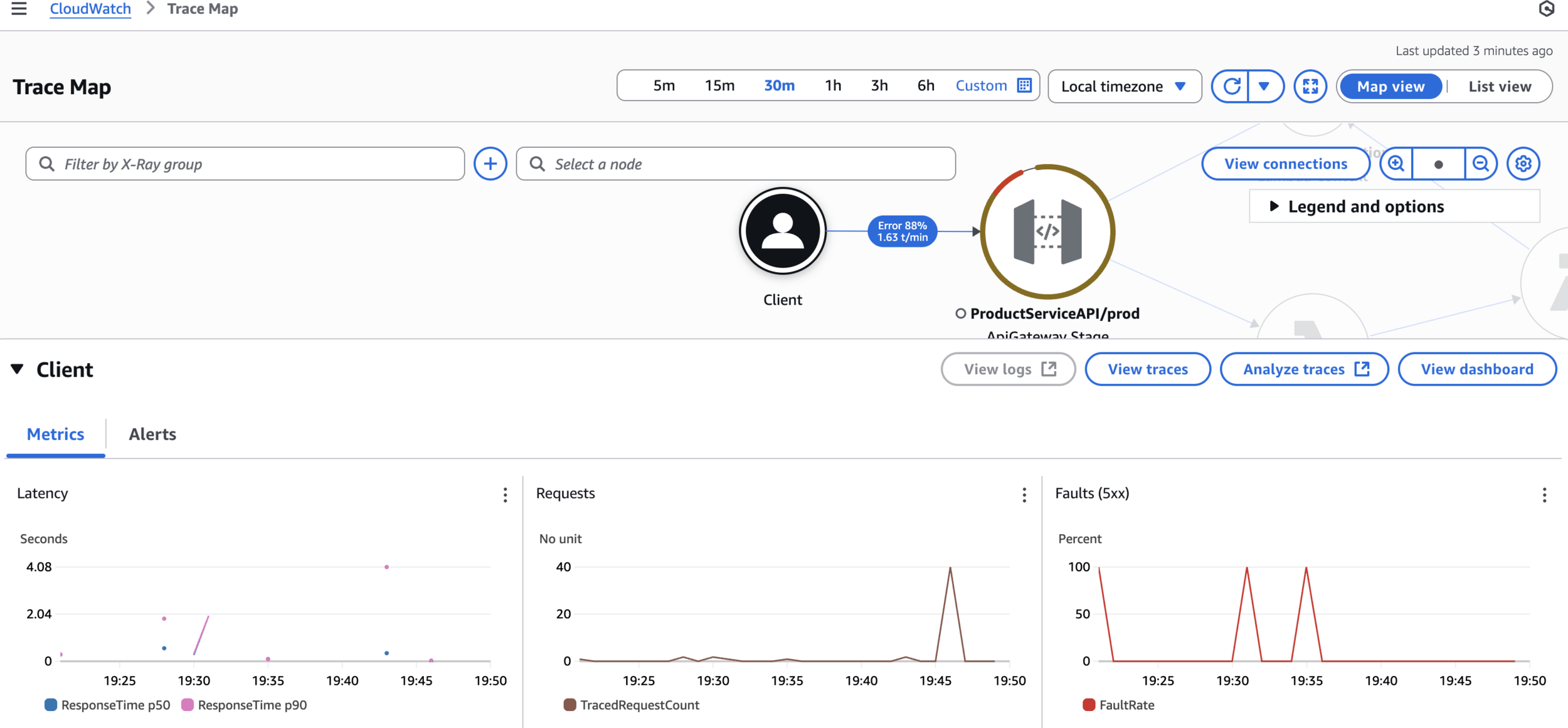
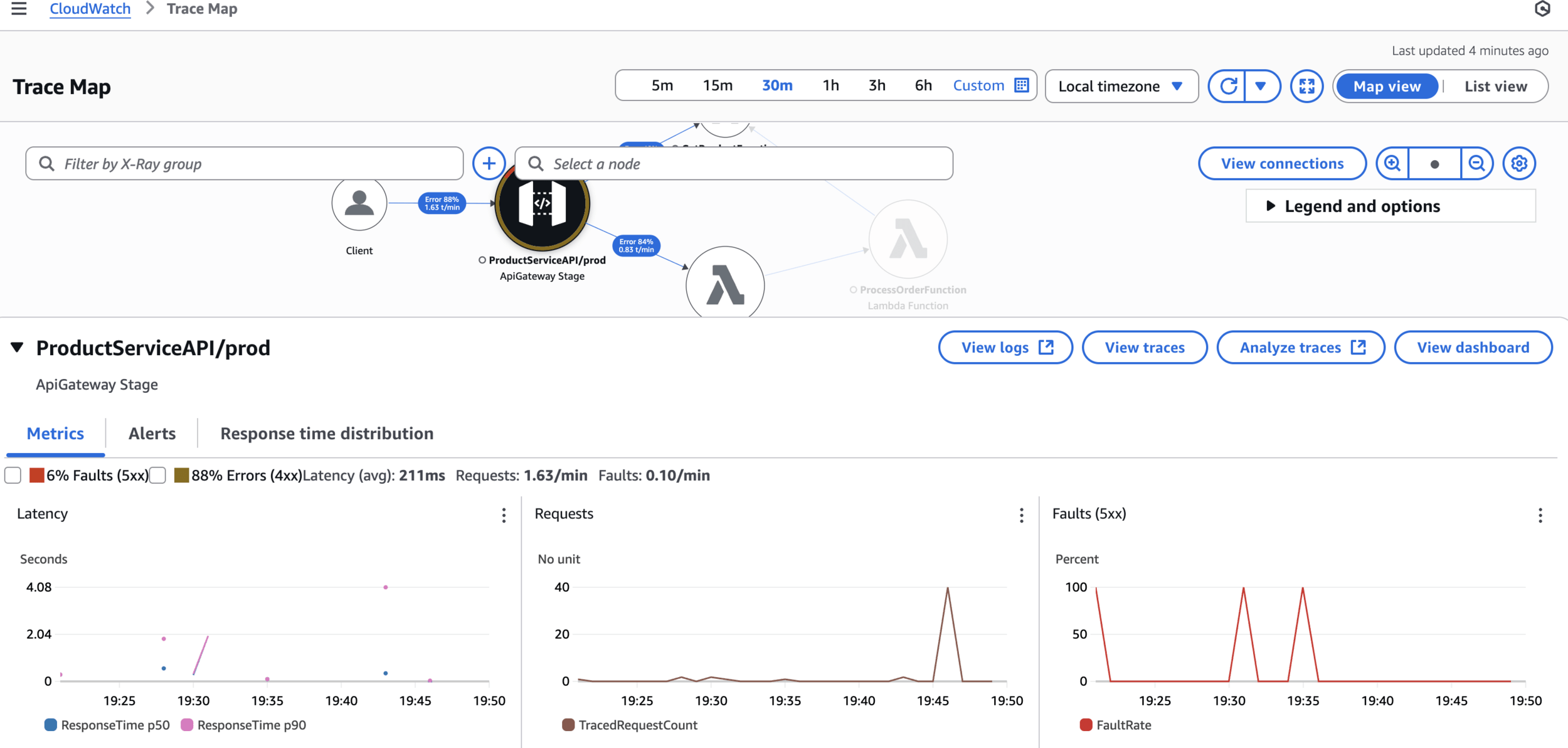
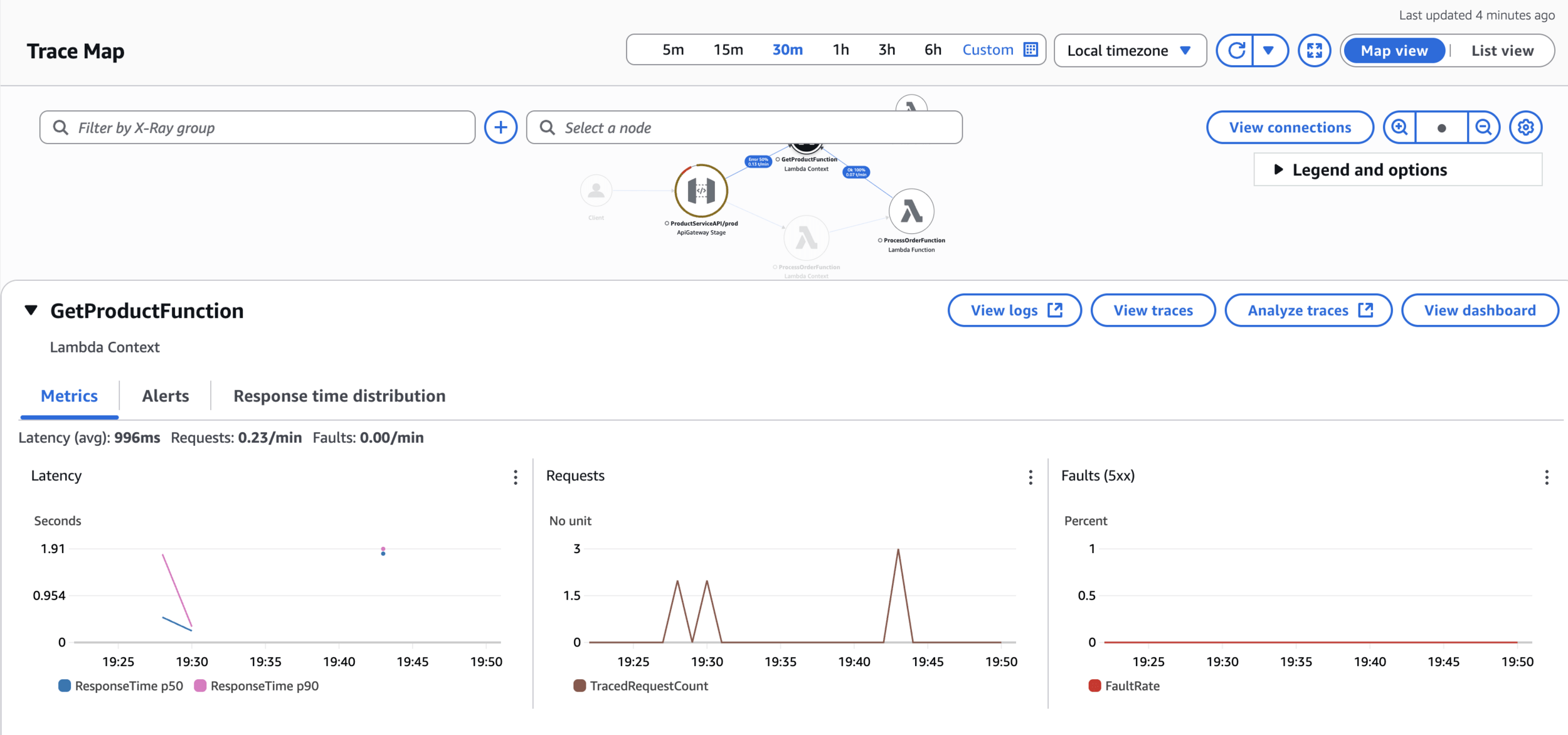
