FLARE
Flipped learning & AI for reflective education
M.Sc. Lauri Hellsten
math and physics teacher in Espoon yhteislyseo
Physics teacher of the year 2025 (Finnish society of sciences and letters)
STEAM teacher of the year 2023 (MAOL ry)
ASEFClassNet EmpowerEd Project 2025
-
Keep Your Microphone Muted 🎤 – Mute yourself when not speaking to avoid background noise.
-
Turn On Your Camera 📷 – Helps create a more engaging and connected atmosphere.
-
Use the Chat & Raise Hand ✋💬 – Share quick thoughts in chat or use “raise hand” before speaking to ensure smooth discussion.
Guidelines for online sessions
-
Pedagogical framework for Flipped learning
-
Examples of Flipped learning from a Finnish upper secondary school
Today
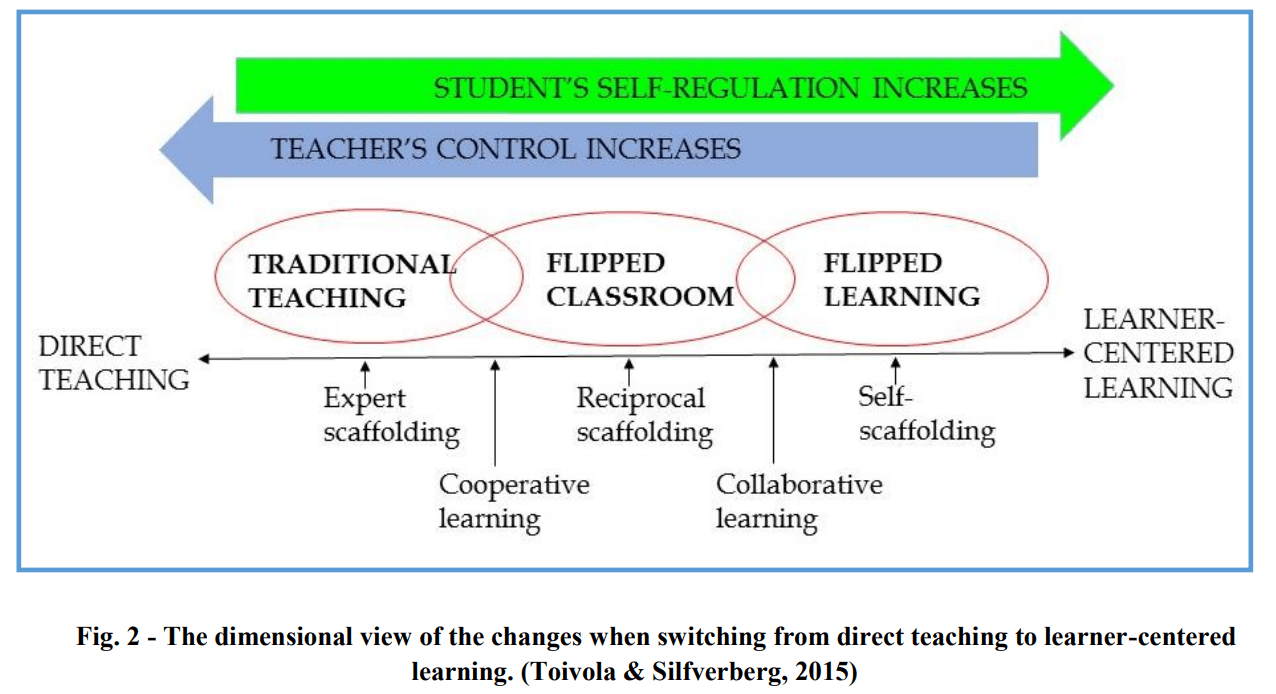
What is Flipped learning (FL)?
FLIPPED LEARNING
”20 % of the students under conventional instruction do about as well as the tutored students”
”80 % of the students do relatively poorly under conventional instruction as compared with what they might do under tutoring”
(Bloom 1984)
CONVENTIONAL INSTRUCTION VS. TUTORING
Students master the subject before moving on to the next subject.
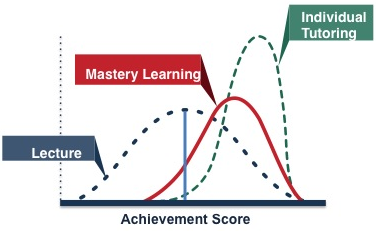
MASTERY LEARNING
Tasks the students can do with help (ZPD)
Tasks the students can do
Tasks the students can't do even with help
Lev Vygotsky 1930
THE ZONE OF PROXIMAL
DEVELOPMENT (ZPD)
- Scaffolding
- Formative feedback
- Differentiated tasks
Self-determination theory
Autonomy
Mastery
Purpose
Motivation
(Competence)
(Relatedness)
Daniel H. Pink The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us

© Marika Toivola
FLIPPED LEARNING
www.flippedlearning.fi (material also in english)
The flipped classroom (FC) is a teaching method that shifts instruction to the home and practice to the classroom, while flipped learning (FL) is a broader pedagogical approach that builds on this model to promote active, student-centered, and flexible learning.
Flipped Classroom Flipped Learning
| Definition 📝 | Lessons at home, practice in class | Broader approach transforming learning |
| Aim 🎯 | Focus on when & where | Focus on how & by whom |
| Output 📊 | Home lectures, class activities | Active, flexible, assessed learning |
| Teacher Role 👩🏫 | Content deliverer, facilitator | Guide, mentor, reflective partner |
| Student Role 👨🎓 | Receive & practice | Active, collaborative, autonomous |
| Technology 💻 | Mainly for delivery | For delivery, assessment, collaboration |
| Scope 🌍 | Narrow: instruction only | Broad: curriculum & pedagogy |
CC BY SA naosuke ii
1. Upper Secondary Schools Act
2. National core curriculum
-
300 pages altogether
-
13 pages math curriculum
-
5 pages physics curriculum
3. Local curriculum (mostly same as #2)
(4. Matriculation exam)
| Summative Assessment | Formative Assessment | |
|---|---|---|
| Time |
At the end of a learning activity | During a learning activity |
| Goal |
To make a decision | To improve learning |
| Feedback | Final judgement | Return to material |
|
Frame of Reference |
Sometimes normative (comparing each student against all others); sometimes criterion |
Always criterion (evaluating students according to the same criteria) |
Law & Assessment
"A student´s assessment is to guide and encourage learning and develop the student's capacity for self-evaluation."
