Offline
roychuang
About Basics
離線基礎
Example input:
items = [[1,2],[3,2],[2,4],[5,6],[3,5]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
每個 item 包含兩個數字,分別為 price 和 beauty
對於每一筆 query,找 price <= q 的最大 beauty 值
$$ 1 \leq items.length, queries.length \leq 10 ^ 5 $$
Ans = [2, 4, 5, 6, 6]
例題
隨便亂做?
離線基礎
Example input:
items = [[1,2],[3,2],[2,4],[5,6],[3,5]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
暴力找
for (auto q : queries) {
int ans = 0;
for (auto item : items) {
if (item[0] <= q) {
ans = max(item[1], ans);
}
}
}T L E
$$ 1 \leq items.length, queries.length \leq 10 ^ 5 $$
例題
離線基礎
Example input:
items = [[1,2],[3,2],[2,4],[5,6],[3,5]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
重新整理一下測資
Input:
items = [[1,2],[2,4],[3,2],[3,5],[5,6]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
如果 items 和 queries 都先排好 ?
例題
離線基礎
Input:
items = [[1,2],[2,4],[3,2],[3,5],[5,6]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
如果 items 和 queries 都先排好 ?
假設目前的查詢是 q ,上一個是 p
max(0 ~ q) = max( max(0 ~ p), max(p + 1 ~ q) )
用 O(n) 就可以搜完 !
queries 的答案要記得還原到原本的位子
例題
離線基礎
Example input:
items = [[1,2],[3,2],[2,4],[5,6],[3,5]]
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
1. 根據 prices sort items
items = [[1,2],[2,4],[3,2],[3,5],[5,6]]
2. sort queries
queries = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
3. 目前最大值 = 前一個最大值 or
從前一個結束地方 ~ 現在 的最大值
max[q] = max( max[p], max[p+1 ~ q] )
例題
離線基礎
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maximumBeauty(vector<vector<int>>& items, vector<int>& queries) {
sort(items.begin(), items.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
});
int N = items.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> proc;
for (int i = 0; i < (int) queries.size(); i++) {
proc.push_back(make_pair(queries[i], i));
}
sort(proc.begin(), proc.end());
vector<int> ans((int) queries.size());
int i = 0; // processed idx
int maxBeauty = 0;
for (auto &q : proc) {
auto [price, idx] = q;
while (i < N && items[i][0] <= price) {
maxBeauty = max(items[i][1], maxBeauty);
i++;
}
ans[idx] = maxBeauty;
}
return ans;
}
};例題
離線基礎
What is Offline ?
- 正式定義:並非可以在線、實時、立刻得到答案的演算法
- 正常來說,queries 會是一問一答
- 但我們投機取巧
- 先讀入所有的 queries , 然後用我們會做的方法做,再一次輸出所有答案
- 單調性是重點
離線基礎
再來一題
Example input:
rooms = [[2,2],[1,2],[3,2]]
queries = [[3,1],[3,3],[5,2]]
每一間房間的組成是 [roomId, size] , 每一筆詢問包含 [preferred, minSize] , 對於所有 size >= minSize 的 room , 找和 preferred 最近的 roomId (取 abs),找不到的話輸出 -1
$$ 1 \leq N \leq 10 ^ 5 , 1 \leq Q \leq 10 ^ 4 $$
Ans = [3, -1, 3]
什麼東西有單調性?
離線基礎
再來一題
Example input:
rooms = [[2,2],[1,2],[3,2]]
queries = [[3,1],[3,3],[5,2]]
什麼東西有單調性?
roomSize >= minSize
越小的 minSize 可以包含越多房間
sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});離線基礎
再來一題
Example input:
rooms = [[2,2],[1,2],[3,2]]
queries = [[3,1],[3,3],[5,2]]
sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});維護好出現過、有機會成為答案的 id
前面出現過的 id 之後都有機會成為答案 (roomSize >= minSize)
怎麼從出現過的 id 中找最適合呢?
set + 二分搜
離線基礎
再來一題
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> closestRoom(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
int Q = queries.size();
int N = rooms.size();
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) queries[i].push_back(i);
sort(rooms.begin(), rooms.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](auto &a, auto &b) {
return a[1] > b[1];
});
vector<int> ans(Q);
set<int> ids;
int i = 0;
for (auto q : queries) {
int prefered = q[0], minSize = q[1], idx = q[2];
while (i < N && rooms[i][1] >= minSize) {
ids.insert(rooms[i][0]);
i++;
}
if (!ids.empty()) {
auto up = ids.upper_bound(prefered);
if (up == ids.begin()) {
ans[idx] = *up;
} else if (up == ids.end()) {
up--;
ans[idx] = *up;
} else {
auto low = up;
low--;
if (*up - prefered < prefered - *low)
ans[idx] = *up;
else
ans[idx] = *low;
}
} else {
ans[idx] = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
};More
Problems
A = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5}
queries:
1 5 1
2 4 3
1 5 2
1 3 3
每一筆 query 包含 \( l, r, x \) (1-based) 找 \( A_l \) 到 \( A_r \) 包含多少 \( x \)
$$1 \leq A_i \leq N \leq 2 \cdot 10 ^ 5$$
Ans = {2, 0, 0, 1}
神作法分享
參考自 看起來是由 AA 競程提供的神解 Orz
更多離線
A = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5}
queries:
1 5 1
2 4 3
1 5 2
1 3 3
神作法分享
紀錄 l, r 分別在哪些位置 詢問了哪些 x
$$ ans[i] = - cnt[l_i-1][x] + cnt[r_i][x] $$
cnt[pos][x] 可以線性做 !