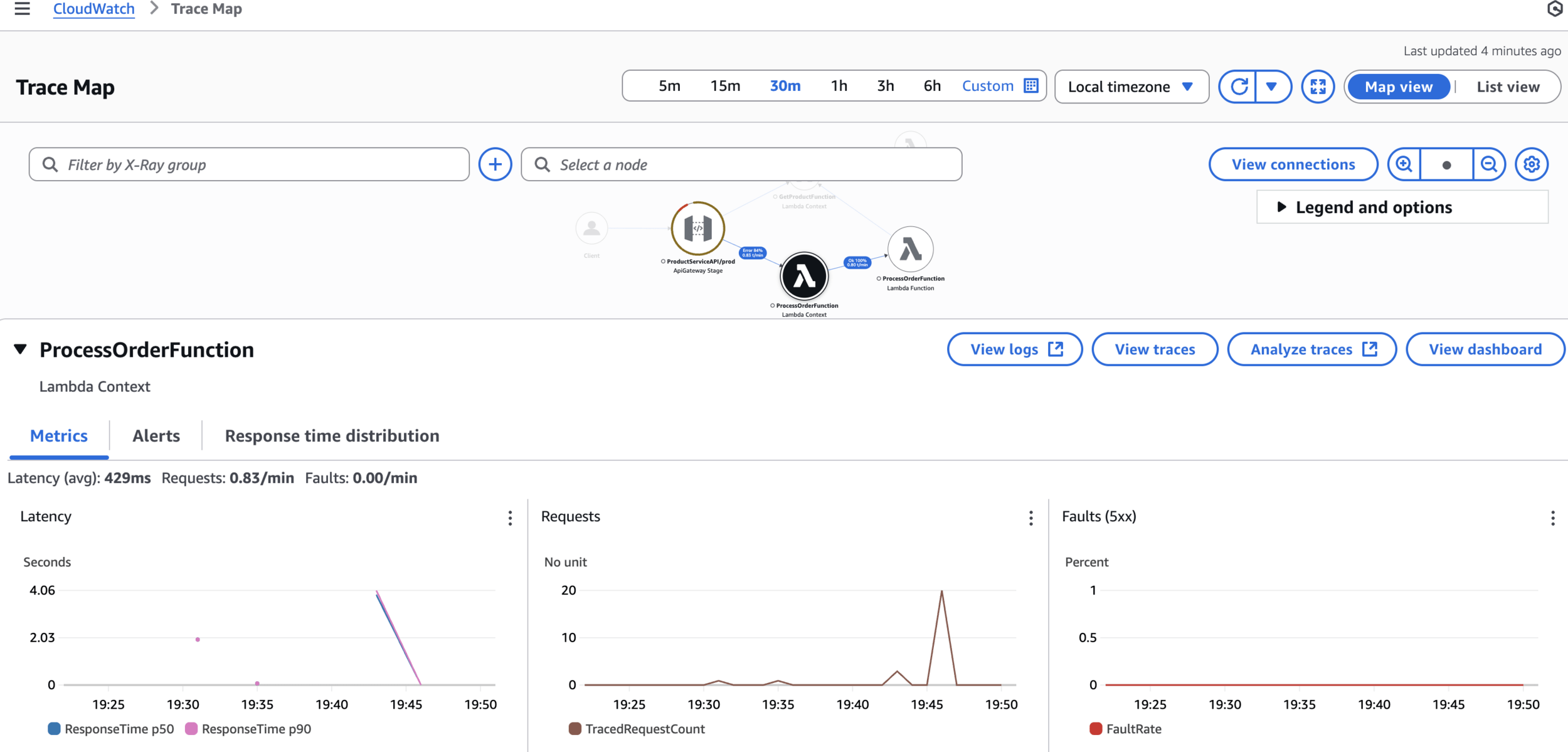
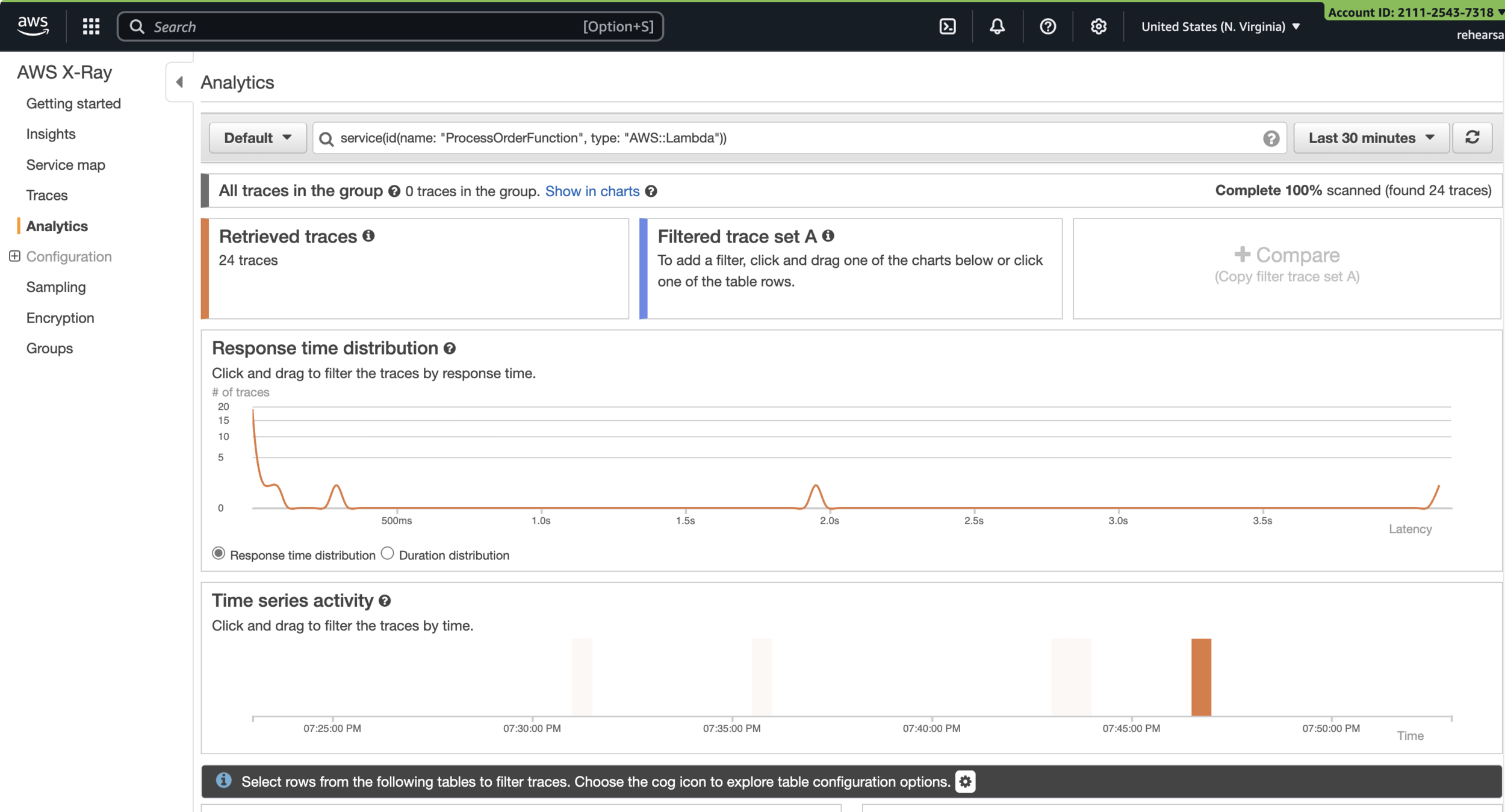
AWS X-Ray