- Basic Education Act and the Upper Secondary Schools Act of 1998 (translated)
Formative assessment is emphasized in the law and curriculum.
Upper secondary school in Finland
1. semester
2. semester
3. semester
1. period
2. period
3. period
4. period
5. period
min. 75 courses and usually 3 years
usually 6 + 1 weeks
5 - 7 courses,
1 course = 3 x 75 min per week
Matriculation exam at the end, min. 4 exams
“The use of ICT changes the role of the teacher, who will be more of a facilitator guiding the students' learning processes than a knowledge provider. The time allocated for the teacher and the pupil to meet in is too valuable to be spent solely on information distribution. The teacher is required to command new skills and to adapt a new approach, which in turn generates pressure on the basic and continuing education of teachers.”
Finnish National Board of Education review, 2011 (translated)
ICT in Learning
Flipped Learning (FL) in practice?
-
Assessment of the course will be agreed upon with the students on the first lesson.
-
The students will work in small table groups during the course.
-
The course is divided into six sections, each of which will be worked on for about a week.
-
individual assignment
-
experimental group work (peer feedback)
-
-
-
multiple-choice test
-
-
At the end of the course there is usually an exam, portfolio or an larger experimental work.
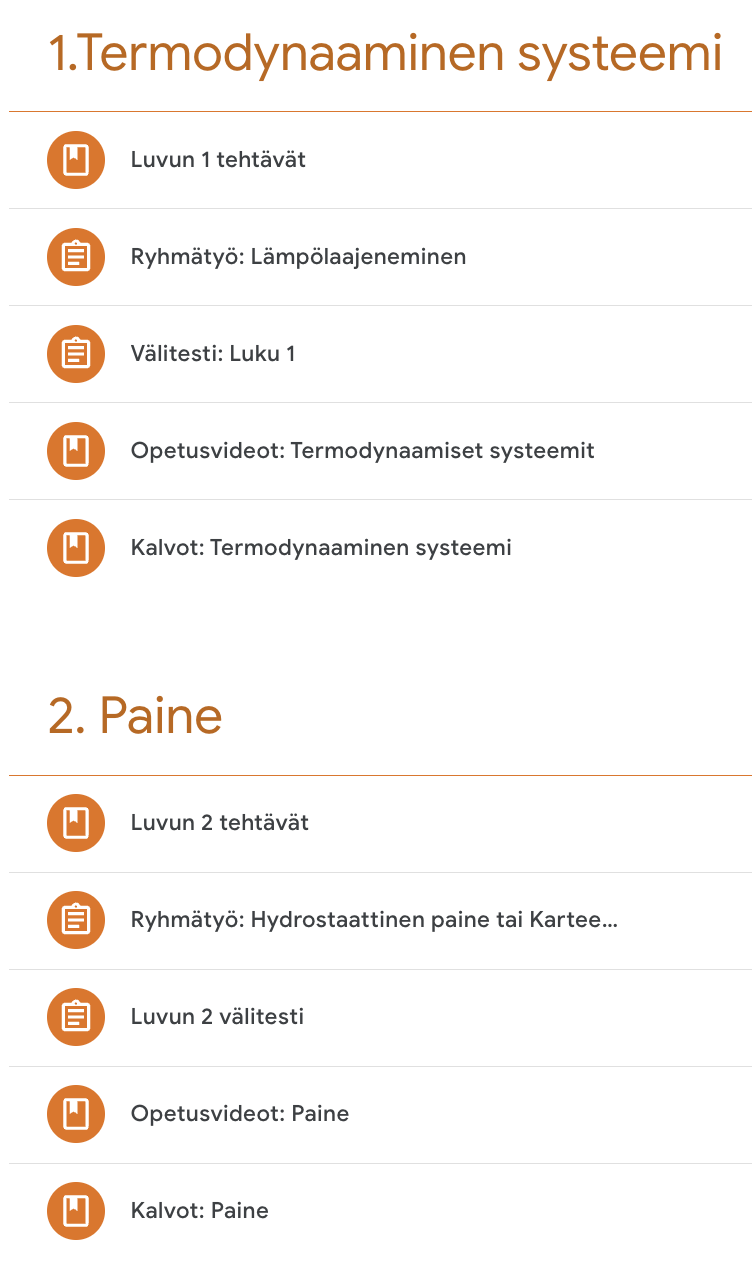
Practices in my courses
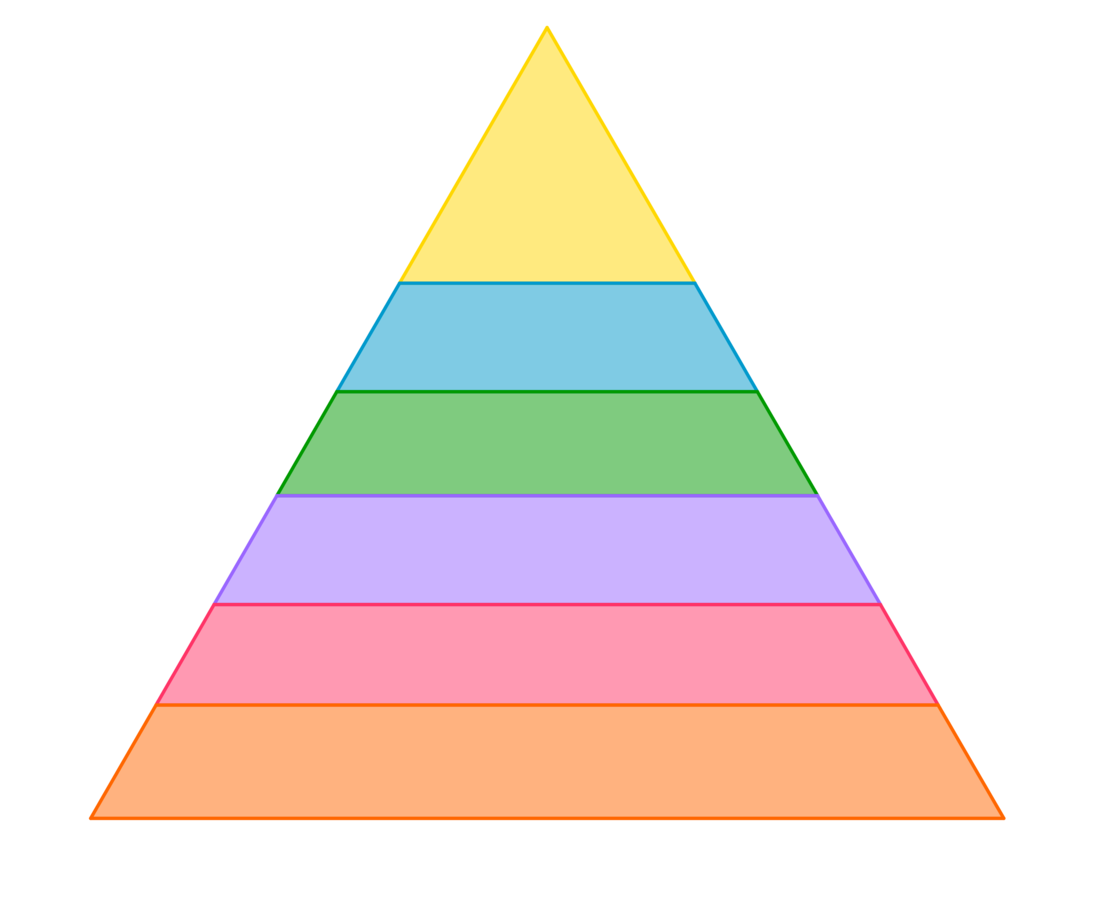
Bloom's taxonomy
Creating
Evaluating
Analyzing
Applying
Understanding
Remembering
Higher order thinking
Lower order thinking
The teacher guides the student to identify what the studied topic is about and compare their own perceptions and views on the whole.
Unit 1
Self-assessment
1A
passed
Unit 2
Self-assesment
2A
failed
Self-assessment
2A
failed
passed


Applying
Understanding
Remembering
Evaluating
Analyzing
Applying
Understanding
Remembering
Evaluating