更多離線
神作法分享
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> queries_L(2e5 + 1);
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> queries_R(2e5 + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
int l, r, x;
cin >> l >> r >> x;
queries_L[l].push_back({x, i});
queries_R[r].push_back({x, i});
}
vector<int> cnt(2e5 + 1, 0);
vector<int> ans(Q);
for (int pos = 1; pos <= N; pos++) {
for (auto [x, i] : queries_L[pos]) {
ans[i] -= cnt[x];
}
cnt[A[pos]]++;
for (auto [x, i] : queries_R[pos]) {
ans[i] += cnt[x];
}
}更多離線
神作法分享
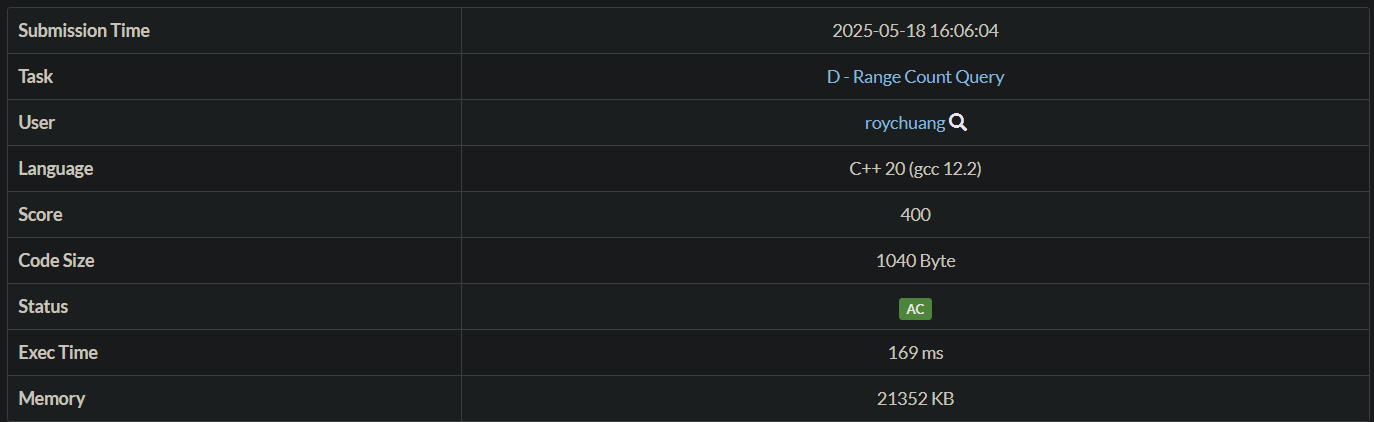
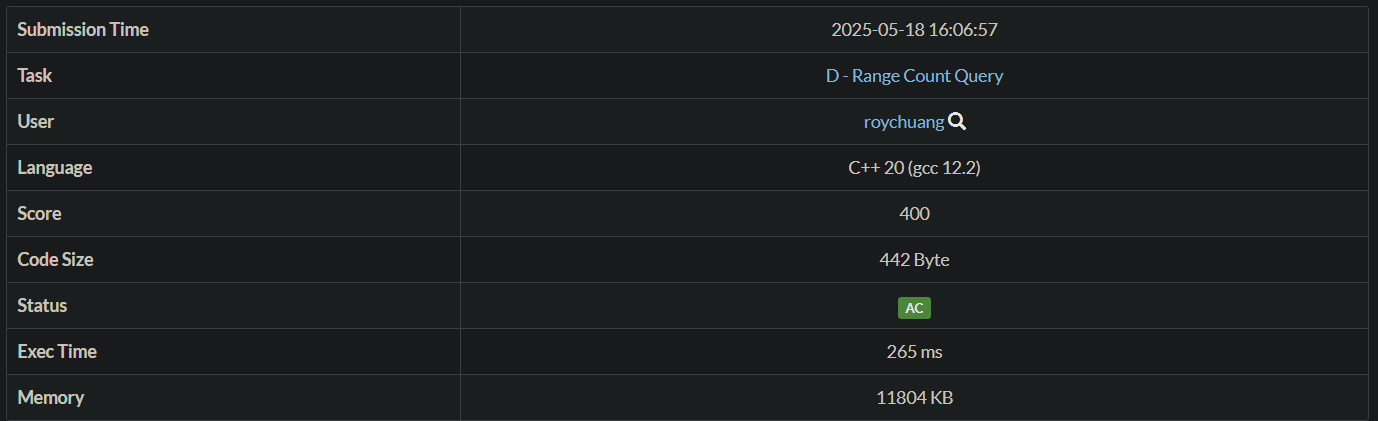
比官解快很多 !