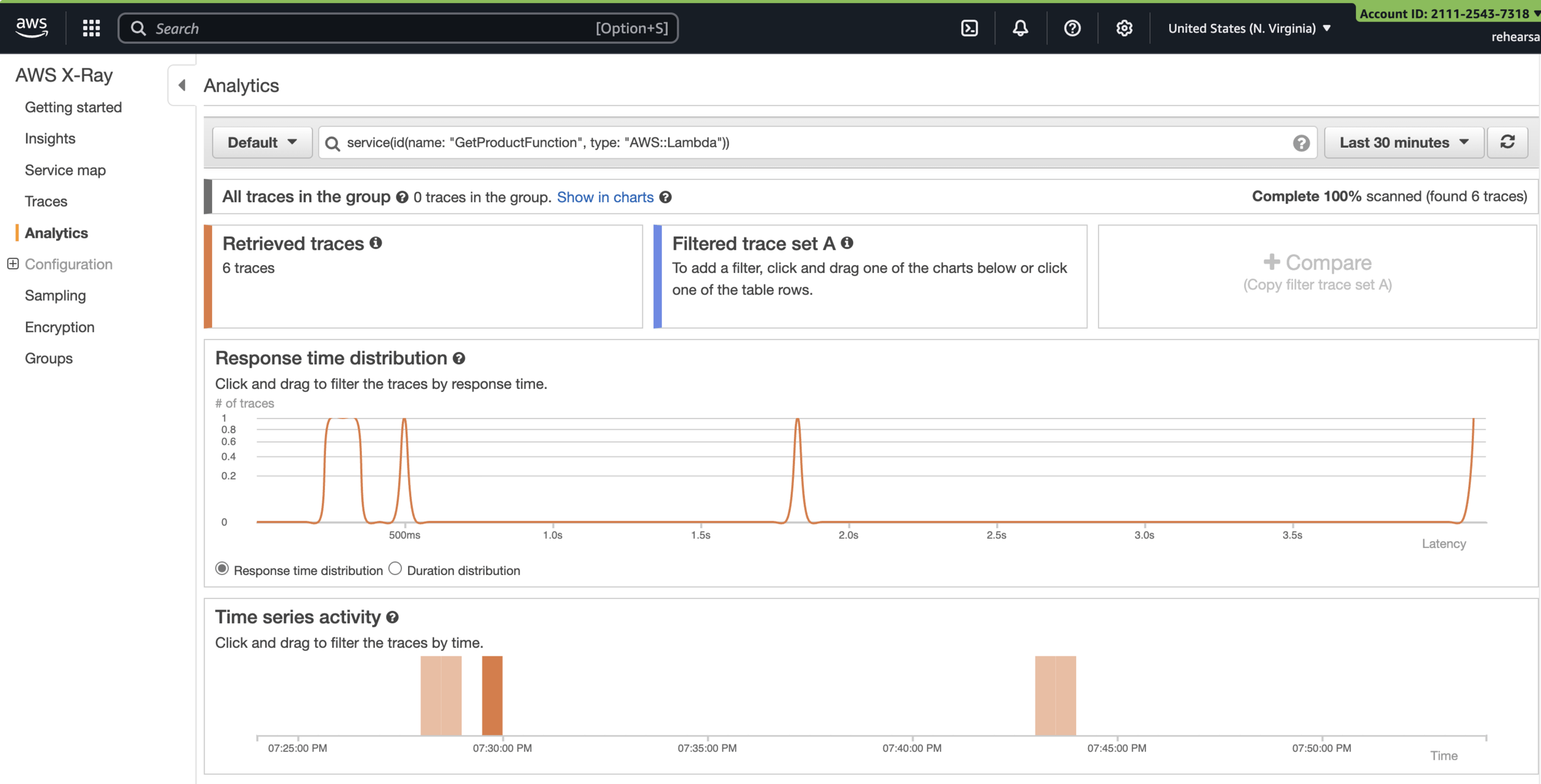
Analytics
Clean Up
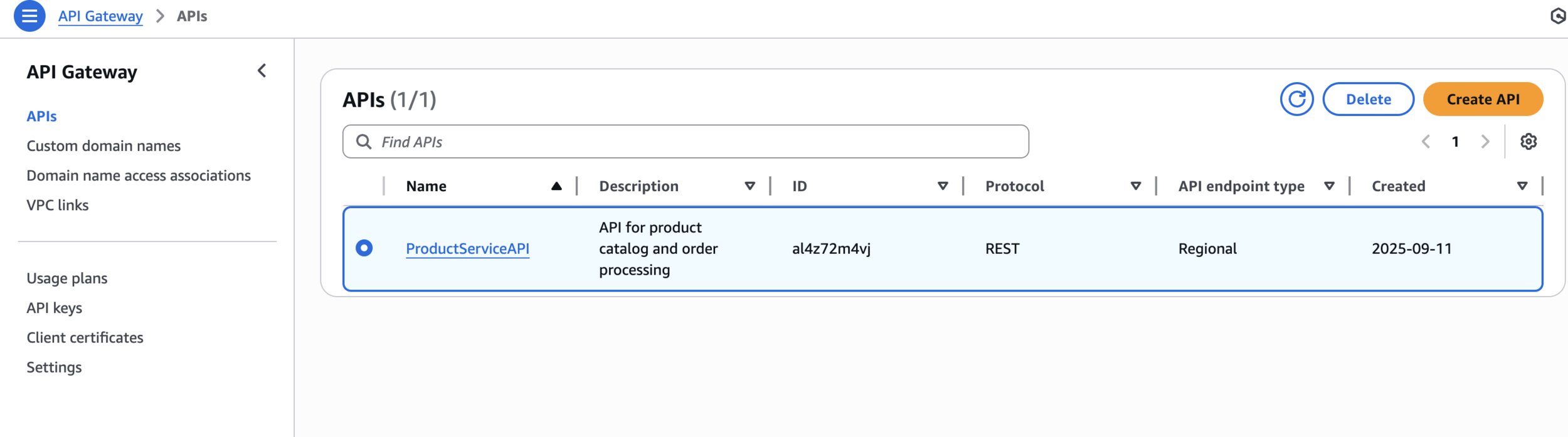
Delete API in API Gateway