Analyzing
passed
Mastery learning + Self-assessment
Students choose their own pace to progress and move on when they have mastered the topic at hand.
- Textbooks
- Learning management system
- Videos
- Simulations
- Flashcards
- Concept maps
- etc...
- Peer instruction & evaluation
- Study groups
- Self-paced learning
- Problems
- Experiments
- Teacher guidance
- Flipped learning
- Self-paced learning
- Mastery learning
- Zone of proximal development
- Social constructivism
- Collaborative learning
- Blended learning
Pedagogical frames of reference
Educational materials and environments
Teaching & study methods
Use of ICT to enhance the learning experience and to learn 21st century skills.
Unit 1 - Sample

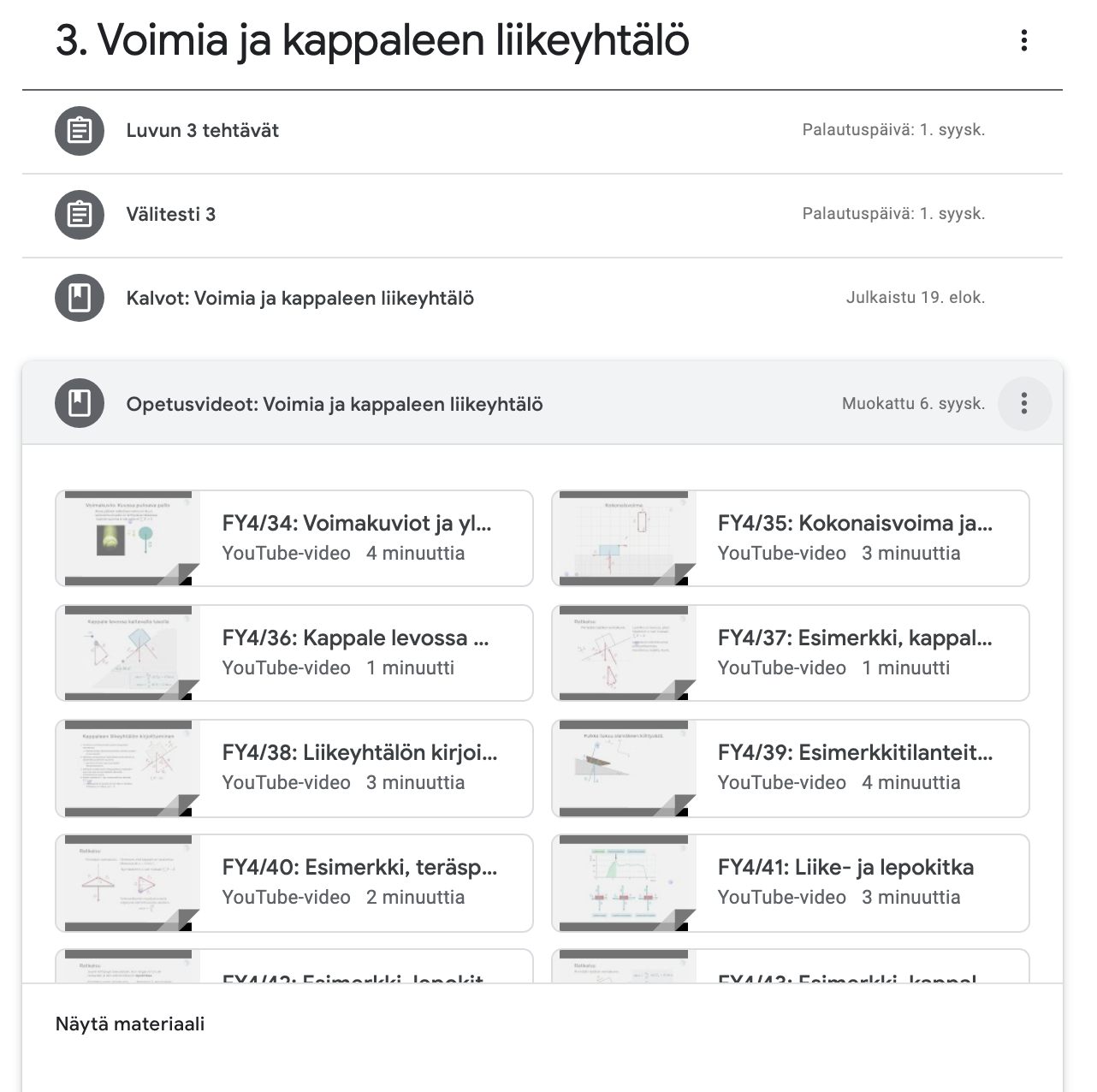
Course material includes videos, about 50 per course
Developing flipped learning
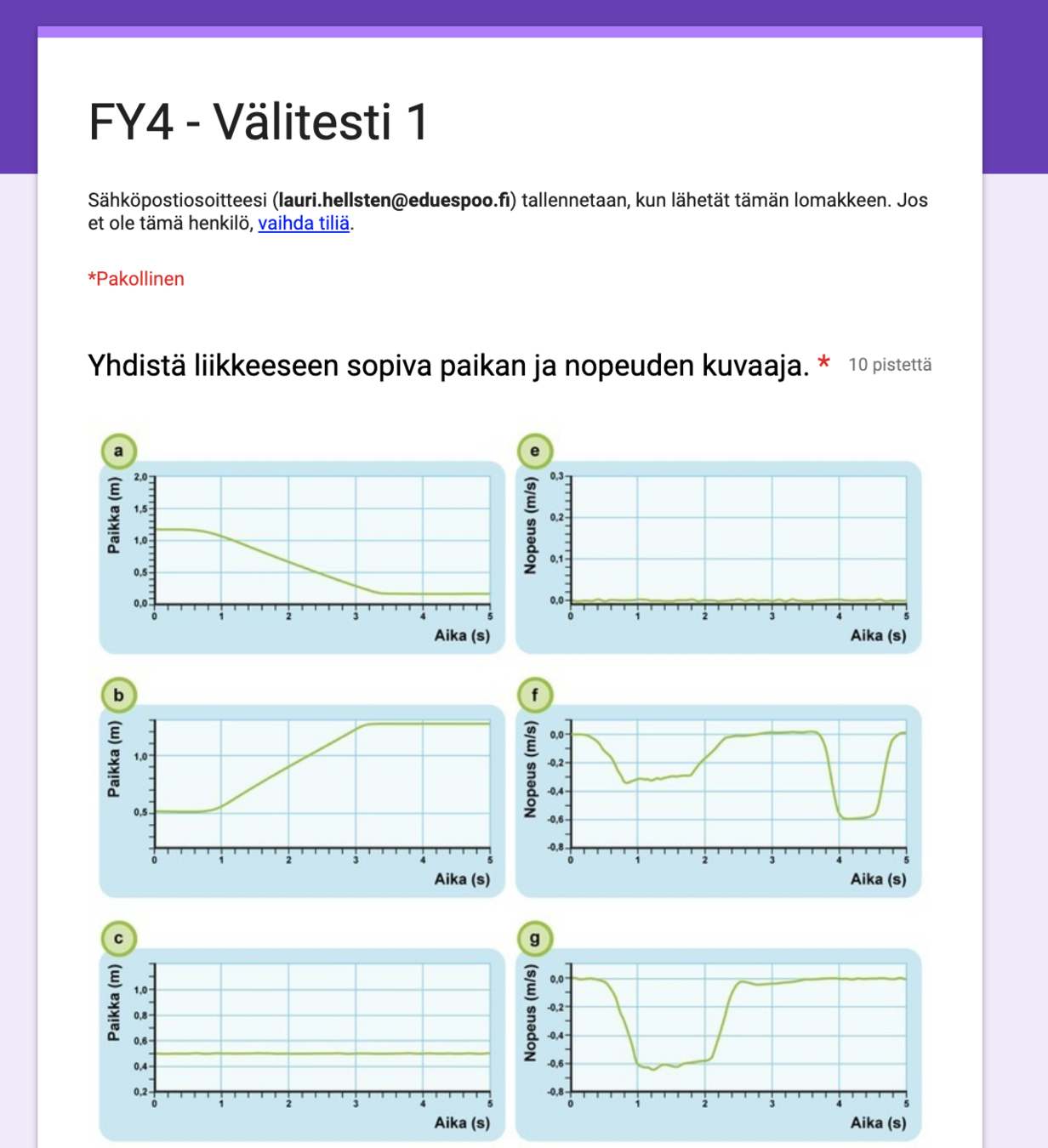
Multiple choice questions after each section so that the student can check his or her understanding.