更多離線
O(N + Q)
O(Q log N)
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
好題
Example Input:
N = 5 M = 5
1 2
1 3
2 3
3 4
4 5
1
2
3
5
4
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
好題
Example Input:
K = 3
1
2
3
5
4
3 4
2 3
4 5
ANS
2
2
3
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
好題
怎麼辦不會做
這我
那試試看時間倒流?
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
好題
Example Input:
K = 3
1
2
3
5
4
3 4
2 3
4 5
ANS
2
2
3
會了?
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
離題
會了?
使用 DSU (並查集)
支援:
1. 找任何兩點是否在同一塊
2. 把兩點連起來 (合併成同一塊)
方法:給每個點定一個祖先
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
離題
方法:給每個點定一個祖先
Example Input:
N = 5
1
2
3
5
4
祖先 = 1
祖先 = 2
祖先 = 3
祖先 = 4
祖先 = 5
祖先 = 1
祖先 = 1
1 2
1 3
更多離線
有 n 個點, m 條連線,然後發生了 k 次斷線
求每次斷線之後的連通元件數量
離題
1
2
3
5
4
祖先 = 1
祖先 = 1
祖先 = 4
祖先 = 5
Example Input:
K = 3
3 4
2 3
4 5
祖先 = 1
祖先 = 4
更多離線
DSU 實作
struct DSU {
int root[100005];
void init (int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) root[i] = i;
}
void unite (int a, int b) {
// find roots
a = find_root(a);
b = find_root(b);
root[b] = a; // merge root
}
int find_root (int x) {
if (root[x] == x) return x;
root[x] = find_root(root[x]); // pre save the roots
return root[x];
}
} dsu;更多離線
set<pair<int, int>> edges;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
pair<int, int> e;
cin >> e;
if (e.first > e.second) swap(e.first, e.second); //為什麼會有人卡這種測資
edges.insert(e);
}
// read all queries and process offline
vector<pair<int, int>> queries(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pair<int, int> e;
cin >> e;
if (e.first > e.second) swap(e.first, e.second);
edges.erase(edges.find(e)); // remove the edge
queries[i] = e;
}
// process DSU
int components = n;
for (auto e : edges) {
auto [a, b] = e;
if (dsu.find_root(a) != dsu.find_root(b)) {
// unite a, b if they aren't at the same component
components--;
dsu.unite(a, b);
}
}
vector<int> ans(k);
// solving backward
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans[i] = components;
auto [a, b] = queries[i];
if (dsu.find_root(a) != dsu.find_root(b)) {
// unite a, b if they aren't at the same component
components--;
dsu.unite(a, b);
}
}好題
A = {2, 4, 1, 3, 3}
queries:
2 5 5 2 5 3
每一筆 query 包含 \( r, x \) (1-based) 找 \( A_1 \) 到 \( A_r \) 之中最長的 (嚴格遞增) LIS 長度,滿足 LIS 內的元素皆 \( \leq x \)
$$1 \leq R_i \leq N \leq 2 \cdot 10 ^ 5, 1 \leq A_i \leq 10 ^ 9, 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \cdot 10 ^ 5$$
Ans = {2, 1, 2}
好題之二
由 cjtsai 提供的好題目 (?
更多離線
離題之二
更多離線
借一下 Ian 的簡報
好題之二
更多離線
那,LIS要怎麼找到 \( \leq x \)???
LIS 的 dp 陣列 其實是經過壓縮過後的
存放的是所有可以成為轉移點的數值與他們在 LIS 中的位置
某數字在 dp 陣列中的 idx , 就是他在 LIS 中的 idx (而且是最後一個) = 以它為最後一個數的 LIS 長度
我們可以從 dp 陣列中 找到小於等於 x 的上一個轉移點的位置
> 二分搜 !
所以我們知道了,我們要從 \( A_1 \) 跑到 \( A_R \) , 接著再對 dp 陣列二分搜
聽起來有點耳熟
> 離線!
好題之二
更多離線
所以我們知道了,我們要從 \( A_1 \) 跑到 \( A_R \) , 接著再對 dp 陣列二分搜
> 離線!
誰應該要有單調性?
> \( R_i \) 單調遞增
好題之二
更多離線
int N, Q;
cin >> N >> Q;
vector<int> A(N + 1);
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> R(2e5 + 1);
vector<int> dp;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) cin >> A[i];
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
int r, x;
cin >> r >> x;
R[r].eb(x, i);
}
vector<int> ans(Q);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (dp.empty() || dp.end()[-1] < A[i]) {
dp.eb(A[i]);
} else {
auto replace = lower_bound(ALL(dp), A[i]);
*replace = A[i];
}
for (auto [x, idx] : R[i]) {
ans[idx] = upper_bound(ALL(dp), x) - dp.begin();
}
}Thanks

離線
By Roy Chuang
離線
- 81