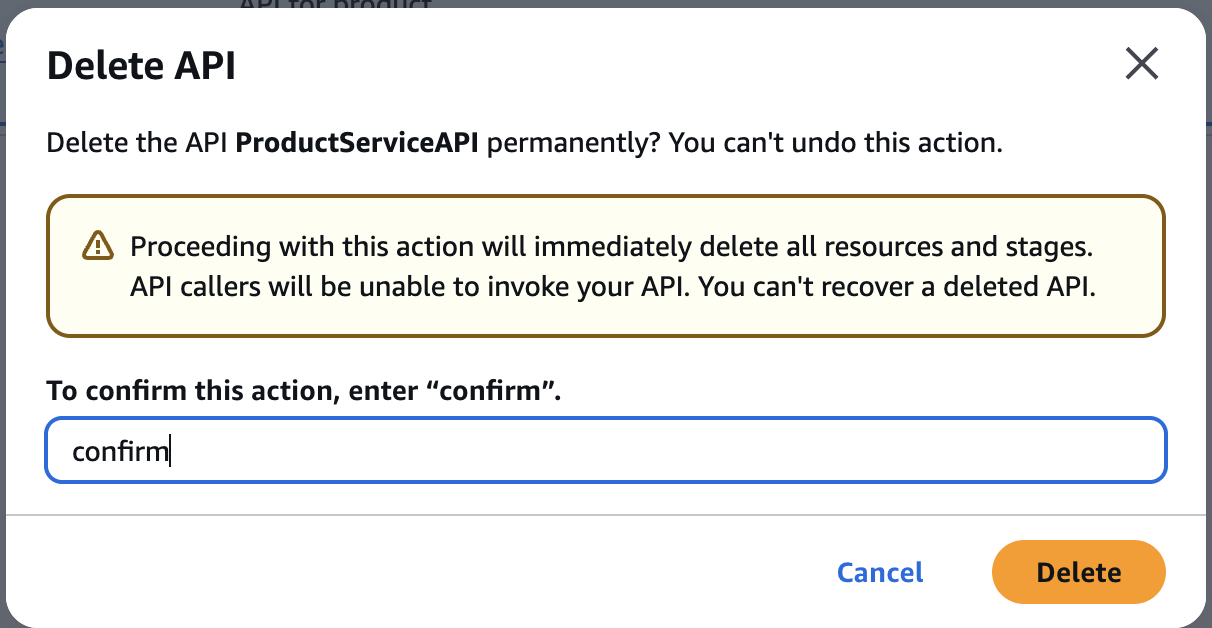
confirmDelete API
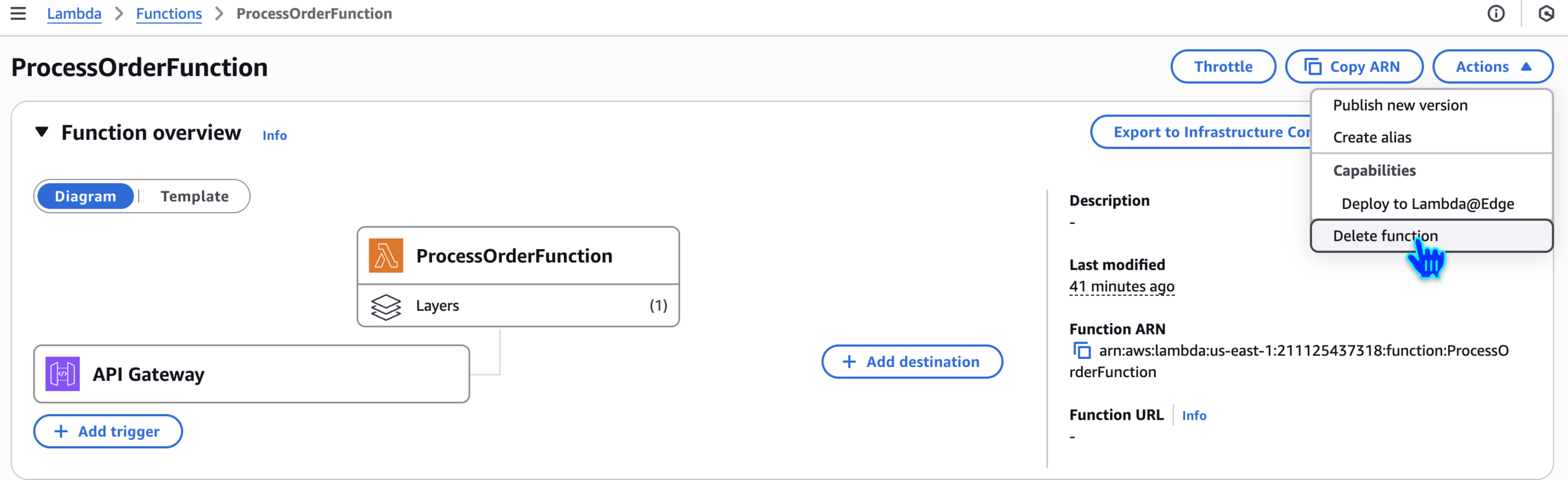