Developing flipped learning
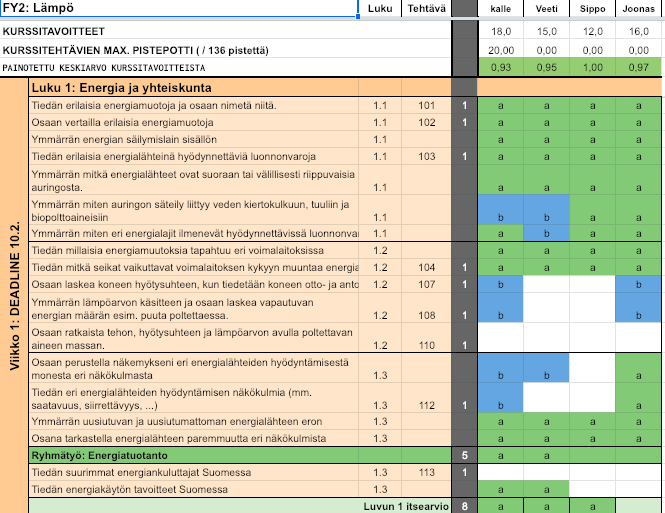
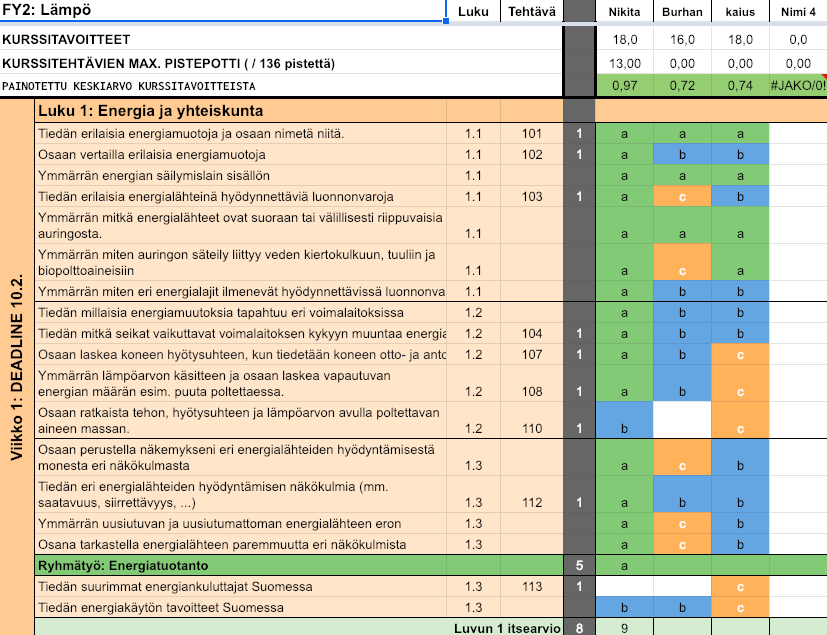

Developing self-assessment
I understand this so well I could
teach it to a friend.
I feel I have understood this.
I feel I somehow understand this, but there still is something unclear to me.
I need more practice and time to understand this.
This is not included in my studies.

Developing self-assessment
I understand this so well I could
teach it to a friend.
I feel I have understood this.