Delete function - ProcessOrderFunction
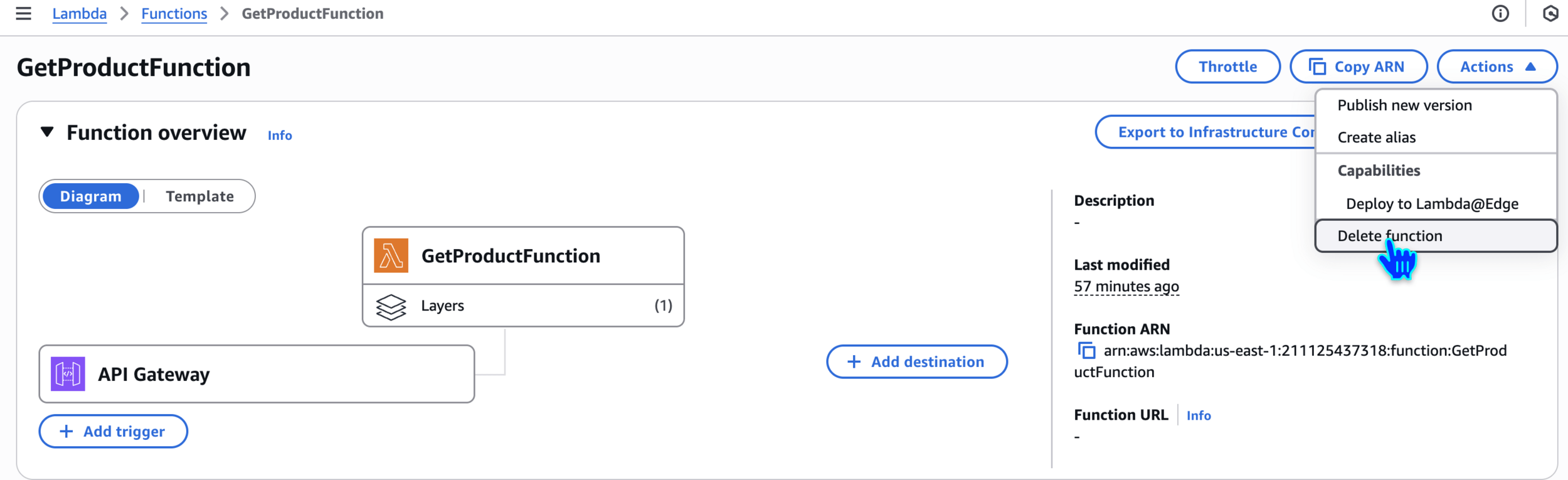
Delete function - GetProductFunction