I feel I somehow understand this, but there still is something unclear to me.
I need more practice and time to understand this.
This is not included in my studies.
Self-assessment throughout the course
Developing self-assessment
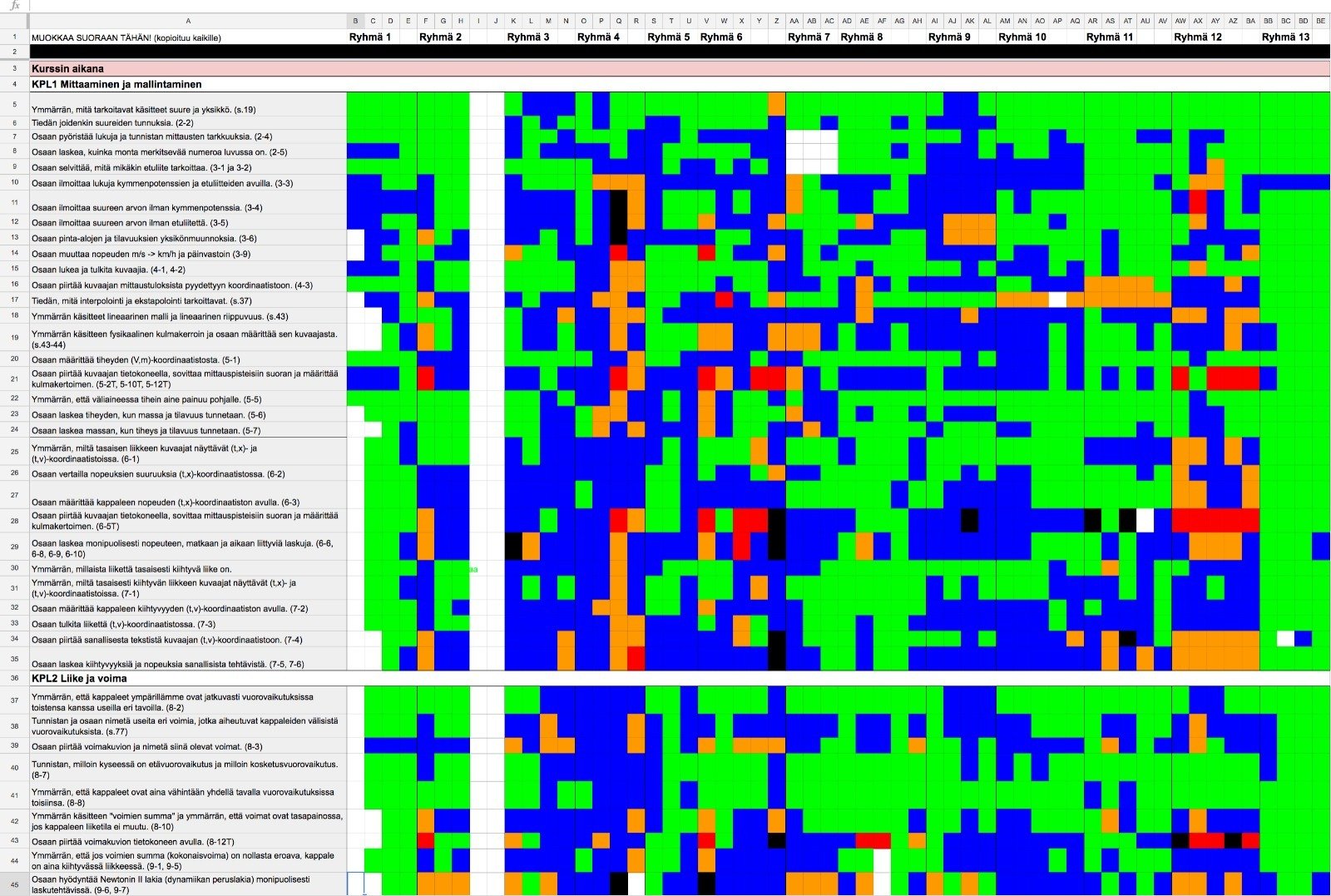
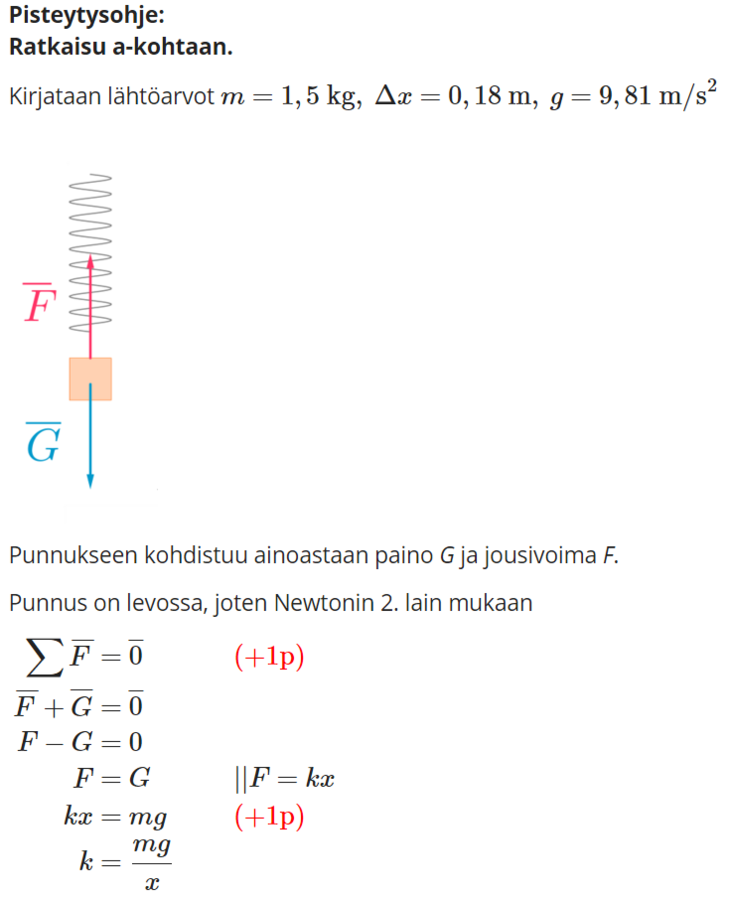
Self-assessment problems
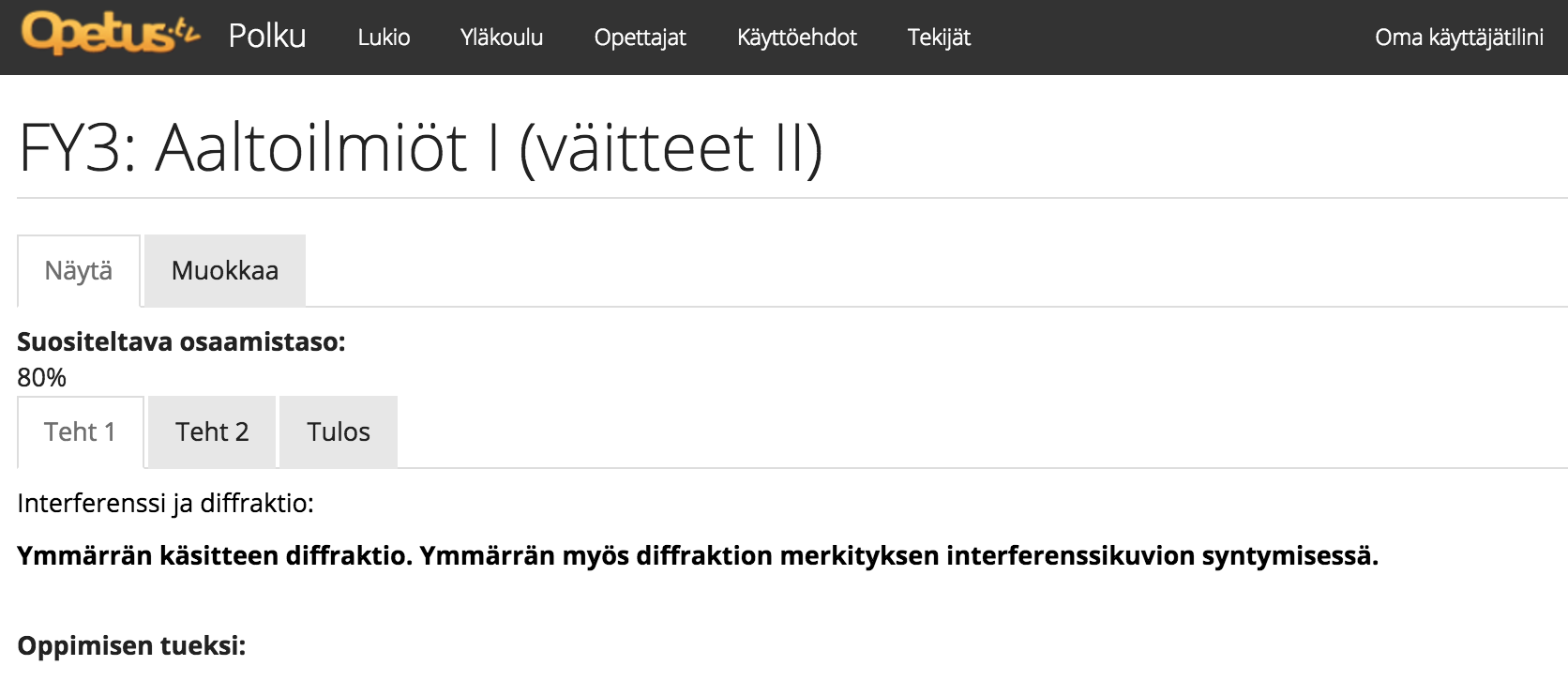
Self-assessment statements
Statement: "I understand the concept of diffraction. I also understand how diffraction is involved in the creation of an interference pattern."