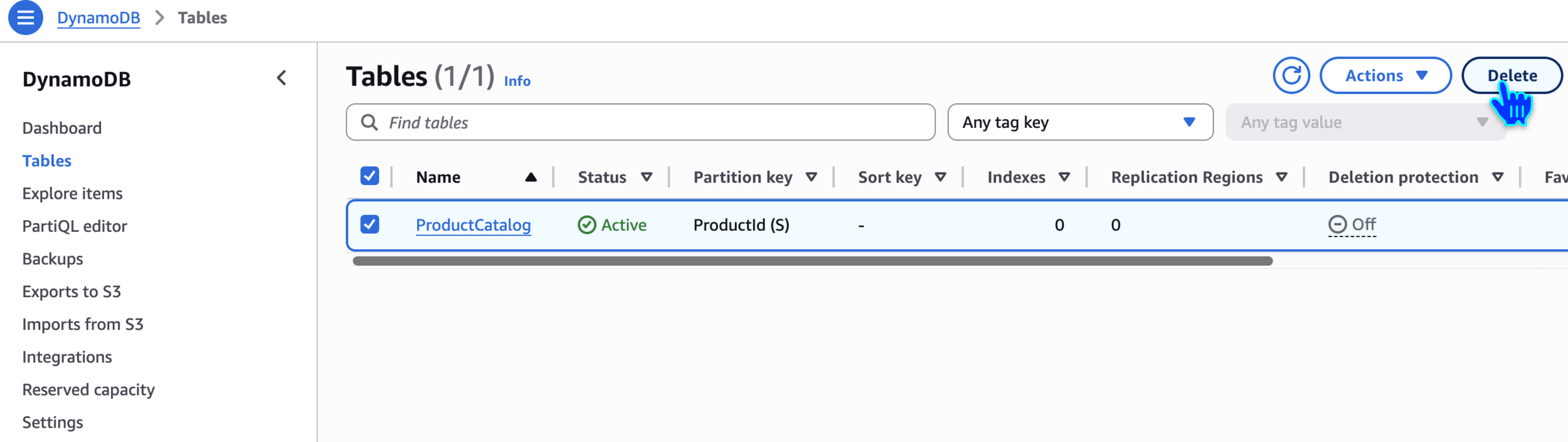
Delete DynamoDB Table
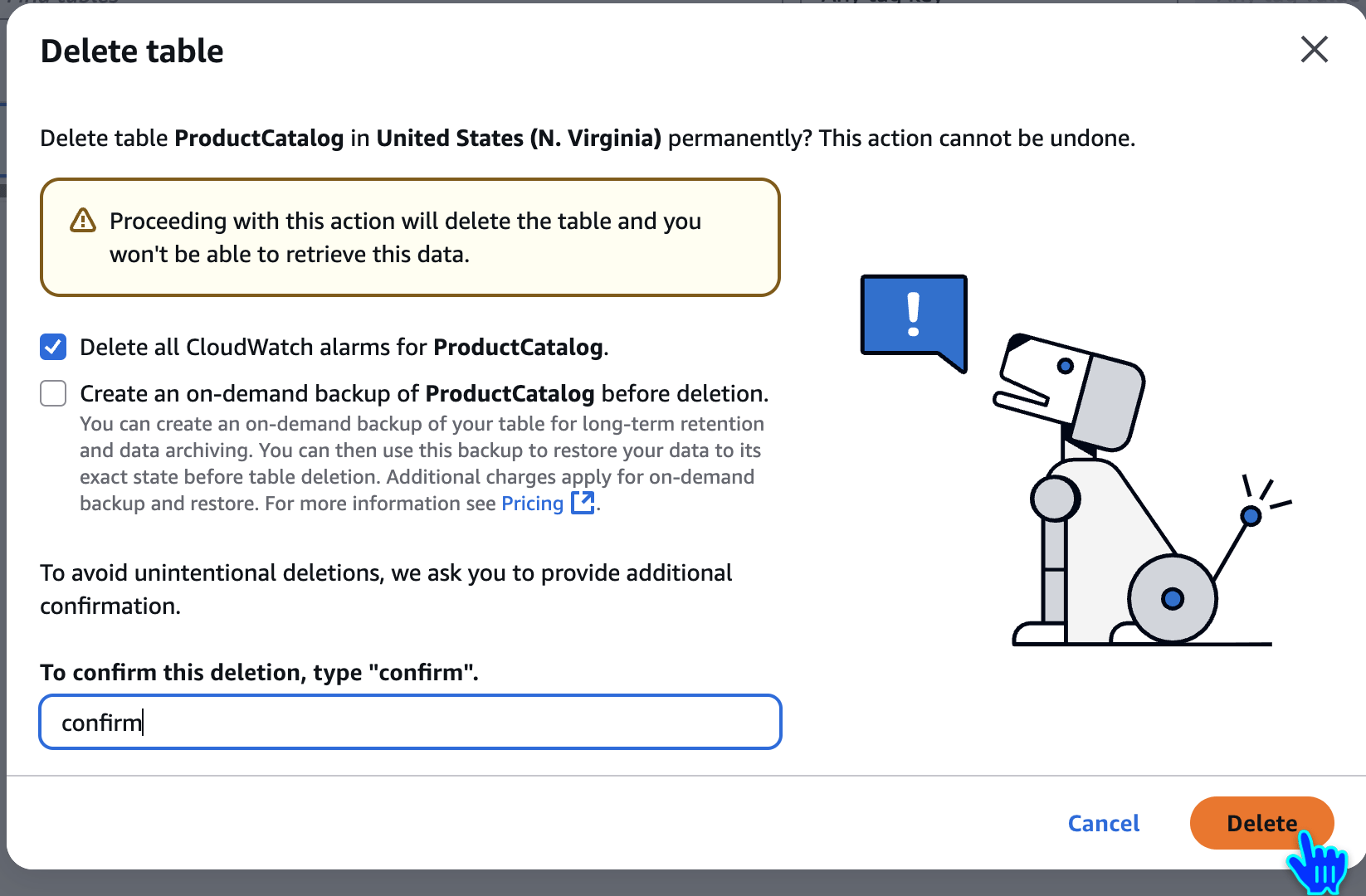
confirm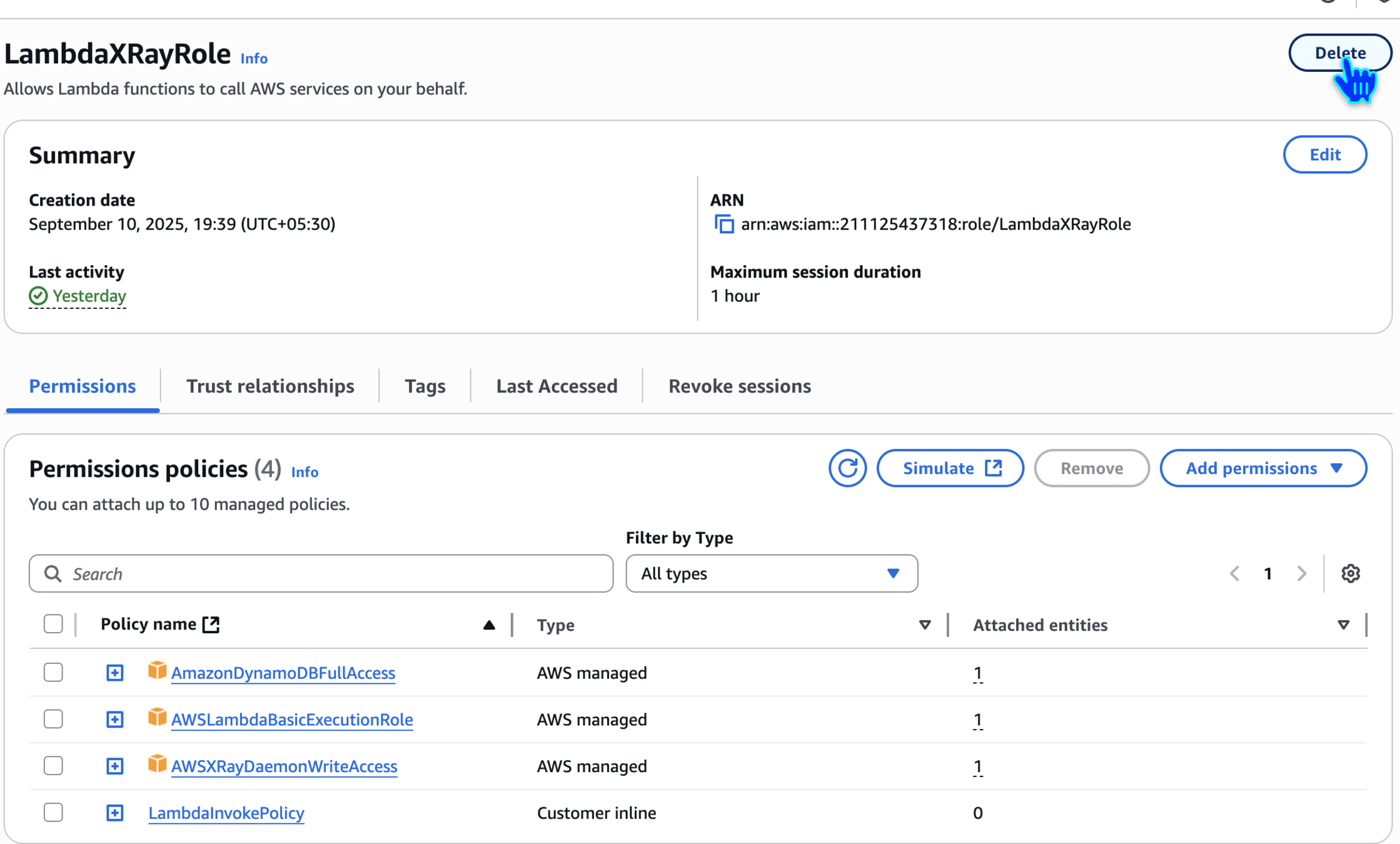
Delete LambdaXRayRole
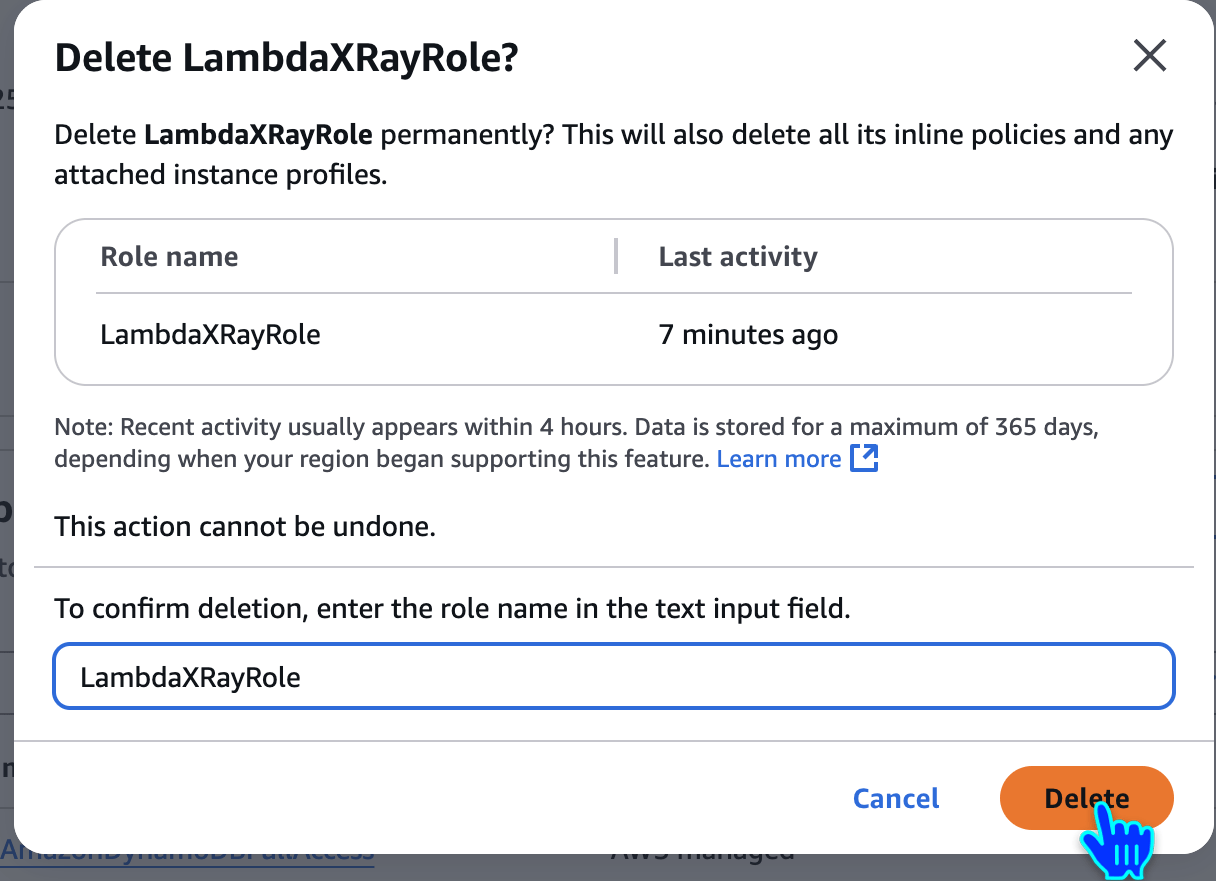
LambdaXRayRole🙏
Thanks
for
Watching
AWS X-Ray - Hands-On Demo
By Deepak Dubey
AWS X-Ray - Hands-On Demo
AWS X-Ray - Hands-On Demo
- 193