Developing digital textbooks
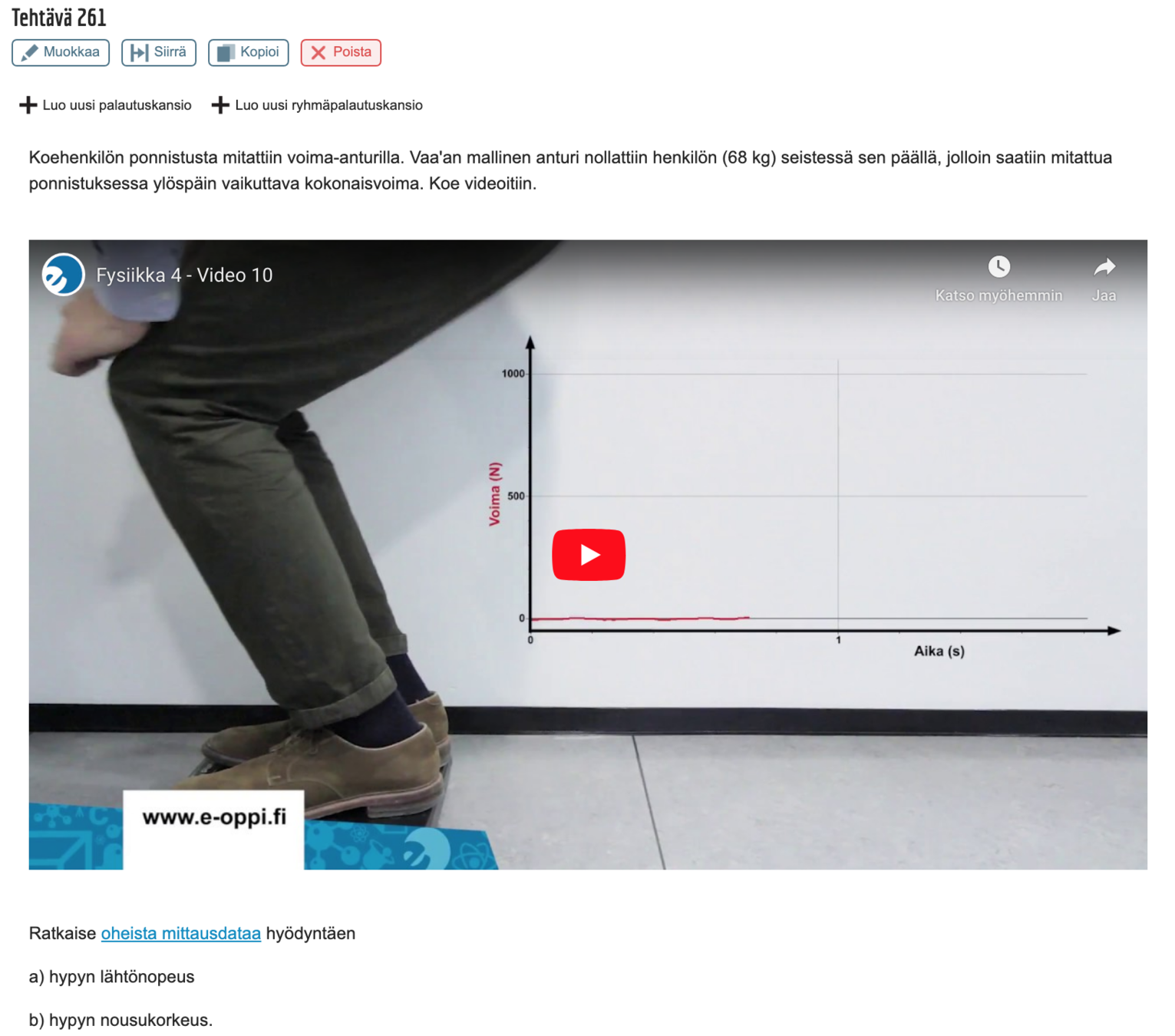
Text
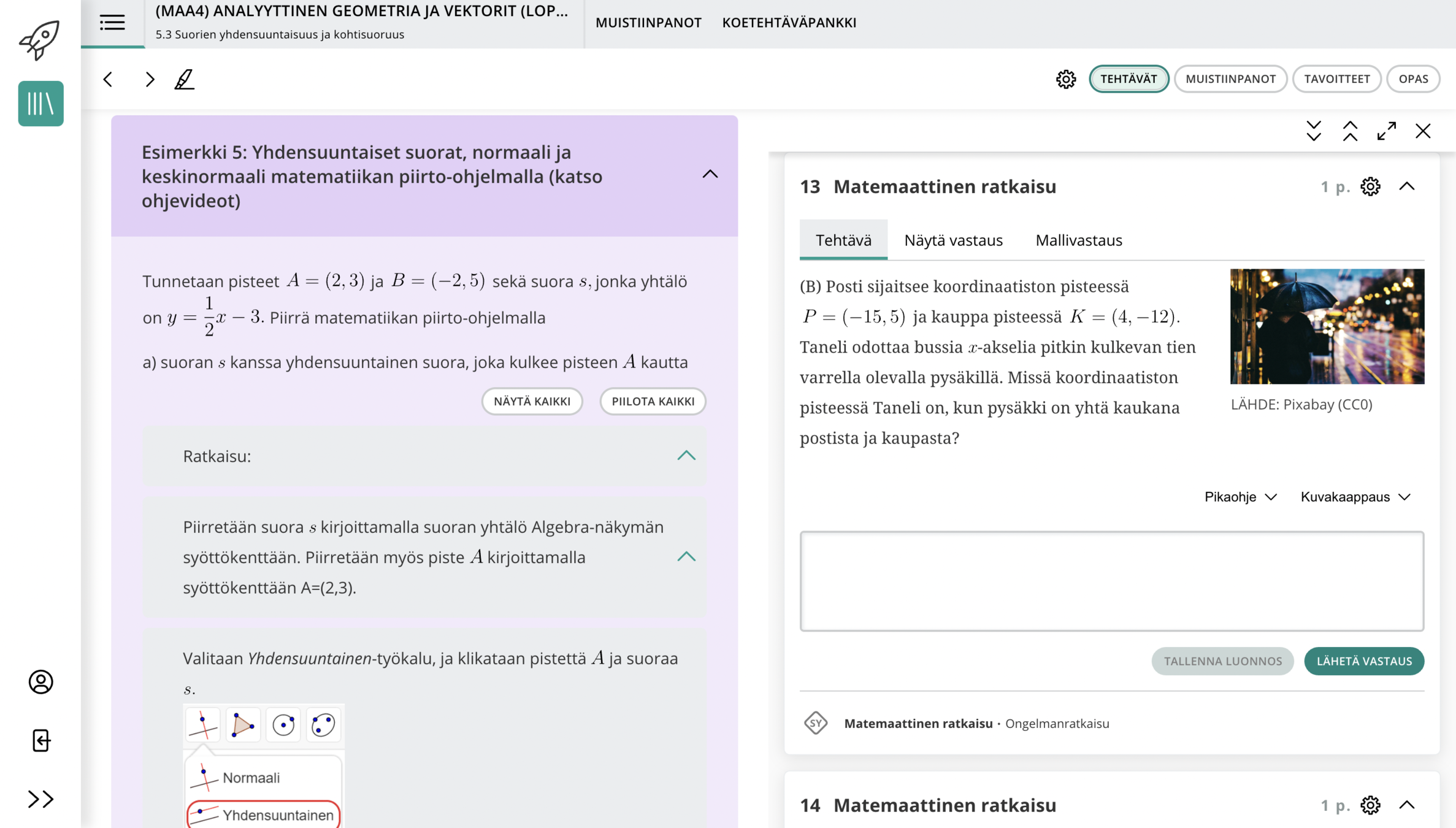
Do you feel that you are receiving teaching and guidance that meets your needs?
2023-2025, n = 382
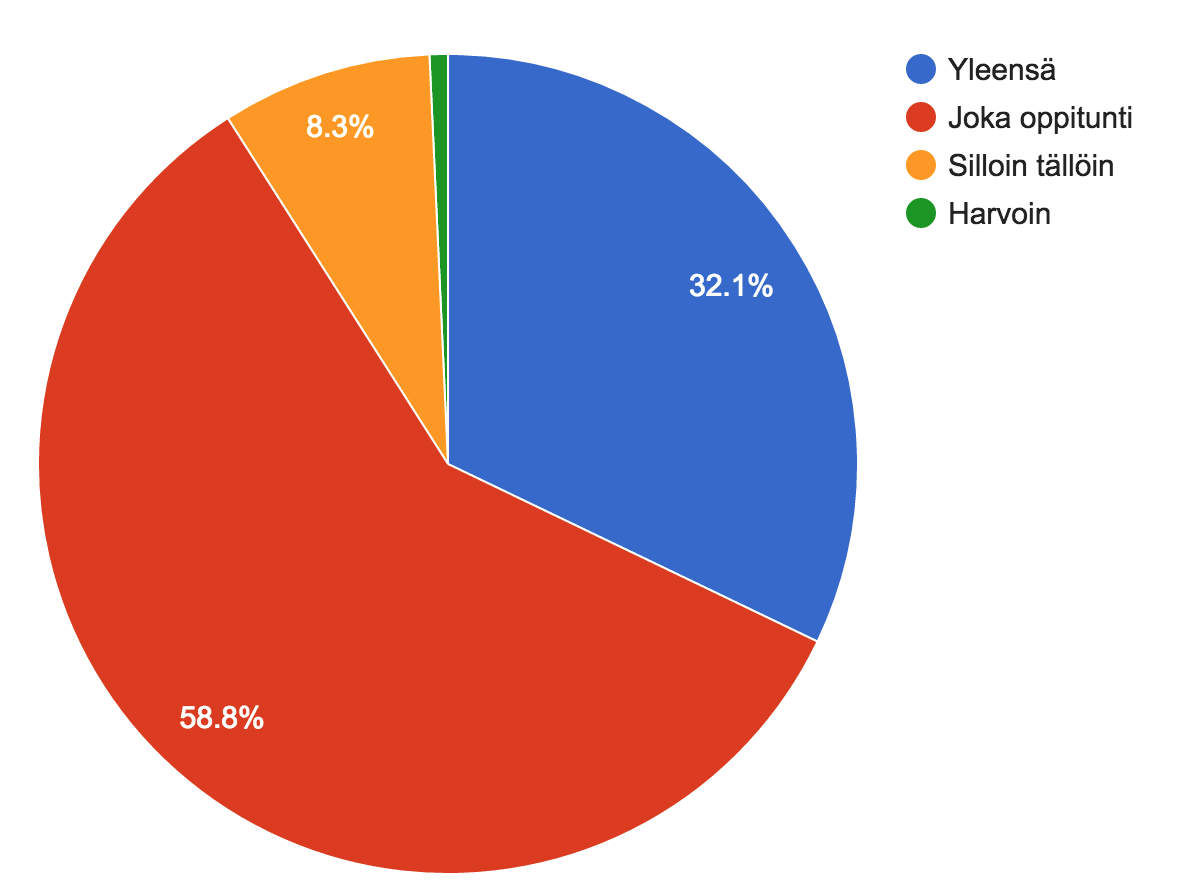
Usually
Each lesson
Sometimes
Course feedbacks
"The motivation for learning is to learn something yourself, not to make the teacher happy during the lesson."
"The course has been enjoyable, and I must say that I am grateful for the fact that I always received help when I needed it."
"The lessons are relaxed and always fun to attend. I never would have believed that I would enjoy math lessons"
Task for next session (8.9.)
Design a mini flipped learning cycle for one topic you teach. Outline what students do before class, in class, and after class. Focus on how your design supports active learning, scaffolding, and student autonomy. Use AI (e.g. Copilot / ChatGPT) to suggest activities, resources, or scaffolding ideas — but remember to adapt and review them for your own students.
Questions:
-
What activities take place before, during, and after class?
-
Which parts of the topic can students handle independently, and which require support?
-
How does the design use the Zone of Proximal Development (peer/teacher scaffolding)?
-
How does it support mastery learning (e.g., re-tries, feedback, pacing)?
-
What is the role of the teacher and the role of the students?
-
How does this cylce align with your curriculum goals (general, subject-specific, course-specific)?
Post your work in Padlet!
